BIO - Chapter 2-5 - Cells, Movement of Substances, Nutrients and Enzymes
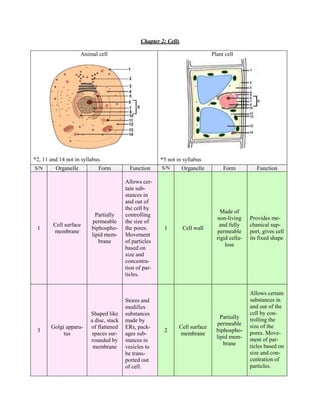
- 1. Chapter 2: Cells Animal cell Plant cell *2, 11 and 14 not in syllabus. *5 not in syllabus S/N Organelle Form Function S/N Organelle Form Function Allows cer- tain sub- stances in and out of the cell by Made of Partially controlling non-living Provides me- permeable the size of Cell surface and fully chanical sup- 1 biphospho- the pores. 1 Cell wall membrane permeable port, gives cell lipid mem- Movement rigid cellu- its fixed shape brane of particles lose based on size and concentra- tion of par- ticles. Allows certain Stores and substances in modifies and out of the Shaped like substances cell by con- Partially trolling the a disc, stack made by permeable size of the Golgi appara- of flattened ERs, pack- Cell surface 3 2 biphospho- pores. Move- tus spaces sur- ages sub- membrane lipid mem- ment of par- rounded by stances in brane ticles based on membrane vesicles to be trans- size and con- ported out centration of of cell. particles.
- 2. Contains en- Gel-like zymes and protoplasm Makes pro- organelles, between 4 Free ribosome - teins for the 3 Cytoplasm medium for nucleus and cell’s usage cell’s bio- cell surface chemical reac- membrane tions. Continuous with nuclear Ribosomes More tubu- envelope, on the RER lar than Smooth en- Rough endop- ribosomes makes pro- RER, con- Synthesis fats doplasmic 5 lasmic reticu- attached to teins usually 4 nected to and steroids, reticulum lum (RER) outer sur- transported RER, no detoxifies cell. (SER) face of RER out of the ribosomes (causes cell. attached roughness) Contains Contains Nucleus Contains Nucleus chromatin, chromatin, Contains ge- 9– genetic in- 9– long thread- long thread- netic informa- 6, 7 (Nucleolus, formation 6, 7 (Nucleolus, like struc- like struc- tion during and Nucleoplasm, during pro- and Nucleoplasm, tures with tures with protein syn- 8 Nuclear tein synthe- 8 Nuclear DNA in DNA in thesis. envelope) sis. envelope) them. them. Continuous More tubu- with nuclear Ribosomes on lar than envelope, Smooth en- Synthesis Rough en- the RER RER, con- ribosomes doplasmic fats and ste- doplasmic makes pro- 10 nected to 10 attached to reticulum roids, detox- reticulum teins usually RER, no outer sur- (SER) ifies cell. (RER) transported ribosomes face of RER out of the cell. attached (causes roughness) Contains enzymes Gel-like and orga- protoplasm nelles, me- Makes pro- between Free ribo- 12 Cytoplasm dium for 11 - teins for the nucleus and some cell’s bio- cell’s usage cell surface chemical membrane reactions.
- 3. Aerobic res- Oval struc- piration oc- tures with Small sau- curs here to membranes Mitochon- Site for photo- 13 sage-shaped provide 12 Chloroplast containing drion synthesis organelle energy for chlorophyll cellular ac- and fluid tivities. stroma Large cen- Contains dis- Essential for tral vacuole solved sub- Small hol- cell division containing stances (eg. - Centriole low cylind- 13 Vacuole (mitosis/ cell sap that sugar, mineral ers meiosis) is enclosed salts and ami- by tonoplast no acids) Aerobic respi- Temporary Contain wa- ration occurs fluid-filled Small sau- ter and food Mitochon- here to pro- - Vacuole spaces en- 14 sage-shaped substances drion vide energy closed by a organelle temporarily. for cellular membrane activities. Plant cell Animal cell Cell wall present since plants do not have a skeletal Cell wall absent since animals have a skeletal sys- system to provide support. tem to provide support. Chloroplasts present to make food during photo- Chloroplasts absent since animals can move about synthesis since they can’t feed. and feed to provide energy for their activities. Centrioles absent for cell division. Centrioles present for cell division. A large central vacuole that is permanent. Numerous, small and temporary vacuoles.
