CCRS Language Arts 4-8 Checklists and Breakdowns
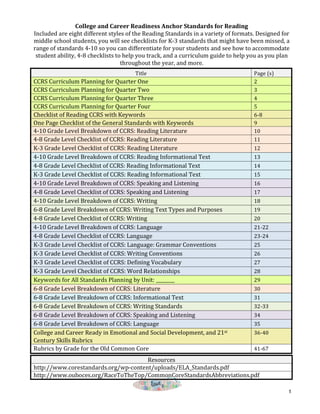
- 1. Included are eight different styles of the Reading Standards in a variety of formats. Designed for middle school students, you will see checklists for K-‐3 standards that might have been missed, a range of standards 4-‐10 so you can differentiate for your students and see how to accommodate student ability, 4-‐8 checklists to help you track, and a curriculum guide to help you as you plan 1 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading throughout the year, and more. Title Page (s) CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter One 2 CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter Two 3 CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter Three 4 CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter Four 5 Checklist of Reading CCRS with Keywords 6-‐8 One Page Checklist of the General Standards with Keywords 9 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Reading Literature 10 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Literature 11 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Literature 12 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Reading Informational Text 13 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Informational Text 14 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Informational Text 15 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Speaking and Listening 16 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Speaking and Listening 17 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Writing 18 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Writing Text Types and Purposes 19 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Writing 20 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Language 21-‐22 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Language 23-‐24 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Language: Grammar Conventions 25 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Writing Conventions 26 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Defining Vocabulary 27 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Word Relationships 28 Keywords for All Standards Planning by Unit: ________ 29 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Literature 30 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Informational Text 31 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Writing Standards 32-‐33 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Speaking and Listening 34 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Language 35 College and Career Ready in Emotional and Social Development, and 21st Century Skills Rubrics 36-‐40 Rubrics by Grade for the Old Common Core 41-‐67 Resources http://www.corestandards.org/wp-‐content/uploads/ELA_Standards.pdf http://www.ouboces.org/RaceToTheTop/CommonCoreStandardsAbbreviations.pdf
- 2. 2 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Keywords for All Standards for Planning by Quarter or Unit CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter One Reading Literaure (RL): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Craft and Structure 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections Craft and Structure 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Writing (W): ✔ Text Types and Purposes 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. Production and Distribution of Writing 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence Range of Writing 10 Range, audience, purpose Speaking and Listening (SL) ✔ Comprehension and Collaboration 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid 6 Range and diversity of writing Language (L): ✔ Conventions of Standard English 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing Knowledge of Language 3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings
- 3. 3 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Keywords for All Standards for Planning by Quarter or Unit CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter Two Reading Literaure (RL): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Craft and Structure 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections Craft and Structure 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Writing (W): ✔ Text Types and Purposes 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. Production and Distribution of Writing 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence Range of Writing 10 Range, audience, purpose Speaking and Listening (SL) ✔ Comprehension and Collaboration 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid 6 Range and diversity of writing Language (L): ✔ Conventions of Standard English 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing Knowledge of Language 3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings
- 4. 4 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Keywords for All Standards for Planning by Quarter or Unit CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter Three Reading Literaure (RL): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Craft and Structure 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections Craft and Structure 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Writing (W): ✔ Text Types and Purposes 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. Production and Distribution of Writing 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence Range of Writing 10 Range, audience, purpose Speaking and Listening (SL) ✔ Comprehension and Collaboration 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid 6 Range and diversity of writing Language (L): ✔ Conventions of Standard English 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing Knowledge of Language 3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings
- 5. 5 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Keywords for All Standards for Planning by Quarter or Unit CCRS Curriculum Planning for Quarter Four Reading Literaure (RL): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Craft and Structure 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections Craft and Structure 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Writing (W): ✔ Text Types and Purposes 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. Production and Distribution of Writing 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence Range of Writing 10 Range, audience, purpose Speaking and Listening (SL) ✔ Comprehension and Collaboration 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid 6 Range and diversity of writing Language (L): ✔ Conventions of Standard English 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing Knowledge of Language 3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings
- 6. 6 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading A Checklist of the General Standards with Keywords Reading Literaure (RL): 1 2 3 4 Key Ideas and Details ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Craft and Structure ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator Integration of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Range of Reading and Level of Complexity ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): 1 2 3 4 Key Ideas and Details ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections Craft and Structure ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Integration of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Range of Reading and Level of Complexity ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Speaking and Listening (SL) 1 2 3 4 Comprehension and Collaboration ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions a. Read material with evidence prior b. Set and track goals c. Elaboration, detail d. Key ideas, multiple perpectives, reflection paraphrasing, justify 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid 6 Range and diversity of writing
- 7. 7 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading A Checklist of the General Standards with Keywords Writing (W): 1 2 3 4 Text Types and Purposes ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. a. Introduce claims, organize reasons and evidence b. Support, credible sources c. Clarify relationship among claims and reasons d. Formal style e. Concluding statement 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. a. Introduce topic, organization, formating, grapics, multimedia b. Develop topic c. Transitions d. Language and vocabulary e. Formal style f. Concluding statement 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐ structured event sequences. a. Establish context, introduce narrators and characters, organize b. Develop story using narrative techniques c. Transition and sequence d. Sensory language e. Conclusion Production and Distribution of Writing ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology Research to Build and Present Knowledge ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence Range of Writing ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 10 Range, audience, purpose
- 8. 8 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading A Checklist of the General Standards with Keywords Language (L): 1 2 3 4 Conventions of Standard English ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing a. Function of phrases and clauses b. Simple, compound, complex, and compound-‐complex sentences to signal differing relationships among ideas c. Place phrases and clauses within a sentence, recognize and correct mislplaced modifiers 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing a. Use a comma to separate cooridinate adjectives b. Spell correctly Knowledge of Language ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening a. Expresses ideas precisely and concisely, eliminating wordiness and redundancy Vocabulary Acquisition and Use ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies a. Use context (e.g., definitions, examples, restatements in text, cause/effect relationships and comparisons in text) as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. Use common, grade-appropriate Greek and Latin affixes and roots as clues to the meaning of a word c. Consult reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation and determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. d. Verify preliminary meaning of words or phrase 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings a. Literary, biblical, mythological allusions b. Use relationship between particular words (cause/effect, part/whole, item/category, synonym/antonym, analogy) to understand each of the words c. Distinguish connotations and denotations
