Contenu connexe
Similaire à Math Matrix (tri 1)
Similaire à Math Matrix (tri 1) (20)
Math Matrix (tri 1)
- 1. Cesar Chavez Academy
6th Grade Math Matrix (Tri 1)
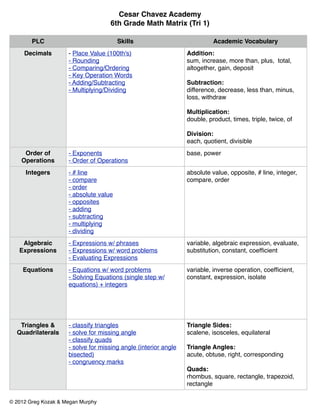
PLC Skills Academic Vocabulary
Decimals - Place Value (100th's) Addition:
- Rounding sum, increase, more than, plus, total,
- Comparing/Ordering altogether, gain, deposit
- Key Operation Words
- Adding/Subtracting Subtraction:
- Multiplying/Dividing difference, decrease, less than, minus,
loss, withdraw
Multiplication:
double, product, times, triple, twice, of
Division:
each, quotient, divisible
Order of - Exponents base, power
Operations - Order of Operations
Integers - # line absolute value, opposite, # line, integer,
- compare compare, order
- order
- absolute value
- opposites
- adding
- subtracting
- multiplying
- dividing
Algebraic - Expressions w/ phrases variable, algebraic expression, evaluate,
Expressions - Expressions w/ word problems substitution, constant, coefficient
- Evaluating Expressions
Equations - Equations w/ word problems variable, inverse operation, coefficient,
- Solving Equations (single step w/ constant, expression, isolate
equations) + integers
Triangles & - classify triangles Triangle Sides:
Quadrilaterals - solve for missing angle scalene, isosceles, equilateral
- classify quads
- solve for missing angle (interior angle Triangle Angles:
bisected) acute, obtuse, right, corresponding
- congruency marks
Quads:
rhombus, square, rectangle, trapezoid,
rectangle
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 2. PLC Skills Academic Vocabulary
Angle Pairs - angle pairs vertical, complementary, supplementary,
(Missing Angles) - multi-step missing angles exterior & interior angles, straight & right
angle
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 3. Place Value
Videos: Place Value 1, Place Value 2
Practice: Place Value, Place Value w/ Decimals
The value given to the space a digit holds because of its place in a numeral. These values are
named according to the spot each takes up.
Example:
Rounding
Videos: Rounding Whole #’s 1, Rounding Whole #’s 2, Rounding Decimals
Practice: Rounding Numbers
Rewriting a number as its nearest multiple of 10, 100, 1,000, and so on.If the circled number to the
right of the place you are rounding to is 0–4, the number stays the same. If it is 5–9, the number
rounds up to the next greater number. The rest of the numbers to the right of the original number
become zeros.
Example 1:
Round 3,294 to the nearest thousand.
Look at the number in the place you are rounding; underline it and circle the number right after it.
3,294
The circled number to the right of the 3 is 2, so the 3 will stay the same. The rest of the numbers will
change to zeros. Therefore, 3,294 rounds to 3,000 when rounding to the nearest thousand.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 4. Example 2:
Round to the nearest 10
566 –––> 570
562 –––> 560
3,049 –––> 3,050
Round to the nearest 100
566 –––> 600
536 –––> 500
Examples:
76,824 –––> 76,800
Round to the nearest 10,000 1) .7 = 7 tenths
2) 3.5 = 3 and 5 tenths
64,340 –––> 60,000 3) .78 = 78 hundredths
868,473 –––> 870,000 4) 9.34 = 9 and 34 hundredths
406,299 –––> 410,000 5) .983 = 983 thousandths
6) 23.802 = 23 and 802 thousandths
Comparing Decimals
Videos: Comparing Decimals, Using a Number Line to Compare Decimals
To determine which decimal is larger or smaller, place value must be compared.
