Transforming the business model with cloud - Practical guide for CxO's
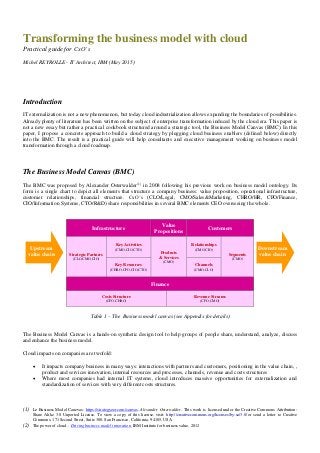
- 1. Transforming the business model with cloud Practical guide for CxO’s Michel REYROLLE - IT Architect, IBM (May 2015) Introduction IT externalization is not a new phenomenon, but today cloud industrialization allows expanding the boundaries of possibilities. Already plenty of literature has been written on the subject of enterprise transformation induced by the cloud era. This paper is not a new essay but rather a practical cookbook structured around a strategic tool, the Business Model Canvas (BMC). In this paper, I propose a concrete approach to build a cloud strategy by plugging cloud business enablers (defined below) directly into the BMC. The result is a practical guide will help consultants and executive management working on business model transformation through a cloud roadmap. The Business Model Canvas (BMC) The BMC was proposed by Alexander Osterwalder(1) in 2008 following his previous work on business model ontology. Its form is a single chart to depict all elements that structure a company business: value proposition, operational infrastructure, customer relationships, financial structure. CxO’s (CLO/Legal, CMO/Sales&Marketing, CHRO/HR, CFO/Finance, CIO/Information Systems, CTO/R&D) share responsibilities in several BMC elements CEO overseeing the whole. Infrastructure Value Propositions Customers Strategic Partners (CLO,CMO,CIO) Key Activities (CMO,CIO,CTO) Products & Services (CMO) Relationships (CMO,CIO) Segments (CMO) Key Resources (CHRO,CFO,CIO,CTO) Channels (CMO,CLO) Finance Costs Structure (CFO,CHRO) Revenue Streams (CFO,CMO) Table 1 – The Business model canvas (see Appendix for details) The Business Model Canvas is a hands-on synthetic design tool to help groups of people share, understand, analyze, discuss and enhance the business model. Cloud impacts on companies are twofold: It impacts company business in many ways: interactions with partners and customers, positioning in the value chain, , product and services innovation, internal resources and processes, channels, revenue and costs structures Where most companies had internal IT systems, cloud introduces massive opportunities for externalization and standardization of services with very different costs structures. (1) Le Business Model Canevas: https://strategyzer.com/canvas, Alexander Osterwalder. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution- Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, 171 Second Street, Suite 300, San Francisco, California, 94105, USA (2) The power of cloud – Driving business model innovation, IBM Institute for business value, 2012 Upstream value chain Downstream value chain
- 2. Strategy for Business Innovation Multiple conditions govern a company success and sustainability, among them strategy, finance, technology, organization, innovation, ecosystem, competition, regulations, economic and natural environments. The IBM Institute for Business Value proposes a cloud enablement framework(2) using “three organizational archetypes - optimizers, innovators and disruptors - that characterize the impact of an organization’s cloud-enabled business strategy”. Figure 2 – The cloud adoption framework Cloud business enablers Cloud services influence many several above conditions that govern company success, IBM identified six cloud business enablers(2) which impact business strategies. Figure 3– Cloud business enablers Business model assessment In order to move forward the cloud strategy, it is necessary to conduct an organization assessment along the three main dimensions (3D) below: 1. Cloud Enabler Levers for business model innovation 2. BMC element Infrastructure, customers, value propositions, finance 3. Organization Roles / processes / tools for business and IT This task requires a broad understanding of the entire organization in order to identify how both business model and organization could/should evolve based on cloud business enablers. Organization and business processes represent static and dynamic views on enterprise. For each 3D cell, one looks for business model inhibitors and accelerators using KPI’s such as value, costs (capex, opex, amortization), revenue, resources, competition, reactivity, quality, priority. KPI’s are used for strategic decision making for business model transformation. CxO’s all contribute to the transformation in many ways: CEO Focus company on core business activities and value creation CMO Innovative value propositions, customer relationships, social networks interactions, channels, pricings CIO Security, business continuity, externalize IT infrastructure & applications, continuous watch of market places CTO Accelerate product innovation by leveraging 3rd party cloud services, enable ecosystem with cloud API’s CFO Optimize costs/revenue structures, favor standardization vs customization of services CHRO Evolve workforce for value creation instead of IT infrastructure, adapt incentive plans to cloud pricing CLO Validate and align cloud partners SLA’s with company SLA’s, compliance The cloud initiative has to be supported at the highest level, so it is recommended to set a cross functional team (eventually supported by external consultants). The team will conduct the 3D scan and select solutions bringing optimal costs/benefits. Team alignment minimizes risk of uncontrolled initiatives (shadow IT). The above process is applied incrementally to cope with business constraints. Each iteration updates cloud roadmap, organization, processes and tools for the new business model.