- 9. 9 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading A Checklist of the General Standards with Keywords Reading Literaure (RL): ✔ (RL): Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue (RL): Craft and Structure 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator (RL): Reading Literaure Knowledge and Ideas 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types (RL): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): ✔ (RI): Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections (RI): Craft and Structure 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose (RI): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation (RI): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Read informational text complexity proficiently Speaking and Listening (SL): ✔ (SL): Comprehension and Collaboration 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence (SL): Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid Writing (W): ✔ (W): Text Types and Purposes 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. (W): Production and Distribution of Writing 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology (W): Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence (W): Range of Writing 10 Range, audience, purpose Language (L): ✔ (L): Conventions of Standard English 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing (L): Knowledge of Language Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening (L): Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings
- 10. 10 Reading Literaure (RL): Key Ideas and Details RL Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RL.1. Textual evidence and inferences Refer to details in text when eplaining text and inferences Quote accurately from a text Cite to support analysis Cite several times Textual evidence that most strongly supports Strong and thorough textual evidence RL.2. Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details Determine theme from details; summarize Include character development when determining theme Use particular sensory details with theme; objective summary Analyze theme’s development over the course of text Analyze theme’s relationship with characters, setting, plot Theme shaped and refined by specific details RL.3. Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Describe a character, setting, or event using specifc details Compare and contrast two or more characters, settings, events Plot unfolds in a series of episodes; characters respond and change as plot developes Interaction of different literary elements Analyze how dialogue or incidents propel action, revealing new aspects of character Complex characters and their development Reading Literaure (RL): Craft and Structure RL Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RL.4. Decipher words and phrases, word choice Determine meaning including allusions found in myths Figurative language: similes and metaphors Figurative, connotative, word choice, tone Rhyme and repetition Analogies and allusions to other texts Word choice and tone; formal and informal RL.5. Text structure Explain major differences between structures and technical jargon with poems, drama, prose Series of chapters, stanzas, scenes fit together in overall structure Specific excerpt connected to plot, theme, setting development Drama or poem form or structure contribute to meaning Compare and contrast structure of two or more texts and the value in different structures Manipulate time for effects (e.g., flashblacks, pacing) RL.6. Author, point of view, narrator Compare and contrast POV of stories: first and third person narrations Narrator’s perspective influences how events are described Author develops into narrator POV Author contrasts narrator’s perspective with other characters Differences in perspective create effects (e.g., suspense or humor) Particular POV or culture of US reflected Reading Literaure (RL): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RL Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5- Less Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RL.7. Compare and contrast, production techniques Connection between text and visual Analyze how visual elements contribute to meaning, tone Compare and contrast reading to listening or viewing same piece Analyze the effects of techniques unique to each medium Analyze how a production stays faithful to or departs from the original, evaluating creative choices used Representiation of a subject in two different artistic mediums RL.9. Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Compare and contrast common themes in myths, traditional literature, stories Compare and contraste stories in same genre Compare and contrast texts in different forms or genres in terms of approaches to similar themes Fictional with nonfiction historical account Modern work with traditional literature in terms of themes, patterns of events, or character types Author draws on and transforms source material in specific work Reading Literature (RL): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity RL Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RL.10. Fictional text complexity 4-5 Scaffolding 4-5 6- 8 Scaffolding 6- 8 6- 8 Independently proficiently 50% Literary Independently Scaffolding 45% Literary 9-10 Scaffolding- Independently 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Reading Literature Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 4-‐10. Use the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth.
- 11. 11 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Literature Reading Literaure (RL): Key Ideas and Details ✔ ✔ RL.1. Textual evidence and inferences Refer to details in text when eplaining text and inferences Cite several times Quote accurately from a text Textual evidence that most strongly supports Cite to support analysis Strong and thorough textual evidence RL.2. Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details Determine theme from details; summarize Analyze theme’s development over the course of text Include character development when determining theme Analyze theme’s relationship with characters, setting, plot Use particular sensory details with theme; objective summary Theme shaped and refined by specific details RL.3. Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Describe a character, setting, or event using specifc details Interaction of different literary elements Compare and contrast two or more characters, settings, events Analyze how dialogue or incidents propel action, revealing new aspects of character Plot unfolds in a series of episodes; characters respond and change as plot developes Complex characters and their development Reading Literaure (RL): Craft and Structure ✔ ✔ RL.4. Decipher words and phrases, word choice Determine meaning including allusions found in myths Rhyme and repetition Figurative language: similes and metaphors Analogies and allusions to other texts Figurative, connotative, word choice, tone Word choice and tone; formal and informal RL.5. Text structure Explain major differences between structures and technical jargon with poems, drama, prose Drama or poem form or structure contribute to meaning Series of chapters, stanzas, scenes fit together in overall structure Compare and contrast structure of two or more texts and the value in different structures Specific excerpt connected to plot, theme, setting development Manipulate time for effects (e.g., flashblacks, pacing) RL.6. Author, point of view, narrator Compare and contrast POV of stories: first and third person narrations Author contrasts narrator’s perspective with other characters Narrator’s perspective influences how events are described Differences in perspective create effects (e.g., suspense or humor) Author develops into narrator POV Particular POV or culture of US reflected Reading Literaure (RL): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ ✔ RL.7. Compare and contrast, production techniques Connection between text and visual Analyze the effects of techniques unique to each medium Analyze how visual elements contribute to meaning, tone Analyze how a production stays faithful to or departs from the original, evaluating creative choices used Compare and contrast reading to listening or viewing same piece Representiation of a subject in two different artistic mediums RL.9. Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Compare and contrast common themes in myths, traditional literature, stories Fictional with nonfiction historical account Compare and contraste stories in same genre Modern work with traditional literature in terms of themes, patterns of events, or character types Compare and contrast texts in different forms or genres in terms of approaches to similar themes Author draws on and transforms source material in specific work Reading Literature (RL): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity ✔ ✔ RL.10. Fictional text complexity proficiently 4-‐5 Scaffolding 50% Literary 6-‐ 8 Independently 45% Literary
- 12. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades K-‐3. Use 12 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Literature the checklists to help evaluate student needs when they are not in the middle school range. Mastery of English Language Arts: Reading Literature RL. K-3. All RL Keywords Reading Literature Standards ✔ Reading Literaure (RL): Key Ideas and Details ✔ RL1. Textual evidence and inferences RL.2.1 Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why, and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text. RL.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, explicitly using text as basis for answers. RL2. Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details RL.1.2 Retell stories, including key details, and demonstrate understanding of their central message or lesson. RL.3.2 Recount stories, including fables, folktales, and myths from diverse cultures, and determine their central message, lesson, or moral. RL3. Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue RL.1.3 Describe characters, settings, and major events in a story using key details. RL.2.3 Describe how characters in a story respond to major events and challenges Reading Literaure (RL): Craft and Structure ✔ RL4. Decipher words and phrases, word choice RL.1.4 Identify words and phrases in stories and poems that suggest feelings or appeal to senses. RL.2.4 Describe how words and phrases (e.g., regular beats, alliteration, rhymes, repeated lines) supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem, or song. RL.3.4 Distinguish literal from nonliteral language RL5. Text structure RL.1.5 Explain differences between books that tell stories and books that give information. RL.2.5 Describe overall structure of a story including beginning as introduction and ending concluding action. RL.3.5 Use technical terms such as chapter, scene, and stanza when refering to stories, dramas, and poems. RL6. Author, point of view, narrator RL.1.6 Identify who is telling the story at different parts. RL.2.6. Acknowledge differents in POV of characters, including speaking in different voices when reading dialogue. RL.3.6 Distinguish own POV from the narrator or characters. Reading Literaure (RL): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ RL7. Compare and contrast, production techniques RL.3.7 Explain how specific aspects of a text’s illustrations contribute to what is conveyed by words in the story (mood, emphasis on aspects of a character or setting). RL9. Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types RL.2.9 Compare and contrast two versions of the same story from different cultures or by different authors. RL.3.9 Compare and contrast themes, settings, and plots written by same author about similar characters.