1. Line up the decimal points.
2. Compare tenths, then hundredths, and then thousandths.
1 Line up decimal points 0.41
0.275
2 Look at place value: 4 tenths is larger than 2 tenths, so 0.41 is larger than 0.275
Key Operation Words
Addition: sum, increase, more than, plus, total, altogether, gain, deposit
Subtraction: difference, decrease, less than, minus, loss, withdraw
Multiplication: double, product, times, triple, twice, of
Division: each, quotient, divisible
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 5. Adding Decimals
Videos: Adding Decimals 1, Adding Decimals 2
Practice: Adding Decimals
1. Line up the decimal points so that the place value is in line.
2. Change all whole numbers into decimals (7 = 7.00, 23 = 23.00)
3. Add as normal. Zeros can be added after the decimal point in order to make adding easier,
and it won’t change the answer.
4. Bring the decimal point straight down into the answer.
Examples:
.75 + 2 + 1.674 = 3.5 + .46 = .4 + 3 + .27 =
.750 3.50 .40
2.000 + .46 3.00
+ 1.674 3.96 + .27
4.424 3.67
Subtracting Decimals
Videos: Subtracting Decimals 1, Subtracting Decimals 2
Practice: Subtracting Decimals, Adding & Subtracting Decimals with Word Problems
1. Line up the decimal points so that the place value is in line.
2. Change all whole numbers into decimals (7 = 7.00, 23 = 23.00)
3. Subtract as normal. Zeros can be added after the decimal point in order to make subtracting
easier, and it won’t change the answer.
4. Bring the decimal point straight down into the answer.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 6. Multiplying Decimals
Videos: Multiplying Decimals 1, Multiplying Decimals 2
Practice: Multiplying Decimals
1. Write and solve the problem as normal.
2. Count the total number of places after each decimal in the numbers being multiplied.
3. Position the decimal the same number of places in the answer.
Dividing Decimals
Videos: Dividing Decimals 1, Dividing Decimals 2, Dividing Decimals 3, Dividing Decimals 4
Practice: Dividing Decimals
Division Terms:
1) Rational Number: Any number that can be written as a ratio, decimal, and fraction (Ex: 3, 3.00,
or 3/1).
2) Terminating Number: A number that stops dividing after a number of decimal points. It does not
go on forever (Ex: .34, 3.45)
3) Irrational Number: A number that cannot be written as a ratio, decimal, or fraction since it goes
on forever and never terminates (Ex: π = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795 (and more...)
4) Non Terminating Number: A number that will not terminate or stop dividing and go on forever.
5) Quotient: The answer to a division problem
6) Dividend & Divisor: The dividend is the number that is to be divided while the divisor is the
number the dividend is being divided by.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 7. Decimal in the dividend only:
1. Write the problem as normal.
2. Bring the decimal point straight up.
3. Divide as normal.
4. No remainders. You must add a zero in the dividend, drop it, and continue dividing.
Example:
Decimal in the dividend and divisor:
1. Move the decimal in the divisor all the way to the right.
2. Move the decimal in the dividend the same number of times as was done in the divisor.
3. Bring the decimal in the dividend straight up.
4. Divided as normal.
5. No remainders. You must add a zero in the dividend, drop it, and continue dividing.
Example:
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 8. Exponent
Videos: Exponents 1, Exponents 2
Practice: Exponents
A small symbol placed above and to the right of a number or letter that shows how many times the
base is to be multiplied by itself.
Example:
64 = 6 x 6 x 6 x 6, so 64 = 1,296
b3 = b x b x b
57 = 5 x 5 x 5 x 5 x 5 x 5 x 5, so 57 = 78,125
72 = 7 x 7, so 72 = 49
Order of Operations
Videos: Operations 1, Operations 2, Operations 3, Operations 4
Practice: Order of Operations
A set of rules agreed upon by mathematicians that outline the steps to take when solving multi-
operational problems. These rules help reduce confusion when solving problems and ensure that
the same answer can be reached every time.
Rules:
1) Complete the work in parentheses (or brackets) first.
2) Simplify exponents.
3) Multiply or divide from left to right.
4) Add or subtract from left to right.
Example:
62 + 15 x (1 + 3) ÷ 5 =
62 + 15 x 4 ÷ 5 =
36 + 15 x 4 ÷ 5 =
36 + 60 ÷ 5 =
36 + 12 = 48
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 9. Sometimes problems may not have all of the components listed above (parentheses, exponents,
multiplication/division, and addition/ subtraction). If so, continue down the list of steps until you
reach a step that fits the problem.