- 4. Cell structure Adaptation 1. No nucleus means more space in the cell to carry more haemoglobin and hence more oxy- gen. Red blood cell 2. Circular biconcave shape increases surface area to volume ratio, increasing the rate of diffusion of oxygen in and out of the cell. 1. Do not have cross walls or protoplasm enables water to move through the lumen easily with little need to diffuse. Xylem vessel 2. Lignin is deposited on the walls to strengthen it and also to prevent the vessels from collapsing. 1. Root hair cell has a long and narrow protrusion, increasing the surface area to volume ration of Root hair cell the cell, increasing the rate of absorption of wa- ter into the root hair cell. Organ Cells Form Organs Form Form Organism systems Stomach cells + other cells Stomach + other organs Digestive system + other systems Organism
- 5. Chapter 3: Movement of Substances (Diffusion, osmosis, active transport) Type of movement Diffusion Osmosis Active transport Diffusion is the net Osmosis is the net Active transport is the movement of particles movement of particles process whereby energy from a region of higher from a region of higher is used to move the par- concentration to a re- water potential to a re- ticles against a concen- gion of lower concentra- gion of lower water po- tration gradient from a Definition tion down a concentra- tential through a partial- region of lower concen- tion gradient without the ly permeable membrane tration to a region of use of energy, with or without the use of ener- higher concentration without a partially per- gy. meable membrane. Nutrients diffuse into Due to turgor pressure Active transport is ameoba to provide food (refer to below), non- needed in the uptake of for the ameoba and woody plants are able to glucose in the villi in waste products diffuse stand firm and erect. the small intestine to out of the ameoba to increase the amount of prevent accumulation of glucose being absorbed harmful waste products. Certain flowers are able because the amount ab- to open in the day and sorbed through diffusion close at night as the is too little and a lot of Oxygen present in the changes in turgidity of glucose will go to waste air we inhale dissolves the cells on opposite if only diffusion is used. into the thin layer of surfaces of the petals moisture on the alveolar causes the petals to wall before diffusing bend. Active transport is through the lung cell needed in the ion uptake into the blood stream to by root hairs. In order to Importance to living be transported to all The leaflets of the Mi- maintain the low water cells parts of the body. Car- mosa plant fold when potential, ions have to bon dioxide moves from touched due to changes be absorbed as much the blood vessels in turgor of cells that hence relying on diffu- through the lung cell to make up small swellings sion alone won’t be suf- the alveolar wall and out at the base of the leaf- ficient. via the respiratory sys- lets. tem. Changes in the turgor of Carbon dioxide diffuses guard cells causes the into the intercellular air opening and closing of spaces before dissolving the stomata (refer to into the moisture to dif- chapter 7) fuse to the palisade me- sophyll to be used in photosynthesis.
- 6. Plant cells Animal cells The cell sap has lower potential that The cytoplasm of the animal cell has a that of the solution outside the living lower water potential than that the out- cell hence water enters the cell by side of the living cell hence water en- osmosis. This increases the vacuole’s ters the cell by osmosis. This increases size and causes the vacuole to push the size of the cell. the cell contents against the cell wall. Since it does not have a cell wall, the Placed in solution of Since the cell wall is strong and rela- cell wall will expand until it bursts due higher water potential tively inelastic, it opposes the pres- to the high pressure against the cell sure to prevent more water from surface membrane. coming in and also prevents over- expansion of the cell. As it expands, it becomes turgid but it doesn’t burst due to the cell wall’s protection. The cell sap has higher water poten- The cytoplasm of the animal cell has a tial that that of the solution outside higher water potential than that of the the living cell hence water leaves the solution outside the living cell hence Placed in solution of cell by osmosis. This decreases the water leaves the cell by osmosis. This lower water potential vacuole’s size and causes the cytop- decreases the cell’s size until eventual- lasm shrinks away from the cell wall. ly it crenates and little spikes appear on This causes the cell to be plasmo- the cell surface membrane. lysed.
- 7. Chapter 4: Nutrients Important substance Characteristics Importance to living organisms body needs General formula: CnH2mOm 1. Substrate for respiration to provide energy for cellular Divided into three groups: Monosaccharides activities (glucose, fructose, galactose), Disaccharides 2. Forms supporting structures (maltose, lactose, sucrose), Polysaccharides (eg. cellulose cell wall) (starch, cellulose, glycogen) 3. Converted to amino acids Glucose + Glucose ⇌ Maltose + Water and fats Glucose + Fructose ⇌ Sucrose + Water Glucose + Galactose ⇌ Lactose + Water 4. Needed for formation of Carbohydrates nucleic acids (eg. DNA) *Reversible reactions catalysed by enzymes *This way is condensation reaction, the other 5. Needed to synthesise lubri- way hydrolytic reaction (occurs in digestive cants (eg. mucus) system) 6. Needed to synthesise nectar Excess sugars are stored are polysaccharides as they are insoluble so they don’t change water potential, are large molecules so cannot diffuse out through cell membranes, are easily hydro- lysed to glucose when needed and are in com- pact shapes which saves space. General formula: No fixed proportions, little 1. Source and store of energy oxygen as compared to hydrogen. Made of C, H and O. 2. Insulating material prevent- ing heat loss Fat molecule + 3Water Glycerol + 3Fatty acid molecules 3. Solvent for fat-soluble vi- tamins Saturated fats Unsatured fats Found mostly in an- Found mostly in 4. Essential part of protoplasm imals vegetables (eg. biphospholipid cell Fats membrane) Fatty acid chains are Fatty acid chains are 5. Reduces water loss by se- straight bent in some places creting an oily substance over skin, reducing rate of Solid at rtp Liquid at rtp evaporation Cholestrol are usually found with polysaturated fats and this may cause coronary heart disease or formation of gallstones.