- 13. 13 Reading Informational Text (RI): Key Ideas and Details RI Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RI.1. Textual evidence and inferences Refer to details in text when eplaining text and inferences Quote accurately Cite to support analysis of what text explicitly sys and draw inferences Cite several times Textual evidence that most strongly supports Strong and thorough evidence RI.2. Central idea, summary, sensory details Determine main idea supported by key details; summarize Two or more main ideas Determine central idea of a text and how it’s conveyed through particular details Two or more central ideas, analyze development; provide summary Include the central idea’s relationship to supporting ideas Theme shaped and refined by specific details RI.3. Developing key details and connections Explain events with content-vocabulary from text Interactions between two or more Analyze key individual, event, idea is introduced, illustrated, and elaborated Interactions between one another in a text; compare multiple events Connections amongst the distinctions through comparisons, analagies, and categories How author unfolds ideas or events, including order and style Reading Informational Text (RI): Craft and Structure RI Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RI.4. Decipher Determine words and meaning of grade phrases, word level academic choice and domain-specific words Figurative, connotative, word choice, tone Rhyme and repetition Technical meanings, analogies and allusions to other texts Tone RI.5. Text structure and development of ideas Describe overall structure Compare and contrast structure Specific excerpt connected to overall structure and development of ideas Analyze structure author uses to organize text Refined key concept Claims developed and refined by author RI.6. Author’s point of view or purpose Compare and contrast firsthand and secondhand account Similarities and differences in multiple accounts Author’s perspective or purpose and how it’s conveyed Author distinguishes perspective from that of others Author acknowledges and responds to conflicting viewpoints Author uses rhetoric to advance perspective Reading Informational Text (RI): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RI Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RI.7. Integrate medias or Integrate Compare and Evaluate formats to Interpret visual Draw on multiple information in contrast text to advantages and develop information sources, locating different formats audio, depicting disadvantages of coherent an answer to develop each portrayal of using different understanding understanding subject mediums Various accounts told in different mediums and emphasized details RI.8. Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence Explain how author uses reasons and evidence to support particular points Identify which evidence supports specific points Evaluate the argument and specific claims; claims supported by reasons and evidence Assess whether the reasoning is sound and evidence is relevant and sufficient Examine and evaluate if the argument is sound; recognize irrelevant evidence Valid, sufficient evidence and false statements RI.9. Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Integrate information from two texts on same topic to speak knowledgeably Several texts Compare and contrast two differing authors’ presentation of events Two or more authors writing to emphasize different interpretations Identify where they disagree on fact or inpretation Analyze U.S. documents of significance in relation Reading Informational Text (RI): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity RI Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 RI.10. Informational 4-5 Scaffolding 6- 8 4-5 Independently text complexity 50% 6- 8 Scaffolding proficiently Informational Independently 55% Informational 9-10 Scaffolding- Independently 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Reading Informational Text Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 4-‐10. Use the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth.
- 14. 14 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Informational Text Reading Informational Text (RI): Key Ideas and Details ✔ ✔ RI.1. Textual evidence and inferences Refer to details in text when eplaining text and inferences Cite several times Quote accurately Textual evidence that most strongly supports Cite to support analysis of what text explicitly sys and draw inferences Strong and thorough evidence RI.2. Central idea, summary, sensory details Determine main idea supported by key details; summarize Two or more central ideas, analyze development; provide summary Two or more main ideas Include the central idea’s relationship to supporting ideas Determine central idea of a text and how it’s conveyed through particular details Theme shaped and refined by specific details RI.3. Developing key details and connections Explain events with content-‐vocabulary from text Interactions between one another in a text; compare multiple events Interactions between two or more Connections amongst the distinctions through comparisons, analagies, and categories Analyze key individual, event, idea is introduced, illustrated, and elaborated How author unfolds ideas or events, including order and style Reading Informational Text (RI): Craft and Structure ✔ ✔ RI.4. Decipher words and phrases, word choice Determine meaning of grade level academic and domain-‐specific words Technical meanings, analogies and allusions to other texts Figurative, connotative, word choice, tone Rhyme and repetition Tone RI.5. Text structure and development of ideas Describe overall structure Analyze structure author uses to organize text Compare and contrast structure Refined key concept Specific excerpt connected to overall structure and development of ideas Claims developed and refined by author RI.6. Author’s point of view or purpose Compare and contrast firsthand and secondhand account Author distinguishes perspective from that of others Similarities and differences in multiple accounts Author acknowledges and responds to conflicting viewpoints Author’s perspective or purpose and how it’s conveyed Author uses rhetoric to advance perspective Reading Informational Text (RI): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ ✔ RI.7. Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding Interpret visual information Compare and contrast text to audio, depicting each portrayal of subject Draw on multiple sources, locating an answer Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of using different mediums Integrate information in different formats to develop understanding Various accounts told in different mediums and emphasized details RI.8. Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence Explain how author uses reasons and evidence to support particular points Assess whether the reasoning is sound and evidence is relevant and sufficient Identify which evidence supports specific points Examine and evaluate if the argument is sound; recognize irrelevant evidence Evaluate the argument and specific claims; claims supported by reasons and evidence Valid, sufficient evidence and false statements RI.9. Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Integrate information from two texts on same topic to speak knowledgeably Two or more authors writing to emphasize different interpretations Several texts Identify where they disagree on fact or inpretation Compare and contrast two differing authors’ presentation of events Analyze U.S. documents of significance in relation Reading Informational Text (RI): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity ✔ ✔ RI.10. Informational text complexity 4-‐5 Scaffolding 50% Informational 6-‐ 8 Independently 55% Informational
- 15. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades K-‐3. Use 15 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Reading Informational Text the checklists to help evaluate student needs when they are not in the middle school range. Primary Mastery of English Language Arts: Reading Informational Text RI. K-‐3. ALL RI Keywords Reading Informational Text Standards ✔ Reading Informational Text (RI): Key Ideas and Details RI.1. Textual evidence and inferences RI.2.1 Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why, and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text. RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, explicitly using text as basis for answers. RI.2. Central idea, summary, sensory details RI.3.2 Recount main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI.3. Developing key details and connections RI.2.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text. Reading Informational Text (RI): Craft and Structure ✔ RI.5. Text structure and development of ideas RI.2.5 Know and use various text features (e.g., captions, bold print, subheadings, glossaries, indexes, electronic menus, icons) to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently. RI.3.5 key words, sidebars, hyperlinks RI.6. Author’s point of view or purpose RI.2.6 Identify the main purpose of a text, including what the author wants to answer, explain, or describe. RI.3.6 Distinguish own POV from that of author. Reading Informational Text (RI): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ RI.7. Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding RI.2.7 Explain how specific images (e.g., a diagram showing how a machine works) contribute to and clarify a text. RI.8. Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence RI.3.8 Describe the logical connection between particular sentences and paragraphs in a text