- 3. Designing the cloud roadmap Based on KPI’s and strategic priorities, the cloud project team will propose business model innovations: value propositions, externalization, standardization, organization, processes, tools, etc. Cloud marketplaces offer a wide spectrum of XaaS services for most activities performed by an enterprise. Some common XaaS services are listed below: A continuous watch of new solutions on market places is mandatory in order to detect relevant opportunities to improve business model while minimizing risks. Examples of services transformations: IT Infrastructure IaaS, DaaS, MDMaaS, DRaaS Internally developed Services IaaS, PaaS, SaaS ISV Services SaaS Integrated Services Industry cloud, SaaS, BPaas Web Services IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, TaaS, BPaaS Public/Private networks Integrated IaaS offerings Once validated and accepted, new processes are put into production under IT team control with eventually additional ecosystem actors such as: integrator to assemble/migrate the solution, Managed Services Provider (MSP) to deploy and manage production in IaaS environment, ISV offering an extension to a selected service. A sample cloud services map is given in Appendix B. Note that each cloud business enabler is seen here through multiple perspectives of BMC elements where it appears. For instance, in the Customer element of the BMC, one will consider business processes in the Channels, Segments, Relationships and search cloud enablers that accelerate the business model. The cloud roadmap belongs to a continuum of hybrid cloud as depicted below. While hybridization level and roadmap dynamics might be constrained by company business and legacy systems, business environment requires rapid business innovations. Mix of infrastructures: on premise vs externalized Mix of XaaS cloud values: IT vs business value Mix of cloud services: private vs public according to criticality Figure 4 – Generic architecture of hybrid cloud
- 4. The value of a cloud service is determined by contribution (costs / benefits ratio) to fulfilling needs of stakeholders here represented by CxO’s. To simplify, all BMC stakeholders will find value in SaaS services while some BMC Infrastructure stakeholders will also be interested by PaaS & IaaS services for financial or operational reasons. For instance, some workloads are eligible to migrate onto IaaS such as critical legacy, on premise legacy ISV applications, customized & home grown applications, test, development). Parts of others workloads such as Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Industrial Control System (ICS), Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) stay on premise for obvious operational reasons. Selecting services and providers One great advantage of cloud is the possibility to easily experiment and acquire services. Selection is done according to criteria which some are interdependent: Cloud layer: IaaS/PaaS/SaaS require different levels of managed services and associated costs Service criticality: business dependency on service will influence public/private choice Service value: coverage of main needs, benefits for business, productivity, quality gains Service connectivity: ability to extend or integrate with other systems / clouds Service compliance: business, technical and quality standards, regulations Service Level Agreement: performance, availability, security, support procedures, backup, disaster recovery Service reversibility: ability to recover data at end of service Service costs: migration and/or integration, recurring, reversibility costs Return on Investment benefits / costs ratio Provider Sustainability: to be considered with care for critical services Provider Ecosystem: partners: integrator, technology, channel, MSP, ISV A controlled selection process is important for optimal benefits of cloud services both at the operational and financial levels. Once selected, services are added to an internal service catalog from which users will be able to apply for access to the service according to the approval process. Conclusion Cloud services offer a great opportunity to revisit the business model in order to reposition enterprise in the value chain. Associating the Business Model Canvas and cloud business enablers provides a holistic tool to adapt the business model and design organizational changes. A cross company cloud team guarantees a shared understanding on the evolving business model by integrating all CxO’s perspectives. Company positioning (Optimizer, Innovator, Disruptor) in the Value Chain - Customer Value space, leads to different speed and breadth of the cloud roadmap. Despite the higher value of SaaS and/or services assembled from PaaS/SaaS, the cloud roadmap may result in a hybrid architecture because of legacy IT and operational constraints. The cloud adoption process is incremental to manage financial and technical risks. It can be summarized by the following activities: continuous watch of cloud market places business model assessment, identify transformations experimentation and selection of services deployment, addition of services to internal catalog Figure 5– The cloud adoption process