Example: (There are no parenthesis or exponents, so start on rule 3)
9–3+2x6=
9 – 3 + 12 =
6 + 12 = 18
Number Line
Videos: Number Line 1, Decimals on a Number Line
Practice: Number Line 1, Number Line 2, Number Line 3, Decimals on a Number Line 1, Decimals on
a number line 2
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 10. Comparing Integers (Integers are counting numbers, their opposites, and zero)
Videos: Comparing Integers 1
1) Create a number line
2) Negative integers are always smaller than positive integers
3) Puts dots on the number line for each integer
4) The integer that is on the left is always the smaller integer of the set of integers
Absolute Value
Videos: Absolute Value 1, Absolute Value 2, Absolute Value 3, Absolute Value 4
Practice: Finding Absolute Value, Comparing Absolute Values
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero.
Example:
|+4| = 4 and |-4| = 4
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 11. Opposites
Opposites are numbers that are the same distance from zero. Therefore, -6 and 6 are opposites.
Example:
-(6) means the opposite of 6 which is -6
6) means the opposite of -6 which is 6
Adding Integers
Videos: Adding Integers w/ Same Signs, Adding Integers w/ Diff Signs 1, Adding Integers w/ Diff
Signs 2
Practice: Adding & Subtracting Integers
When the signs are the same:
1) Positive + Positive = Positive (+5) + (+10) = (+15)
2) Negative + Negative = Negative (-3) + (-4) = (-7)
When the signs are different:
If the signs are different (one is positive and one negative) you must subtract. The larger number
goes on top and use the sign of the larger number in your answer.
(+9) + (-12) = (-3)
(-10) + (+4) = (+6)
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 12. Using a number line to add integers:
1) If the second integer is positive then you move right on the number line
2) If the second integer is negative then you move to the left on the number line
Subtracting Integers (Add the second integer’s opposite)
Videos: Subtracting Integers
Practice: Adding & Subtracting Integers
Subtracting Integers
1) Change the subtraction sign into a plus sign
2) Change the sign of the 2nd integer
3) use addition rules to add
Example: (-10) - (+3) =
(-10) + (-3) = -13
Example: (+7) – (+2) =
(+7) + (-2) = +5
Area of a rectangle or square
Area = Length x Width (A=lw)
(area is always squared)
©Example: Kozak & Megan Murphy
2012 Greg
- 13. larger #.
Example: (-10) + (+3) = -7
Multiplying Integers
Example: (+15) + (-6) = +9
Videos: Multiplying Integers 1
Area of a rectangle or square
Multiply & Dividing Integers
Practice: Multiplying & Dividing Integers
Area = Length x Width (A=lw)
1) If the signs of the integers are the same then (area is always squared)
your answer is always positive (+) Example:
Example: (+5) x (+4) = +20
Adding Integers Subtracting Integers
Example: (-12) ÷ (-3) = +4
1) If the integers have the same sign (either both 1) Change the subtraction sign into a plus
2) If theor negative) then you just add
positive signs of the integers are different then 2) Change the sign of the 2nd integer
your answer is always= +9
Example: (+5) + (+4) negative (-) 3) use addition rules to add
Example: (-10)+x(-3) ==-7
Example: (-4) (+3) -30 Example: (-10)x- Width
Area = Length (+3) =
Example: (+54) ÷ (-6) = -9 Area = 14 x 7 + (-3) = -13
(-10)
2) If the signs of the integers are different (one is Area = 98cm²
positive and one negative) then you must subtract. Example: (+7) – (+2) =
Area of a triangle on top and use the sign of the
The larger # goes (+7) + (-2) = +5
Area of a parallelogram
larger #.