- 16. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 4-‐10. Use 16 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Speaking and Listening the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth. Speaking and Listening (SL): Comprehension and Collaboration SL Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 SL.1. Engage Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions with diverse partners of grade level Express own in dicussions topics, texts, issues; build on other’s ideas and express own clearly persuasively a. Read material with evidence prior Come prepared, read or studied material; refer to evdience to probe and reflect on ideas under discussion Read research material to prepare Refer to evidence from texts b. Set and track goals Follow agreed-upon rules and carry out assigned roles Rules for collegial discussions, set goals and deadlines, define individual roles Track progress towards goals Follow rules for decision making Set rules, goals, deadlines, and individual roles c. Elaboration, detail Pose and respond to specific questions; make releveant and linking comments Make comments that contribute to discussion and elaborate on remarks of others Comments that contribute to the topic, text, issue under discussion Respond with relevant observations and ideas that bring the discussion back on topic as needed Questions connect ideas of several speakers and respond to others’ with relevant evidence Relate to braoder themes, actively incorporate others, challenge ideas d. Key ideas, multiple perpectives, reflection paraphrasing, justify Review key ideas expressed and explain own ideas and understanding Draw conclusions from discussion Demonstrate understanding of multiple perspectives through reflection and paraphrasing Acknowledge new information expressed; modify own views as needed When warranted, qualify or justify own views with evidence presented Respond thoughtfully to diverse perspectives; summarize points of agreement SL.2. Use evidence to support with diverse media Paraphrase portions of information read aloud or in diverse media and formats Summarize Intrepet information presented, explain contribution to topic, text, issue under study Analyze main ideas and supporting details presented; explain how the ideas clarify Analyze the purpose of information presented and evaluate motives behind its presentation Integrate multiple sources, evaluating credibility and accuracy of each SL.3. Reliability of claims and evidence Identify reasons and evidence a speaker provides Summarize points made and how each is supported by reasons and evidence Examine a speaker’s argument and claims, distinguishing those supported by reasons and evidence Evaluate the soundness of reasoning Evaluate relevance and credibility of the evidence; identify irrelevant evidence Speaker’s point of view, rhetoric, identify fallacious or exaggerated, distorted evidence Speaking and Listening (SL): Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas SL Keywords Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-10 SL.4. Sequence findings, appropriate body language Report on topic or tell story in an organized manner with facts and relevant details; speak clearly Present an opinion, sequence ideas logically; speak at understandable pace Pertinent descriptions to accentuate themes and main ideas; use eye contact, volume, ponounciation Emphasize salient points in a focused, coherent manner Relevant evidence, sound valid reasononing, well- chosen details Present supporting evidence clearly, concisely, logically for an active audience SL.5. Visual Aid Add audio and visual displays to enhance development of main ideas or themes Include multimedia components in presentations Use to emphasize salient points Use to strengthen claims and evidence, and add interest Strategic use of digital media to enhance understanding SL.6. Range and diversity of writing Differentiate use formal or informal Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and tasks; formal English when appropriate
- 17. 17 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Speaking and Listening Speaking and Listening (SL): Comprehension and Collaboration ✔ ✔ SL.1. Engage in dicussions Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions with diverse partners of grade level topics, texts, issues; build on other’s ideas and express own clearly Express own persuasively a. Read material with evidence prior Come prepared, read or studied material; refer to evdience to probe and reflect on ideas under discussion Refer to evidence from texts Read research material to prepare b. Set and track goals Follow agreed-‐upon rules and carry out assigned roles Follow rules for decision making Rules for collegial discussions, set goals and deadlines, define individual roles Set rules, goals, deadlines, and individual roles Track progress towards goals c. Elaboration, detail Pose and respond to specific questions; make releveant and linking comments Respond with relevant observations and ideas that bring the discussion back on topic as needed Make comments that contribute to discussion and elaborate on remarks of others Questions connect ideas of several speakers and respond to others’ with relevant evidence Comments that contribute to the topic, text, issue under discussion Relate to braoder themes, actively incorporate others, challenge ideas d. Key ideas, multiple perpectives, reflection paraphrasing, justify Review key ideas expressed and explain own ideas and understanding Acknowledge new information expressed; modify own views as needed Draw conclusions from discussion When warranted, qualify or justify own views with evidence presented Demonstrate understanding of multiple perspectives through reflection and paraphrasing Respond thoughtfully to diverse perspectives; summarize points of agreement SL.2. Use evidence to support with diverse media Paraphrase portions of information read aloud or in diverse media and formats Analyze main ideas and supporting details presented; explain how the ideas clarify Summarize Analyze the purpose of information presented and evaluate motives behind its presentation Intrepet information presented, explain contribution to topic, text, issue under study Integrate multiple sources, evaluating credibility and accuracy of each SL.3. Reliability of claims and evidence Identify reasons and evidence a speaker provides Evaluate the soundness of reasoning Summarize points made and how each is supported by reasons and evidence Evaluate relevance and credibility of the evidence; identify irrelevant evidence Examine a speaker’s argument and claims, distinguishing those supported by reasons and evidence Speaker’s point of view, rhetoric, identify fallacious or exaggerated, distorted evidence Speaking and Listening (SL): Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas ✔ ✔ SL.4. Sequence findings, appropriate body language Report on topic or tell story in an organized manner with facts and relevant details; speak clearly Emphasize salient points in a focused, coherent manner Present an opinion, sequence ideas logically; speak at understandable pace Relevant evidence, sound valid reasononing, well-‐ chosen details Pertinent descriptions to accentuate themes and main ideas; use eye contact, volume, ponounciation Present supporting evidence clearly, concisely, logically for an active audience SL.5. Visual Aid Add audio and visual displays to enhance development of main ideas or themes Use to emphasize salient points Include multimedia components in presentations Use to strengthen claims and evidence, and add interest Strategic use of digital media to enhance understanding SL.6. Range and diversity of writing Differentiate use formal or informal Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and tasks; formal English when appropriate
- 18. 18 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Writing Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 4-‐10. Use the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth.
