Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX (Shell Script Project)
- 1. ATHLONE IT SHELL SCRIPT PROJECT 3.2 Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX By controlling users processes Dmitrijus Ponomarenko 4/28/2014
- 2. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 1 Contents Purpose of Program...................................................................................................................... 2 Description...................................................................................................................................2 Technical Description.................................................................................................................... 2 User Manual.................................................................................................................................6 Other Information ........................................................................................................................ 8
- 3. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 2 Purpose ofProgram The general idea of this project is to create a shell script which will monitor CPU usage in the background and once it exceeded 75% it should make the action to minimize the CPU utilization. To achieve this I wrote the shell script which should monitor CPU usage utilized by users of Linux server. Description Every 15 minutes the script should check the CPU usage and if it is higher than 75% but less than 85% it should send warning message to the administrator’s email with an attachment of the top 10 processes and to each user of top 10 processes asking them to shut down the running process. If the CPU usage exceeded 85%, then the script should find top 10 processes, copy them and send to them to the administrator’s email. Then, the script should kill the first of the user’s top processes and send the information of each killed process to the user’s email. If CPU utilization is still too high the script should repeat this action with the second process and so on until the CPU utilization is below the limit. To run the shell script on the background I used the utility named Cron. Crontab is a time- based scheduler in Unix-Linux operating system. Technical Description This project was created by using shell script. A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by the Unix shell, a command line interpreter. The first line of the script indicates which interpreter should execute the rest of the script (#!/bin/sh). To find the CPU usage utilized by the users I used the `top` utility. Top provides an ongoing look at processor activity in real time. It displays a listing of the most CPU-intensive tasks on the system.
- 4. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 3 From the `top` utility output, see above, I need to extract information about CPU usage and the 10 top processes. To do that I used commands such as: cpu=`top -d 0.5 -b -n2 | grep "Cpu(s)"|tail -n 1 | awk '{print $2}'` Where -d specifies the delay between screen updates (-d 0.5 sec), -b is used to send the output from `top` to next the program -n represent number of iterations requested (-n2). Grep is a command-line utility for searching plain-text data sets for lines matching a regular expression (grep "Cpu(s)"). This is the output after first two commands: Next command (tail -n 1) says, give me a bottom line (only after update we get real cpu utilization) and the last command says give me a second argument of this line and assign it to the variable `cpu`. So the output that we should get is: cpu=1.9%us, The Next command I used to extract the whole number from the first commands line output (1.9%us,) and assign it to the variable. let cpu_usage=`echo $cpu | cut -f1 -d'.'` The cpu_usage=1 Both this commands are represent a function called cpu_stat. function cpu_stat() { cpu=`top -d 0.5 -b -n2 | grep "Cpu(s)"|tail -n 1 | awk '{print $2}'` let cpu_usage=`echo $cpu | cut -f1 -d'.'` }
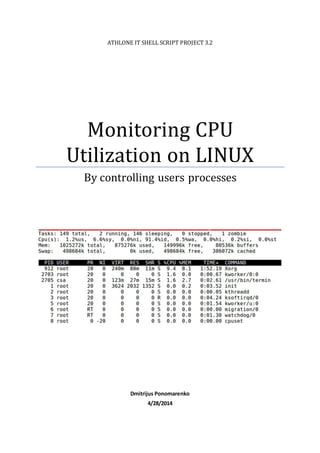
- 5. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 4 To get top 10 processes running on the system and save output in the file I used command as: top -b -n 1 | sed -e "1,6d" | head -11 >> file_name This command says, give me the output of first iterations and pass it to the next command. The second command (sed -e "1,6d" ) should remove first six line from the previous command output and pass it to the last command which should cut top 11 lines and save output to the file. See output of 10 top processes below: Another very important Linux utility used in this program is the mail utility. Mail utility allows it to send emails through the command line and also send emails with attachments. To send contents of a file (such as /path /to/message) as a mail body to the each of registered user, I used the following syntax: $ mail -s 'Test' test@gmail.com < /path /to/message All information about registered users stored in the file called users_info.txt. This file contains the information’s about all registered users, such as usernames and email addresses. Program using this file to compare usernames of running processes with the usernames in the file and if they match make an action, such as sending warning messages or killing processes. File users_info.txt
- 6. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 5 Also in this script I used: logical condition such as ( if-elif-else, while, while read), logical operators such as (and, or, not), arithmetic such as ( let ) and functions. cron To run the shell script in the background I used the utility named Cron. Cron is a Unix, Linux utility that allows tasks to be automatically run in the background at regular intervals by the cron daemon. These tasks are often termed as cron jobs in Unix , Linux. Crontab (CRON TABle) is a file which contains the schedule of cron entries to be run and at specified times. Crontab file: A crontab file has five fields for specifying day , date and time followed by the command to be run at that interval. * * * * * command to be executed - - - - - | | | | | | | | | +----- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0) | | | +------- month (1 - 12) | | +--------- day of month (1 - 31) | +----------- hour (0 - 23) +------------- min (0 - 59) Crontab example: A line in crontab file like below removes the tmp files from /home/someuser/tmp each day at 6:30 PM. 30 18 * * * rm /home/someuser/tmp/* To set up new crontab or edit current crontab, used command 'crontab -e', display current crontab 'crontab -l', delete current crontab 'crontab -r'.
- 7. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 6 User Manual This program can be executed in two ways. First way is to run the program manually using the command line, the second way is to run program using cron utility. Run Manually In this method (use file called cpu_monitor_test1.sh), script is executed through command line by using 'bash' command. 1. change directory to directory contained executed file 2. use bash to execute shell file 3. if CPU usage exceeded 75% the program will display and send to administrator cpu statistic and top 10 processes
- 8. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 7 4. also the script will display and send warning message to the each user of the top processes 5. if cpu usage exceeded 90% the script should kill the top process and display a send message to the process user Using cron To run script in the background (use file called cpu_monitor_test2.sh) at a specific period of time we need set up the crontab file. In the file we need to specify a day, date and time followed by the command to be run at that interval. 1. run 'crontab -e' command to set up new crontab file
- 9. Monitoring CPU Utilization on LINUX April 28, 2014 Page 8 2. specify time and command (for example run every 15 minutes) and save the file After that the cron will run the script every 15 minutes 24/365. Other Information To run the script fromotherPCs youshouldchange all pathsto the file dependingof directoryon whichyoulocate executedfiles.