Dividing Integers
Area = 1/2(-10) + (+3) height (A= 1/2bh)
Example: x base x = -7
Videos: Dividingsquared) = +9
(area is always Integers 1
Example: (+15) + (-6) Area = base x height (A= bh)
Practice: Multiplying & Dividing Integers (area is always squared)
Area of a rectangle or square
Multiply & Dividing Integers
Area = Length x Width (A=lw)
1) If the signs of the integers are the same then (area is always squared)
your answer is always positive (+) Example:
Example: (+5) x (+4) = +20
Example: (-12) ÷ (-3) = +4
Example:
Example:
2) If the signs of the integers are different then
your answer is always negative (-)
Example: (-10) x (+3) = -30 Area = Length x Width
Example: (+54) ÷ (-6) = -9 Area = 14 x 7
Area = 98cm²
Area = 1/2 triangle height
Area of a x base x Area of a parallelogram
Area = 1/2 x 12 x 15 Area = base x height
Area = 180/2 x base x height (A= 1/2bh)
Area = 1/2 Area = 15 x 5
Area is always
(area = 90m² squared) Area = 75cm²x height (A= bh)
Area = base
(area is always squared)
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 14. Expressions with Phrases
Practice: Writing Expressions, Writing Expressions 2
Terms:
1) Algebraic Expression - a mathematical phrase that has at least one variable and one operation
(+, -, x, ÷)
Example: 6n (multiplication), n + 6 (addition), n - 6 (subtraction), n/6 or 6/n (division)
2) Evaluate - to determine the value or amount
3) Variable (unknown quantity) - a quantity that can be change or vary and is often represented by
a letter.
Example: 5n + 4 (n is the variable or unknown quantity)
4) Coefficient - The numerical part of an algebraic expression
Examples:
3x2 3 is the coefficient.
2y 2 is the coefficient.
5(a + b) 5 is the coefficient.
5) Constant - a number that is on its own, or a fixed number
Example: 5n + 4 (4 is the constant)
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 15. Phrases:
Word Phrase Operation Algebraic Expression
3 more than a number n addition n+3
6 less than a number n subtraction n-6
five times a number n multiplication 5n
a number divided by 4 division n/4
4 divided by a number n division 4/n
five less than three times a multiplication & division 3n - 5
number n
two less than a number n division & subtraction n/4 - 3
R A D E CA L I F O R N I A S TA N DA R D S T E S T
divided by 4
6 Math Released Test Questions
Expressions with Word Problems
ᮀ
46 1) Substitute company charges $0.05 per minute
A telephone any number for the variable
for local calls and $0.12 per minute for long-
ᮀ
48 The steps Quentin took to evaluate the
expression 3m − 3 ÷ 3 when m = 8 are
2) Determine which operation would be used to solve the problem once the variable is substituted
distance calls. Which expression gives the total shown below.
cost in dollars for x minutes of local calls and
3) minutes ofkey operation words if possible
y Use your long-distance calls? 3m – 3 ÷ 3 when m = 8
3 ¥ problem
4) write0the+ 0.12 y expression to match the operation to be used to solve the 8 = 24
A 0. 5 x correct 24 – 3 = 21
B 0.05 x − 0.12 y 21 ÷ 3 = 7
C 0.17( x + y)
What should Quentin have done differently
D 0.17xy in order to evaluate the expression?
CSM01299
A divided (24 − 3) by (24 × 3)
Example:
B divided (24 − 3) by (24 − 3)
ᮀ
47 Rita is moving a pile of 120 rocks by hand to
build a rock wall. If h represents the number
C subtracted (3 ÷ 3) from 24
of rocks that she can carry in one load, which D subtracted 3 from (24 ÷ 3)
expression represents the total number of loads CSM10804
needed to move the entire pile of rocks?
120 + h
A 4 rocks in one load.
4, ᮀ
1) Substitute a number for the variable h. Let’s use 49 so that will represent8that + 2 =can move
8 + ÷ 2 Rita
A 4
2) No key operation words can help us here. Since Rita needs to move 120 rocks and can only
B 8
B move 4 at a time, the only way to find out the total amount of loads needed is to divide
120h
3) So our expression will be 120/4 which is 120/n whenC 10 we re-substitute the variable.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
D 14
C 120 − h
CSM02058
- 16. Evaluating Expressions
Videos: Expressions 1, Expressions 2, Expressions w/ 2 Variables
Practice: Evaluating Expressions w/ 1 Variable, Evaluating Expressions w/ 2 Variables
1) Determine the operation to be used based on the algebraic expression
2) Substitute the number given for the variable
3) Solve or evaluate using order of operations
Example: Evaluate the expression 3n + 2 when n = 5
1) This expression includes two operations (multiplication and addition)
2) Next substitute 5 for the variable n
3) Your problem will now look like this: 3 x 5 + 2
4) Based on the order of operations, we must first multiply then add
5) Our problem will be solve in the following manner:
3 x 5 + 2 (multiply first)
15 + 2 (now add)
17 (our answer)
Equations with Word Problems
1) Determine the operation that would be used to solve the problem normally (try using the key
operation words)
2) Write the equation that would allow you to perform the operation to solve the problem
3) The equation is always the opposite or inverse of the operation used to solve the problem. For
example if you need to add to solve the problem then you would write a subtraction equation and
if you need to multiply to solve the problem then you would need to write a division equation to
solve the problem.