- 19. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 6-‐8. Use 19 6-‐8 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Writing Text Types and Purposes the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth. Writing (W): Text Types and Purposes W1. Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. W.1. Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 a. Introduce argumentative claims, organize reasons and evidence Introduce claims and organize reasons and evidence clearly Acknowledge alernate claims; organize logically Distinguish claim from alternate b. Support, credible sources Support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence, using credible sources to demonstrate understanding Logical reasoning; accurate sources c. Clarify relationship among claims and reasons Use words, phrases, clauses to clarify relationship among claims and reasons Create cohesion to clarify; evidence Counterclaims d. Formal style Establish and maintain a formal style e. Concluding statement Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from argument presented Support argument presented W2. Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. W.2. Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 a. Introduce topic, organization, formating, grapics, multimedia Inroduce a topic; organize ideas, concepts, and information using strategies such as definition, classification, comparison, contrast, and cause and effect; include formatting, graphics, and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension Introduce and preview what is to follow Organize into broader categories b. Develop topic Develop topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, other information, examples Well-‐chosen facts c. Transitions Use appropriate transitions to clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts Create cohesion Varied d. Language and vocabulary Use precise language and domain-‐ specific vocabulary to inform and explain e. Formal style Establish and maintain formal style f. Concluding statement Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from information presented W3. Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences W.3. Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 a. Establish context, event sequence, introduce narrators and characters Engage and orient the reader by establishing a context and introducing a narrator and/or characters; organize an event sequence that unfolds naturally and logically Establish point of view b. Develop story using narrative techniques Use narrative techniques, such as dialogue, pacing, and description, to develop experiences, events, characters Reflection to develop c. Transition and sequence Use a variety of transition words, phrases, clauses to convey sequence and signal shifts from one time frame or setting to another Show relationships among events d. Sensory language Use precise words and phrases, relevant descriptive details, and sensory language to convey experiences and events e. Conclusion Provide conclusion that follows from narrated experiences or events
- 20. ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ 20 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Writing
- 21. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 4-‐10. Use 21 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Language the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth. Language (L): Conventions of Standard English L Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-‐10 L.1. Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing a. a. Use relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, why) a. Explain the function of conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections in general and their function a. Pronouns in proper case (subjective, objective, possessive) a. Function of phrases and clauses a. Explain function of verbals (gerunds, participles, infinitives) a. Use parallel structure b. b. Form and use the progressive (e.g., I was walking; I am walking; I will be walking) verb tenses b. Form and use the perfect (e.g., I had walked; I have walked; I will have walked) verb tenses b. Use intensive pronouns (e.g., myself, ourselves) b. Simple, compound, complex, and compound-‐ complex sentences to signal differing relationships among ideas b. Form and use verbs in the active and passive voice b. Use various types of phrases (noun, verb, adjectival, adverbial, participal, preopsitional, absolute) and clauses to convey meanings c. c. Use modal auxiliaries (e.g., can, may, must) to convey various conditions c. Use verb tense to convey various times, sequences, states, and conditions c. Recognize and correct inapropriate shifts in pronoun number and person c. Place phrases and clauses within a sentence, recognize and correct mislplaced modifiers c. Form and use verbs in the indicative, imperative, interrogative, conditional, and subjunctive mood d. d. Order adjectives within sentences according to conventional patterns (e.g., a small red bag rather than a red small bag) d. Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb tense d. Recognize and correct vague pronouns d. Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb voice and mood e. e. Form and use prepositional phrases e. Use correlative conjunctions (e.g., either/or, neither/nor) e. Recognize variations in own and others’ writing and speaking; identify and use strategies to improve f. f. Produce complete sentences, recognizing and correcting inappropriate fragments and run-‐ons g. g. Correctly use frequently confused words (e.g., to, too, two; there, their) L.2. Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing a. a. Use correct capitalization. a. Use punctuation to separate items in a series a. To set off nonrestrictive and parenthetical elements (commas, parentheses, dashes) a. Use a comma to separate cooridinate adjectives a. Indicate a pause or break (comma, ellipsis, dash) a. Hyphenation conventions b. b. Use commas and quotation marks to mark direct speech from a text b. Use a comma to separate an introductory element from the rest of the sentence b. Use an ellipsis to indicate an ommission c. c. Use a comma before a coordinating conjunction in a compound sentence c. Use a comma to set off the words yes and no, to set off a question from rest of sentence, to indicate direct address d. d. Spell grade-‐ appropriate words correctly, consulting references as needed d. Use underlining, quotation marks, or italics to indicate titles of work
- 22. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades 4-‐10. Use 22 4-‐10 Grade Level Breakdown of CCRS: Language the chart to help evaluate student needs in order to maximize student growth. Language (L): Knowledge of Language L Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-‐10 L.3. Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. a. a. Choose words and phrases to convey ideas precisely a. Expand, combine, and reduce sentences for meaning, reader/listener interest, and style a. Vary sentence patterns for meaning, reader, listener interest, style a. Expresses ideas precisely and concisely, eliminating wordiness and redundancy a. Use verbs in active and passive voice and in the conditional and subjunctive mood to achieve effects a. Write and edit to guidelines in a style manual appropirate for writing type b. b. Choose punctuation for effect b. Compare and contrast the varieties of English (e.g., dialects, registers) used in stories, dramas, or poems b. Maintain consistency in style and tone c. c. Differentiate between contexts that call for formal English and situations where to use informal Language (L): Vocabulary Acquisition and Use L Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-‐10 L.4. Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies a. a. Use context (e.g., definitions, examples, restatements in text, cause/effect relationships and comparisons in text) as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. b. Use common, grade-‐appropriate Greek and Latin affixes and roots as clues to the meaning of a word b. Identify patterns of word changes c. c. Consult reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation and determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases d. d. Verify preliminary meaning of words or phrase L.5. Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings a. a. Explain meaning of figurative language (similes and metaphors) in context a. Figures of speech including personification a. Literary, biblical, mythological allusions a. Verbal irony, puns a. Euphemism, oxymoron b. b. Recognize and explain common idioms, adages, proverbs b. Use relationship between particular words (cause/effect, part/whole, item/category, synonym/antonym, analogy) to understand each of the words b. Analyze nuances in words with similar denotations c. c. Demonstrate understanding of words by relating them to particular words (antonyms, synonyms, homographs) c. Distinguish connotations and denotations L.6. Aquire and use grade-‐appropriate general academic and domain-‐specific words and phrases; gather vocabulary
