Vietnam war for Cambridge IGCSE History
- 1. 1
- 2. 2
- 3. 3
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 7. The War in VietnamThe War in Vietnam Cold War turns very Hot http://www.slideshare.net/guimera/a-look-back-at-the-vietnam-war-on-th
- 8. What we need to know... 1. Who were the Vietcong? 2. How did it all begin? 3. Why did USA got involved? 4. Why USA lost?
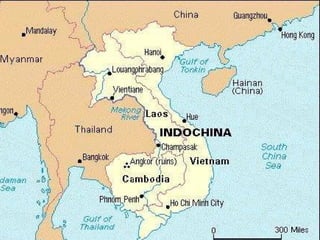
- 9. Background French colony Viet Minh starts as independence movement in 1941, adopts communism in 1950’s. Geneva Conference split Vietnam at 17th parallel. Country-wide elections to be held in 1956 to decide on single government for entire country. South refused to participate. North invaded South.
- 10. 10 The red lines show the invasion of the North Vietnamese army.
- 11. 11 South Vietnam North Vietnam United States Vietcong The Players
- 12. North Communist Backed by USSR and China Govt led by Ho Chi Minh (“Uncle Ho”) Fought both the French and the Japanese! Experienced South Semi-democratic Backed by USA Govt led by Diem Corruption and nepotism Persecuted Buddhists Favoritism for Catholics → angered Buddhist majority. Overthrown by group of generals in Nov 1963.
- 13. Increasing involvement... "If we withdrew from Vietnam, the Communists would control Vietnam. Pretty soon, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Malaya, would go...“ Kennedy The “domino theory”! - 1961: Jan -- 900 advisors - 1963: Nov – 16,000 advisors NVA regulars invade RVN - 1964: Summer – 27,000 advisors US begins covert raids against targets in NV and surveillance missions. - 1965: 200,000 troops!!!
- 14. *Military build-up in Vietnam intensified to 500,000 by 1967 What is the objective in Vietnam? CONTAINMENT: Problem? U.S. sponsored gov’t not popular in democratic South Lyndon Baines Johnson (LBJ)
- 16. Gulf of Tonkin August 1964, two US destroyers allegedly fired on by NV gunboats.
- 17. 1964 - Gulf of Tonkin Resolution North Vietnamese patrol boats fired on the USS Mattox in the Gulf of Tonkin on August 2. On August 7, the U.S. Congress approves the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, granting President Johnson authority to send U.S. troops to South Vietnam.
- 18. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Johnson passed Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. – Approved nearly unanimously. – Gave him authority to “to take all necessary measures to repel any armed attack against the forces of the US and to prevent further aggression.”
- 19. - The National Liberation Front, who fought against USA. - included opponents of the South Vietnamese government and North Vietnamese communists under Ho Chi Minh. - fought against both the South Vietnam government and the American armed forces between 1959-75. - Initially a group of communist guerrilla fighters, it increased in numbers over the course of the conflict. - had the support of the peasants as they treated them well.
- 20. VietcongVietcong: Farmers by day; guerillas at night.Farmers by day; guerillas at night. Very patient people willing to endureVery patient people willing to endure sufferings and accept manysufferings and accept many casualties.casualties. The US grossly underestimated theirThe US grossly underestimated their determination, popularity anddetermination, popularity and resources.resources.
- 21. Why did the USA get involved in the war in Vietnam? - In 1954 the French were driven from their colony and the Viet Minh movement became popular. - The USA feared the expansion of communism across Europe and Asia. They believed the future of US prosperity and democracy was at risk if communism spread. - The USA had to practise 'Containment policy'. Communism was spreading in China, eastern Europe and North Korea. Americans felt increasingly threatened by the spread of communism. This fear was the “domino theory” - if one country became communist others would follow. If South Vietnam fell it would be followed by Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, Burma... - In the Tonkin incident in August 1964, North Vietnamese opened fire on the US navy and the US Congress passed the Tonkin Resolution. It gave Johnson opportunity to let American troops be involved.
- 22. Why did the Americans lose the Vietnam War?
- 23. 23 The difficulty of the terrain meant young American soldiers could not get used to fighting in a foreign jungle. The guerrillas merged with the people and the jungle. American soldiers were inexperienced and unable to cope with a warfare so different to what they were used to.