4) Your variable will be the unknown quantity that is to be found.
Example: Lindsi had 8 apples on Monday and then lost 2 on Wednesday, how many apples
does she have left.
1) First determine the operation to solve the problem. The key words “have left and lost” indicate
that subtraction is the operation to use.
2) The correctly solve this problem we need an equation that will give us 8 - 2.
3) Since we need to subtract, we will write an equation with the opposite or inverse operation which
would be addition.
4) Our variable is the unknown quantity this is to be found.
5) The equation would be x + 2 = 8
6) When worked out, the equation will give us the operation we need of 8 - 2.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 17. Solving Single Step Equations (equations with only one operation)
Videos: Single Step 1, Single Step 2, Single Step 3, Single Step 4
Practice: Single Step Equations
Terms:
1) Equation - a number sentence that uses an equal sign. Everything on one side an equal sign
has to equal everything on the other side. Equations normally have a variable or unknown quantity
that must be found to make the number sentence true.
2) Inverse Operation - Operations that are opposite and undo each other. Addition and subtraction
are inverses of each other as well as multiplication and division.
3) Variable (unknown quantity) - a quantity that can be change or vary and is often represented by
a letter.
Example: 5n + 4 (n is the variable or unknown quantity)
4) Coefficient - The numerical part of an algebraic expression
Examples:
3x2 3 is the coefficient.
2y 2 is the coefficient.
5(a + b) 5 is the coefficient.
5) Constant - a number that is on its own, or a fixed number
Example: 5n + 4 (4 is the constant)
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 18. Solving One Step Equations:
1) Perform the inverse or opposite operation to both sides of the equations in order to isolate or get
the variable all by itself.
2) Evaluate or solve each side of the equation.
3) Check your answer by substituting your answer for the variable. Both sides of the equal sign
should equal each other if your answer is correct.
Examples:
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 19. Classifying Triangles
Practice: Classifying Triangles
Triangle - A polygon with three segments as sides and three angles. The sum of the three angles of
a triangle equals 180 degrees.
Classifying Triangles by Sides:
1) Scalene Triangle - A triangle with no sides congruent or the same length. All of its angles will be
different sizes as well.
2) Isosceles Triangle - A triangle with two opposite sides congruent or the same length. The base
angles opposite the equal sides will also be equal.
3) Equilateral Triangle - A triangle with all sides congruent or the same length. The angles are also
all congruent and will always be 60 degrees.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 20. Classifying Triangles by Angles
1) Acute Triangle - A triangle with all acute angle (less than 90 degrees).
2) Obtuse Triangle - A triangle with one obtuse angle (more than 90 degrees).
3) Right Triangle - A triangle with one right angle (exactly 90 degrees)
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 21. Finding Missing Angles of Triangles
Video: Triangle Missing Angles
Practice: Triangle Missing Angles
1) Add the two angles that are present together
2) Subtract by 180 (all three angles in a triangle must add up to 180 degrees)
Example: (find the measure of ∠ABC)
1) add the two given angles together (39 + 55 = 94)
2) subtract 94 from 180 (180 - 94 = 86)
3) ∠ABC = 86°
For Isosceles Triangles:
1) Subtract the given angle from 180
2) divide your answer by two (both angles opposite the congruent sides are equal which is why you
divide by 2)
Example: (find the measure of ∠ACB and ∠BAC)
1) Subtract 120 from 180 (180 - 120 = 60)
2) Divide your answer (60) by two since the base angles are congruent (60 ÷ 2 = 30)
3) So both angles are 30°
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 22. Classifying Quadrilaterals (A Polygon with Four Sides. All angles add up to 360°)
Videos: Quadrilaterals
Practice: Classifying Quadrilaterals
1) Square - a quadrilateral with four right angles and all sides congruent or the same length. A
square can also be a rectangle, a rhombus, and a parallelogram.