- 23. 23 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Language (1/2) Language (L): Conventions of Standard English ✔ ✔ L.1. Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing a. a. Use relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, why) a. Function of phrases and clauses a. Explain the function of conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections in general and their function a. Explain function of verbals (gerunds, participles, infinitives) a. Pronouns in proper case (subjective, objective, possessive) a. Use parallel structure b. b. Form and use the progressive (e.g., I was walking; I am walking; I will be walking) verb tenses b. Simple, compound, complex, and compound-‐complex sentences to signal differing relationships among ideas b. Form and use the perfect (e.g., I had walked; I have walked; I will have walked) verb tenses b. Form and use verbs in the active and passive voice b. Use intensive pronouns (e.g., myself, ourselves) b. Use various types of phrases (noun, verb, adjectival, adverbial, participal, preopsitional, absolute) and clauses to convey meanings c. c. Use modal auxiliaries (e.g., can, may, must) to convey various conditions c. Place phrases and clauses within a sentence, recognize and correct mislplaced modifiers c. Use verb tense to convey various times, sequences, states, and conditions c. Form and use verbs in the indicative, imperative, interrogative, conditional, and subjunctive mood c. Recognize and correct inapropriate shifts in pronoun number and person d. d. Order adjectives within sentences according to conventional patterns (e.g., a small red bag rather than a red small bag) d. Recognize and correct vague pronouns d. Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb tense d. Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb voice and mood e. e. Form and use prepositional phrases e. Recognize variations in own and others’ writing and speaking; identify and use strategies to improve e. Use correlative conjunctions (e.g., either/or, neither/nor) f. f. Produce complete sentences, recognizing and correcting inappropriate fragments and run-‐ ons g. g. Correctly use frequently confused words (e.g., to, too, two; there, their) L.2. Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing a. a. Use correct capitalization. a. Use a comma to separate cooridinate adjectives a. Use punctuation to separate items in a series a. Indicate a pause or break (comma, ellipsis, dash) a. To set off nonrestrictive and parenthetical elements (commas, parentheses, dashes) a. Hyphenation conventions b. b. Use commas and quotation marks to mark direct speech from a text b. Use an ellipsis to indicate an ommission b. Use a comma to separate an introductory element from the rest of the sentence c. c. Use a comma before a coordinating conjunction in a compound sentence c. Use a comma to set off the words yes and no, to set off a question from rest of sentence, to indicate direct address d. d. Spell grade-‐appropriate words correctly, consulting references as needed d. Use underlining, quotation marks, or italics to indicate titles of work
- 24. 24 4-‐8 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Language (2/2) Language (L): Knowledge of Language ✔ ✔ L.3. Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening a. a. Choose words and phrases to convey ideas precisely a. Expresses ideas precisely and concisely, eliminating wordiness and redundancy a. Expand, combine, and reduce sentences for meaning, reader/listener interest, and style a. Use verbs in active and passive voice and in the conditional and subjunctive mood to achieve effects a. Vary sentence patterns for meaning, reader, listener interest, style a. Write and edit to guidelines in a style manual appropirate for writing type b. b. Choose punctuation for effect b. Maintain consistency in style and tone b. Compare and contrast the varieties of English (e.g., dialects, registers) used in stories, dramas, or poems c. c. Differentiate between contexts that call for formal English and situations where to use informal Language (L): Vocabulary Acquisition and Use ✔ ✔ L.4. Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies a. a. Use context (e.g., definitions, examples, restatements in text, cause/effect relationships and comparisons in text) as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. b. Use common, grade-‐appropriate Greek and Latin affixes and roots as clues to the meaning of a word b. Identify patterns of word changes c. c. Consult reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation and determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases d. d. Verify preliminary meaning of words or phrase L.5. Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings a. a. Explain meaning of figurative language (similes and metaphors) in context a. Verbal irony, puns a. Figures of speech including personification a. Euphemism, oxymoron a. Literary, biblical, mythological allusions b. b. Recognize and explain common idioms, adages, proverbs b. Use relationship between particular words (cause/effect, part/whole, item/category, synonym/antonym, analogy) to understand each of the words c. c. Demonstrate understanding of words by relating them to particular words (antonyms, synonyms, homographs) c. Distinguish connotations and denotations L.6. Aquire and use grade-‐appropriate general academic and domain-‐specific words and phrases; gather vocabulary
- 25. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades K-‐3. Use 25 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Language: Grammar Conventions the checklists to help evaluate student needs when they are not in the middle school range. Mastery of English Language Arts: Grammar Conventions L. K-‐3. 1 L.1 Language (L): Conventions of Standard English: Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. L.1.1 ✔ a. Print all upper-‐ and lowercase letters. b. Use common, proper, and possessive nouns. c. Use singular and plural nouns with matching verbs in basic sentences (e.g., He hops; We hop). d. Use personal, possessive, and indefinite pronouns (e.g., I, me, my; they, them, their; anyone, everything). e. Use verbs to convey a sense of past, present, and future (e.g., Yesterday I walked home; Today I walk home; Tomorrow I will walk home). f. Use frequently occurring adjectives. g. Use frequently occurring conjunctions (e.g., and, but, or, so, because). h. Use determiners (e.g., articles, demonstratives). i. Use frequently occurring prepositions (e.g., during, beyond, toward). j. Produce and expand complete simple and compound declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences in response to prompts. L.2.1 ✔ a. Use collective nouns (e.g., group). b. Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g., feet, children, teeth, mice, fish). c. Use reflexive pronouns (e.g., myself, ourselves). d. Form and use the past tense of frequently occurring irregular verbs (e.g., sat, hid, told). e. Use adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. Produce, expand, and rearrange complete simple and compound sentences (e.g., The boy f. watched the movie; The little boy watched the movie; The action movie was watched by the little boy). L.3.1 ✔ a. Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. b. Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns. c. Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood). d. Form and use regular and irregular verbs. e. Form and use the simple (e.g., I walked; I walk; I will walk) verb tenses. f. Ensure subject-‐verb and pronoun-‐antecedent agreement.* g. Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. h. Use coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. i. Produce simple, compound, and complex sentences.