- 24. Who Is the Enemy? The conventional army loses if it does not win. The guerillaThe conventional army loses if it does not win. The guerilla wins if he does not lose.wins if he does not lose. -- Mao ZedongMao Zedong
- 25. In the jungle, the Vietcong built extensive networks of underground tunnels with storehouses, workshops, and hospitals. These were very difficult to find and destroy! (Bombing won't work)
- 26. Why Americans were no match for a bunch of Asian rice farmers? The principles of guerrilla tactics : Retreat when enemy attacks, raid when enemy camps, attack when enemy tires and pursue when enemy retreats. - a nightmare for the invaders! Guerrillas had no uniform and no base camps. It was hard to tell them from the village peasants. They attacked, disappeared into the jungle, and carried out sudden ambushes or booby traps. Aim: to wear down the enemy in both strength and morale. US soldiers lived in constant fear.
- 27. 1965: US begins ROLLING THUNDER, an extensive bombing campaign Good idea? Operation Rolling Thunder
- 28. Air Campaign Johnson places extensive restrictions on targets due to concerns over public opinion and Soviet and Chinese response. 7 million tons of bombs and defoliants were dropped in total and 2.6 million Vietnamese were killed. :( ROLLING THUNDER Planned for 8 weeks, lasted 3 years. 500 US aircraft shot down NV use captured US aviators as propaganda weapons.
- 29. USA wanted to end the war quickly by “search and destroy” tactics.
- 30. Ambush following battle inflicts heavy casualties
- 31. American troops had increasingly low morale. They were young and inexperienced. They became frustrated at the defeats, and were losing both military and psychologically.
- 32. 32
- 33. 33 The Vietcong... - fighting in their own country. They knew their own terrain well. - continued to receive supplies from North Vietnam and China down the Ho Chi Minh Trail. - had support of many Vietnamese people - easily absorbed back into village life. - bases were well hidden in extensive underground bunkers making it very difficult to destroy.
- 34. The Ho Chi Minh Trail! - An effective link route between North and South Vietnam. - A network of jungle tracks for bicycles, trucks, tanks passing through Laos and Cambodia. It was used to move troops from North Vietnam after 1964. - Major supply route from North to Vietcong in the south!
- 35. Turning Point: Tet Offensive- January 30, 1968 Vietcong launched series of surprise attacks in South Vietnam during new year festivities (TET) U.S. took back cities, kill 32,000 Vietcong….but Tet proves that enemy is not prepared to surrender.
- 36. Max. psychological impact by attacking political centers, (Saigon and US Embassy) Sought to incite a uprising among the people tactical surprise by attacking on Lunar New Year
- 37. Tet Offensive-turning point in war Though USA militarily won the battle, the American public realized their government had lied to them. From then on, the war ($30 billion/year) was considered as un-winnable by the Americans. It was only a matter of time before US was humiliatingly forced to withdraw. TV shows that victory was NOT near!! Who do you believe?? Westmoreland ask for 200,000 more troops – People said NO!! LBJ did not seek re-election
- 38. 1968 - Tet Offensive In March, Johnson ordered a halt to the U.S. bombing of North Vietnam and offered peace talks.
- 39. However, the protests did not end
- 40. Agent Orange Defoliant-kills all vegetation-eliminates the jungle-easier to fight During the war in Vietnam more than 18 million gallons of Agent Orange were sprayed over 10% of S.Vietnam, poisoning millions of hectares of forest and croplands.
- 42. Protest Movement 1965 – 60% support war – 100 people-antiwar demonstrators in Boston – 380 draft evaders prosecuted By 1969 -60% opposed the war -100,000 anti-war demonstrators in Boston -33,960 draft evaders prosecuted
- 43. The war was losing support rapidly esp. due to media images sent from journalists at the front
- 44. a few chants became the common cry of the protestors: "Hell no; we won't go!" "Hey, hey, LBJ, how many kids did you kill today?"
- 45. My Lai Massacre 1968 300+ civilians intentionally slaughtered by USA platoon. Not “discovered” until 1969. Horrific images were shown on American media
- 46. On Oct 15 1969, people called for the total cessation of all military activity in Vietnam. 100,000 people gathered in the Boston Commons and 250,000 in Washington. On Nov 15, 500,000 protestors marched on Washington (the largest demonstration in U.S. history).