- 8. General formula: Contains amino group (- 1. Needed in synthesis of new NH2), acidic group (-COOH) and a side chain protoplasm, for growth and (R). R can contain sulfur, acidic groups, amino repair of worn-out body groups and/or hydroxyl groups. cells 2. Needed in the synthesis of enzymes and some hor- mones Proteins 3. Needed for the formation of antibodies to combat dis- eases *A peptide bond is formed between the two joined amino acids (polypeptides), one water molecules is formed. 1. Medium for biochemical reactions in our body 2. Transports digested prod- ucts, waste products and hormones around the body 3. Key component of protop- lasm, lubricants in joints, digestive juices, blood and tissue fluid 4. Needed for certain reactions (eg. hydrolysis in digestion Water - and photosynthesis) 5. Component of sweat, when evaporated, removes latent heat of vaporisation cooling us down 6. Maintains turgor pressure in plants to allow them to be firm and erect 7. Needed to transport mineral salts and food substances from respective parts
- 9. Substance to be Test If present, … If absent, … tested Add 2 drops of potassium Iodine will turn bluish- Starch Iodine remains brown. iodide to test sample. black. Add equal volumes of Bene- dict solution (copper (II) sul- Solution will turn from, Reducing sugars fate) and test solution into a with increasing concen- (eg. glucose, mal- test tube. Place the test tube Solution remains light tration of reducing sug- tose, fructose, lac- into a beaker of boiling water blue. ar, green to yellow to tose) and remove within 5 mins or orange to brick-red. when the solution changes colour. Add half the volume of so- dium hydroxide to the volume of test sample. Add 1% cop- Solution will turn vio- Solution remains light Protein per (II) sulfate solution, drop let. blue. by drop, shaking after every drop. Add ethanol to test solution Cloudy white emulsion and shake thoroughly. Add will form in the solu- Solution remains co- Fats water to the mixture and tion and sinks to the lourless throughout. shake. bottom. Small molecules Large molecules Amino acids Polypeptides form proteins Glucose Maltose, sucrose, galactose Glycerol and fatty acids Fats
- 10. Chapter 5: Enzymes Characteristic Explanation Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation Speed up chemical reactions energy needed to start the reaction. Since they remain unchanged after a reaction, they can be used over Required in very small amounts and over again. This means a small amount of enzyme is able to cata- lyse a large number of chemical reactions. Enzymes are highly specific due to its 3-dimensional shape. The lock and key hy- pothesis is able to explain why. According to the lock and key hypothesis, enzyme reaction Highly specific depends on the presence of active sites, depressions on the surface of an enzyme molecule into which the substrate mole- cule(s) can fit. When a substrate with a complementary shape to the shape of the active site binds to the enzyme, an enzyme-substrate complex is formed and reactions take place at the active sites to con- vert substrate molecule(s) to product molecule(s). The product mole- cule(s) separates, leaving the enzyme unchanged and free to recom- bine with more substrate molecule(s). Before optimum temperature: After optimum temperature: Raising the temperature in- Enzymes are made of protein which creases the kinetic energy of denatures under high temperatures. the substrates and the en- High temperatures cause the atoms in Affected by temperature zymes. This causes them to the enzyme to vibrate very violent that collide more often, increas- they break the hydrogen bonds in the ing the chance of substrates enzyme causing it to lose its shape fitting into active sites. The and active site (denaturation). With rate of formation of the en- this the substrate cannot fit in the en- zyme-substrate complex in- zyme anymore. creases leading to a higher rate of products formed. *Denaturation is irreversible. Usually, per 10°C increase in temperature, the rate of reac- tion doubles. * Inactiveness is reversible.
- 11. Affected by pH Changes in pH may cause the acidity or alkalinity to break the hydro- gen bonds holding the coils in place. This extreme acidity or alkalinity causes the enzymes to be denatured losing their ability to catalyse the reactions. *Denaturation is irreversible. Enzymes catalyse reactions in the direction where there is a higher Catalyse reversible reactions concentration of reactants to the lower concentration of reactants.