- 26. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades K-‐3. Use 26 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Writing Conventions the checklists to help evaluate student needs when they are not in the middle school range. Mastery of English Language Arts: Writing Conventions L.K-‐3. 2 L Language (L): Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. L.K.2 ✔ a. Capitalize the first word in a sentence and the pronoun I. b. Recognize and name end punctuation. c. Write a letter or letters for most consonant and short-‐vowel sounds (phonemes). d. Spell simple words phonetically, drawing on knowledge of sound-‐letter relationships. L.1.2 ✔ a. Capitalize dates and names of people. b. Use end punctuation for sentences. c. Use commas in dates and to separate single words in a series. d. Use conventional spelling for words with common spelling patterns and for frequently occurring irregular words e. Spell untaught words phonetically, drawing on phonemic awareness and spelling conventions. L.2.2 ✔ a. Capitalize holidays, product names, and geographic names. b. Use commas in greetings and closings of letters. c. Use an apostrophe to form contractions and frequently occurring possessives. d. Generalize learned spelling patterns when writing words (e.g., cage → badge; boy → boil). e. Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. L.3.2 ✔ a. Capitalize appropriate words in titles. b. Use commas in addresses. c. Use commas and quotation marks in dialogue. d. Form and use possessives. e. Use conventional spelling for high-‐frequency and other studied words and for adding suffixes to base words (e.g., sitting, smiled, cries, happiness). f. Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-‐based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. g. Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings.
- 27. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades K-‐3. Use 27 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Defining Vocabulary the checklists to help evaluate student needs when they are not in the middle school range. Mastery of English Language Arts: Defining Vocabulary L. K-‐3. 4 L Language (L): Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases L.K.4 ✔ a. Identify new meanings for familiar words and apply them accurately (e.g., knowing duck is a bird and learning the verb to duck). b. Use the most frequently occurring inflections and affixes (e.g., -‐ed, -‐s, re-‐, un-‐, pre-‐, -‐ful, -‐less) as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word. L.1.4 ✔ a. Use sentence-‐level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. Use frequently occurring affixes as a clue to the meaning of a word. c. Identify frequently occurring root words (e.g., look) and their inflectional forms (e.g., looks, looked, looking). L.2.4 ✔ a. Use sentence-‐level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a known prefix is added to a known word (e.g., happy/unhappy, tell/retell). c. Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root (e.g., addition, additional). d. Use knowledge of the meaning of individual words to predict the meaning of compound words (e.g., birdhouse, lighthouse, housefly; bookshelf, notebook, bookmark).
- 28. Description: This checklist contains College and Career Ready Standards for Reading in grades K-‐3. Use 28 K-‐3 Grade Level Checklist of CCRS: Word Relationships the checklists to help evaluate student needs when they are not in the middle school range. Mastery of English Language Arts: Word Relationships L. K-‐3. 5 L Language (L): Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings. L.K. 5 ✔ a. Sort common objects into categories (e.g., shapes, foods) to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent. b. Demonstrate understanding of frequently occurring verbs and adjectives by relating them to their opposites (antonyms). c. Identify real-‐life connections between words and their use (e.g., note places at school that are colorful). d. Distinguish shades of meaning among verbs describing the same general action (e.g., walk, march, strut, prance) by acting out the meanings. L.1.5 ✔ a. Sort words into categories (e.g., colors, clothing) to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent. b. Define words by category and by one or more key attributes (e.g., a duck is a bird that swims; a tiger is a large cat with stripes). c. Identify real-‐life connections between words and their use (e.g., note places at home that are cozy). d. Distinguish shades of meaning among verbs differing in manner (e.g., look, peek, glance, stare, glare, scowl) and adjectives differing in intensity (e.g., large, gigantic) by defining or choosing them or by acting out the meanings. L.2.5 ✔ a. Identify real-‐life connections between words and their use (e.g., describe foods that are spicy or juicy). b. Distinguish shades of meaning among closely related verbs (e.g., toss, throw, hurl) and closely related adjectives (e.g., thin, slender, skinny, scrawny). L.3.5 ✔ a. Distinguish the literal and nonliteral meanings of words and phrases in context (e.g., take steps). b. Identify real-‐life connections between words and their use (e.g., describe people who are friendly or helpful). c. Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered).