- 5. APPENDIX A - Details of the Business Model Canvas(3) (3) Le Business Model Canevas: https://strategyzer.com/canvas, Alexander Osterwalder. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, 171 Second Street, Suite 300, San Francisco, California, 94105, USA STRATEGIC PARTNERS KEY ACTIVITIES VALUE PROPOSITIONS CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS CUSTOMER SEGMENTS Who are our Key Partners? Who are our key suppliers? Which Key Resources are we acquiring from partners? Which Key Activities do partners perform? motivations for partnerships Optimization and economy Reduction of risk and uncertainty Acquisition of particular resources and activities What Key Activities do our Value Propositions require? Our Distribution Channels? Customer Relationships? Revenue streams? Sales & Marketing, Manufacturing Customer support, Logistics, R&D Finance, HR, IT CATEGORIES Production Problem Solving Platform/Network What value do we deliver to the customer? Which one of our customer’s problems are we helping to solve? What bundles of products and services are we offering to each Customer Segment? Which customer needs are we satisfying? characteristics Newness Performance Customization “Getting the Job Done” Design Brand/Status Price Cost Reduction Risk Reduction Accessibility Convenience/Usability What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to establish and maintain with them? Which ones have we established? How are they integrated with the rest of our business model? How costly are they? examples Personal assistance Dedicated Personal Assistance Self-Service Automated Services Communities Co-creation For whom are we creating value? Who are our most important customers? Mass Market Niche Market Segmented Diversified Multi-sided Platform KEY RESOURCES CHANNELS What Key Resources do our Value Propositions require? Our Distribution Channels? Customer Relationships? Revenue Streams? types of resources Physical Intellectual (brand patents, copyrights, data) Human Financial Through which Channels do our Customer Segments want to be reached? How are we reaching them now? How are our Channels integrated? Which ones work best? Which ones are most cost-efficient? How are we integrating them with customer routines? channel phases 1. Awareness How do we raise awareness about our company’s products and services? 2. Evaluation How do we help customers evaluate our organization’s Value Proposition? 3. Purchase How do we allow customers to purchase specific products and services? 4. Delivery How do we deliver a Value Proposition to customers? 5. After sales How do we provide post-purchase customer support? COST STRUCTURE REVENUE STREAMS What are the most important costs inherent in our business model? Which Key Resources are most expensive? Which Key Activities are most expensive? is your business more Cost Driven (leanest cost structure, low price value proposition, maximum automation, extensive outsourcing) Value Driven (focused on value creation, premium value proposition) sample characteristics Fixed Costs (salaries, rents, utilities) Variable costs Economies of scale Economies of scope For what value are our customers really willing to pay? For what do they currently pay? How are they currently paying? How would they prefer to pay? How much does each Revenue Stream contribute to overall revenues? types Asset sale Usage fee Subscription Fees Lending/Renting/Leasing Licensing Brokerage fees Advertising fixed pricing List Price Product feature dependent Customer segment dependent Volume dependent dynamic pricing Negotiation (bargaining) Yield Management Real-time-Market Auction
- 6. APPENDIX B – Sample cloud services map Below, for each canvas element and cloud enabler, are given examples of solutions that may improve the business model. Again, since the business model canvas itself is a hands-on tool, the sample table below is a possible starting point for organizations willing to question and evolve their business model in the cloud context. Infrastructure Propositions de valeur Clients Cost flexibility Pay per use model Continuous testing Dev & Test environments Business scalability Test as a Service (functional, performance) Seasonal elasticity Market adaptability Variability of test beds Compliance (PCI/DSS, SOC, ISO, etc) Masked complexity Hybrid cloud Desktop as a Service Mobile Device Mgmt as a Service Storage as a Service Backup as a Service Disaster Recovery as a Service Integrated value chain w/ network providers Increased Datacenter security CRM/ERP as a Service Context driven variability Social Media Analytics Real-time marketing Ecosystem connectivity BPaaS Virtual PLM platform Internet of Things Collaborative design, digital mockup Integrated value chain w/ network providers Online training (MOOC) Industry clouds Cost flexibility Freemium / Premium Yield management Business scalability Cloud elasticity (OSS/BSS interface) Content Delivery Network Application Delivery Network Product ranges Market adaptability Content Delivery Network Application Delivery Network Product ranges Time to market Masked complexity Self service Secured Payments Context driven variability Location based services Virtual immersion, Augmented reality Mobile applications Internet of Things, Big data Value creation from analytics Ecosystem connectivity Customers communities, user groups Online training (MOOC) Shipment traceability Cost flexibility Pay per use Time-based pricing Business scalability Buyers groups Market adaptability Co-creation Gamification Reachable niche markets WW WW 24/7 support Services internationalization Masked complexity Self service Automatic updates Customer reach through Market Places Integrated value chain w/ network providers Context driven variability Customer preferences Virtual immersion, augmented reality Location based services Mobile applications Real-time marketing Desktop/Mobile continuity Internet of things: monitor, alert Ecosystem connectivity Interfaces with social networks Inbound Marketing Loyalty programs Collaborative workspaces Online training (MOOC), customers, channel Customers communities, user group, intimacy Channel integration Finance Cost flexibility Commodity cloud services: Desktop, Storage, Desktop tools, Collaboration, Communication Pay per use from suppliers Lower costs through seamless geographically distributed value chain (ex: PLM) Public vs Private cloud for different purposes Lower costs of pre-integrated value chains Yield management ERP externalization Business scalability Rapid geographic development Market adaptability Currency rates Compliance Financial analytics Masked complexity Self-service through cloud market places Standardization vs costly customization Context driven variability Logistics optimization Ecosystem connectivity Purchase through Market place Table 6 – Sample cloud services initiatives