2) Rectangle - a quadrilateral with four right angles. A rectangle is also a parallelogram.
3) Parallelogram - a quadrilateral with two pairs of opposite sides parallel. The opposite sides and
angles congruent.
Rhombus - a quadrilateral with all sides congruent. A rhombus is also a parallelogram and a
square.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 23. 5) Trapezoid - a quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides parallel. An Isosceles trapezoid is
one with both base angles congruent.
Finding Missing Angles of Quadrilaterals
Practice: Missing Angles of Quadrilaterals
1) Add the given angles together
2) subtract your answer from 360 (all 4 angles in a quadrilateral add up to 360°)
Example: (Find the measure of ∠PQR)
1) Add the given angles together (120 + 60 + 70 = 250)
2) Now subtract your answer (250) from 360 since all four angles in a quadrilateral add up to 360°
(360 - 250 = 110)
3) So ∠PQR is 110°
Example: (When Missing Angle is Bisected) Find the measure of ∠MNO
1) Add all of the given angles together (55 + 125 + 55 = 235)
2) Subtract your answer (235) from 360 (360 - 235 = 125)
3) The measure of ∠MNO is 125°
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 24. Congruency Marks (≅ means congruent or the same size and shape)
Congruency Marks - The corresponding congruent sides of triangles are marked with small straight
line segments called hash marks. The corresponding congruent angles are marked with arcs.
Examples:
1) ∠ABC ≅ ∠DFE
2) Line CB ≅ Line FE
Angle Pairs
Videos: Complementary & Supplementary, Complementary & Supplementary 2, Measuring Angles
Practice: Angle Types, Corresponding & Congruent Angles, Supplementary, Complementary,
Vertical, Complementary & Supplementary, Measuring Angles
Terms:
1) Angle - a figure formed by two rays, called sides, that share a
common endpoint called a vertex.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 25. Angle Pairs
1) Complementary Angles - Two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees.
2) Supplementary Angles - Two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees
3) Vertical Angles - A pair of angles that are formed by intersecting lines and have no side in
common.
4) Corresponding Angles - When two lines are crossed by another line (called a transversal) the
matching corner angles are corresponding angles and are congruent (same measure).
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 26. Multi-Step Missing Angles
Videos: Missing Angles 1, Missing Angles 2, Missing Angles 3, Missing Angles 4
Practice: Multi-Step Missing Angles, Multi-Step Missing Angles 2
1) Highlight the missing angle that is to be found
2) Decide what other angles need to be found in order to find the angle that you need
3) Use your knowledge of triangles (all angles add up to 180), quadrilaterals (all angles add up to
360), supplementary angles (add up to 180) complementary angles (add up to 90), and vertical
angles (opposite angles that are congruent) to help find any angles that you need.
Example 1: (Find ∠JGI)
Step 1: Highlight the angle that is to be found
Step 2: Use supplementary angles. Notice that ∠EGJ and ∠JGI are supplementary angles and
thus should together add up to 180 degrees.
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 27. Step 3: Add ∠EGK and ∠KGJ (46 + 83 = 149). This gives you ∠EGJ
Step 4: Now subtract 149 from 180 (180 - 149 = 31). This will give you ∠JGI
Step 5: ∠JGI = 31°
Example 2: (Find ∠EFB)
Step 1: Highlight the angle that is to be found
48°
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy
- 28. Step 2: See what other angles you need to help you find your answer
• Notice that ∠EFB is in a triangle. You know that all 3 angles of a triangle add up to 180 degrees.
• If you knew ∠EBF then you could add that to ∠BEF and then subtract it from 180 to get your
answer. We need to find what ∠EBF is.
Step 3: Find ∠BEF
• Notice that ∠EBF is vertical to 48°. Remember that vertical angles are opposite angles that are
congruent which means that ∠EBF is also 48°.
Step 4: Finding ∠EFB
• Now add ∠EBF (48°) and ∠BEF (66°) together. 48 + 66 = 114°
• Next subtract 114 from 180 since all of the angles in a triangle add up to 180
• 180 - 114 = 66°
• ∠EFB = 66°
© 2012 Greg Kozak & Megan Murphy