- 29. 29 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Keywords for All Standards Planning by Unit: _________________________________________________________ Reading Literaure (RL): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Craft and Structure 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion 5 Text structure 6 Author, point of view, narrator Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Reading Informational Text (RI): ✔ Key Ideas and Details 1 Textual evidence and inferences 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details 3 Developing key details and connections Craft and Structure 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice 5 Text structure and development of ideas 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Integration of Knowledge and Ideas 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Range of Reading and Level of Complexity 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Writing (W): ✔ Text Types and Purposes 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. Production and Distribution of Writing 4 Development, organization, style, task, purpose, audience 5 Develop writing, planning, revising, editing, rewriting 6 Use technology Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7 Research, question, sources 8 Relevant and credible resources, quotes, paraphrase, bibliography 9 Literary and informational text-‐based evidence Range of Writing 10 Range, audience, purpose Speaking and Listening (SL) ✔ Comprehension and Collaboration 1 Engage in collaborative dicussions 2 Use evidence to support with diverse media 3 Reliability of claims and evidence Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4 Sequence findings, appropriate body language 5 Visual Aid 6 Range and diversity of writing Language (L): ✔ Conventions of Standard English 1 Standard English grammar and usage conventions when speaking and writing 2 Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing Knowledge of Language 3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4 Determine meaning of unknown and multiple-‐meaning words and phrases using strategies 5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings
- 30. 30 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Reading Standards for Literature 6-‐8 Reading Literaure (RL): Key Ideas and Details RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 1 Textual evidence and inferences Cite to support analysis of what text says explicitly and inferences drawn Cite several times Textual evidence that most strongly supports 2 Theme or central idea, summary, sensory details Determine how theme is conveyed through particular sensory details and objective summary Analyze its development over the course of text Specifically, analyze theme’s relationship with characters, setting, plot 3 Development of literary elements including plot, characters, dialogue Plot unfolds in a series of episodes as well as how characters respond and change as plot moves toward a resolution How different literary elements interact Analyze how dialogue or incidents propel action, revealing new aspects of character Reading Literaure (RL): Craft and Structure RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 4 Words and phrases: figurative, connotative, rhyme, repitition word choice, tone, analogies, allusion Determine meaning of words and phrases: figurative, connotative, word choice, tone Rhyme and repetition Analogies and allusions to other texts 5 Text structure Specific excerpt connected to whole structure and plot, theme, setting development Drama or poem form or structure contribute to meaning Compare and contrast structure of two or more texts and the value in different structures 6 Author, point of view, narrator Explain how author develops into narrator POV. Author contrasts narrator’s perspective with other characters Analyze how differences in perspective create effects (such as suspense or humor) Reading Literaure (RL): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 7 Compare and contrast, production techniques Compare and contrast reading to listening or viewing same piece Analyze the effects of techniques unique to each medium Analyze how a production stays faithful to or departs from the original, evaluating creative choices used 9 Compare and contrast style, purpose, genre, multiple texts on same theme, patterns of events character types Compare and contrast texts in different forms or genres in terms of approaches to similar themes Fictional with nonfiction historical account Modern work with traditional literature in terms of themes, patterns of events, or character types Reading Literature (RL): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 10 Fictional text complexity proficiently Scaffolding Scaffolding Independently
- 31. 31 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Reading Standards for Informational Text 6-‐8 Reading Informational Text (RI): Key Ideas and Details RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 1 Textual evidence and inferences Cite to support analysis of what text explicitly says and draw inferences Cite several times Textual evidence that most strongly supports 2 Central idea, summary, sensory details Determine central idea of a text and how it’s conveyed through particular details Two or more central ideas, analyze development; provide summary Include the central idea’s relationship to supporting ideas 3 Developing key details and connections Analyze key individual, event, idea is introduced, illustrated, and elaborated Interactions between one another in a text; compare multiple events Connections amongst the distinctions through comparisons, analagies, and categories Reading Informational Text (RI): Craft and Structure RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 4 Decipher words and phrases, word choice Determine meaning of words and phrases: figurative, connotative, word choice, tone Rhyme and repetition Technical meanings, analogies and allusions to other texts 5 Text structure and development of ideas Specific excerpt connected to overall structure and contribution to development of ideas Analyze structure author uses to organize text Analyze specific excerpt in detail, including the role of particular sentences to development and refining key concept 6 Author’s point of view or purpose Author’s point of view or purpose and how it’s conveyed Author distinguishes perspective from that of others Analyze how the author acknowledges and responds to conflicting evidence or viewpoints Reading Informational Text (RI): Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 7 Integrate medias or formats to develop coherent understanding Integrate information presentated in different medias or formats to develop coherent understanding Compare and contrast text to audio version, depicting each medium’s portrayal of subject Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of using different mediums to present a particular topic and idea 8 Evaluate the argument and specific claims; evidence Trace and evaluate the argument and specific claims; distinguishing claims supported by reasons and evidence from those not Assess whether the reasoning is sound and evidence is relevant and sufficient Examine and evaluate if the argument is sound; recognize when irrelevant evidence is introduced 9 Compare and contrast one author’s presentation Compare and contrast one author’s presentation of events with that of another Two or more authors writing about the same topic emphasize different evidence or interpretations of facts Analyze texts which provide conflicting information; identify where the texts disagree on matters of fact or inpretation Reading Informational Text (RI): Range of Reading and Level of Complexity RL Keywords Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 10 Informational text complexity proficiently Scaffolding Scaffolding Independently
- 32. 32 College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Writing Standards 6-‐8 Writing (W): Text Types and Purposes W Base Grade 6 Grade 7-‐ Add on Grade 8-‐ Add on 1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. a. Introduce claims, organize reasons and evidence Introduce claims and organize reasons and evidence clearly Acknowledge alernate claims; organize logically Distinguish claim from alternate b. Support, credible sources Support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence, using credible sources to demonstrate understanding Logical reasoning; Accurate sources c. Clarify relationship among claims and reasons Use words, phrases, clauses to clarify relationship among claims and reasons Create cohesion to clarify; evidence Counterclaims d. Formal style Establish and maintain a formal style e. Concluding statement Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from argument presented Support argument presented 2 Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic, convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection , organization, and analysis of relevant content. a. Introduce topic, organization, formating, grapics, multimedia Inroduce a topic; organize ideas, concepts, and information using strategies such as definition, classification, comparison, contrast, and cause and effect; include formatting, graphics, and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension Introduce and preview what is to follow Organize into broader categories b. Develop topic Develop topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, other information, examples Well-‐chosen facts c. Transitions Use appropriate transitions to clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts Create cohesion Varied d. Language and vocabulary Use precise language and domain-‐ specific vocabulary to inform and explain e. Formal style Establish and maintain formal style f. Concluding statement Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from information presented 3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-‐structured event sequences. a. Establish context, introduce narrators and characters, organize Engage and orient the reader by establishing a context and introducing a narrator and/or characters; organize an event sequence that unfolds naturally and logically Establish point of view b. Develop story using narrative techniques Use narrative techniques, such as dialogue, pacing, and description, to develop experiences, events, characters Reflection to develop c. Transition and sequence Use a variety of transition words, phrases, clauses to convey sequence and signal shifts from one time frame or setting to another Show relationships among events d. Sensory language Use precise words and phrases, relevant descriptive details, and sensory language to convey experiences and events e. Conclusion Provide conclusion that follows from narrated experiences or events