- 47. Burning of draft cards
- 49. Public opinion was changing. US atrocities in the use of horrific weapons against civilians and the use of chemical defoliants horrified people.’ The Americans lost support at home when it became clear after the Tet Offensive that the USA could not win the war. ‘It led to open criticism of Johnson – “Hey, Hey, LBJ, how many kids did you kill today”. ‘The USA had no support of the Vietnamese peasants. They generally viewed the Americans as invaders and chose to support the Vietcong who offered to improve their lives.’
- 50. Media Impact Only 3 network TV stations T.V. coverage U.S. public saw dirty war This eroded support for the war Reporters highly educated, skeptical, resistant to appeals of loyalty to govt. U.S. public started to see war as un-winnable & immoral
- 51. Economic cost... By 1968 the war cost $30,000 million a year. This meant cutbacks on spending on social reform. By the Tet Offensive, the 500,000 troops was spending $20-30 billion a year. In 1967 ‘Life Magazine’ calculated it cost $400,000 for each Vietcong guerrilla killed.
- 52. Mary Ann Vecchio screaming as she discovered her friend Jeffrey Miller and three other schoolmates were killed by National Guardsmen. Kent State University, 1970
- 53. The Media had a significant impact. As the War was the first televised war, American public became aware of what was happening. Americans realized the stark reality of war and were horrified at the barbaric nature of American attacks.
- 54. Over 50,000 troops lost their lives. By 1968, 300 were dying each week. Most Americans knew a relative or friend who had died.
- 55. 1968, 60% of Americans disapproved of LBJ’s handling of Vietnam LBJ announced he will not seek another term as president.
- 56. 1969 - Vietnamization 1968, Richard Nixon elected President June 8, 1969 U.S. Nixon announced his "Vietnamization" plan to withdraw U.S ground forces from Vietnam and turn control over to South Vietnamese forces. Cold War 11/24 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L9LKSx7yyCQ (36:41)
- 57. Vietnamization The plan was to encourage the South Vietnamese to take more role in fighting the war. It was hoped to eventually enable the United States to withdraw gradually all their soldiers from Vietnam.
- 58. The End Peace treaty signed on 27 Jan 1973. US would withdraw all forces. NV would repatriate all POWs. April-May 1975 Operation FREQUENT WIND evacuated remaining US and many South Vietnamese from Saigon as it fell to NVA. Last helicopter lifted remaining Marines from the embassy roof on 30 April.
- 59. 59 Longest war in American history (11 years) Total U.S. bomb dropped: World War II = 2,057,244 tons Vietnam War = 7,078,032 tons The power of mass media in wars
- 60. Compared with World War II.…. • The average infantryman in WWII had 40 days of combat in 4 years. •The average infantryman in Vietnam had 240 days of combat in 1 year due to the helicopter. • 1 out of 10 Americans who served in Vietnam was a casualty. • Amputations or crippling wounds were 300 % higher than in WWII. 75,000 were severely disabled. • 4 million civilians were killed in the war
- 61. 61 In 1975, North VietnamIn 1975, North Vietnam captured Saigon, thecaptured Saigon, the capital of South Vietnam.capital of South Vietnam. Vietnam became aVietnam became a unified communist state.unified communist state.
- 62. 62 Phan Thi Kim Phuc
- 63. 63 Forgiveness made me free from hatred. I still have many scars on my body and severe pain most days but my heart is cleansed. Napalm is very powerful, but faith, forgiveness, and love are much more powerful. We would not have war at all if everyone could learn how to live with true love, hope, and forgiveness. If that little girl in the picture can do it, ask yourself: Can you? ” — Kim Phúc, NPR in 2008
- 64. 64 (1) ‘The USA was unsuccessful in Vietnam because of the opposition’s use of guerrilla tactics.’ How far do you agree? (2) How far can the American withdrawal from Vietnam be blamed on military failure? (3) How far was the US public opinion the most important reason for America's withdrawal from Vietnam?
- 65. 65 Art of War part 1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6d2CAQRbRnc (start 6:03) Part 2 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1ZRAS2MJsQ8 (2:52 chess) Watchmojo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G9PNAUjDnGU
