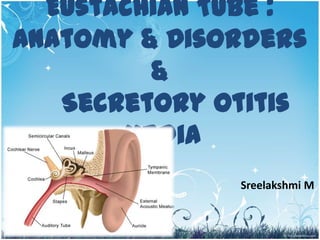
Eustachian tube
- 1. Eustachian Tube : Anatomy & Disorders & Secretory Otitis Media Sreelakshmi M 1
- 2. Anatomy 2
- 3. 3
- 4. Muscles Related to E.T 4
- 5. Lining of Eustachian Tube • Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium interspersed with mucous secreting goblet cells • Submucosa of cartilagenous part rich in seromucinous gland • Cilia beat in direction of nasopharynx 5
- 6. Nerve Supply • Sensory & parasympathetic : tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal N • Tensor veli palatini: V3 • Levator veli palatini pharyngeal plexus • Salpingopharyngeus (cranial part of XI N via vagus) 6
- 7. Infant ET v/s Adult ET INFANT ADULT LENGTH 13-18 mm at birth 36 mm DIRECTION More horizontal Forms an angle of 45 with the horizontal ANGULATION AT ISTHMUS No angulation Angulation present BONY VERSUS Bony part> 1/3 of the total Bony part 1/3; cartilaginous CARTILAGINOUS PART length part2/3 TUBAL CARTILAGE flaccid Comparatively rigid DENSITY OF ELASTIN AT THE Less dense More dense HINGE OSTMANN’S PAD OF FAT Less in volume Large & helps to keep the tube closed 7
- 8. 8
- 9. Functions 1. Ventilation & regulation of ME pressure 2. Protective funtions – Nasopharyngeal sound pressure – Reflux of nasopharyngeal secretions 3. Clearance of ME secretions 9
- 10. ET Function Tests • VALSALVA TEST – Principle: positive pressure in the nasopharynx causes air to enter the Eustachian tube 10
- 11. – Tympanic membrane perforation- a hissing sound – Discharge in the middle ear- cracking sound – Only 65% of persons can do this test. – Contraindications: • Atrophic scar of tympanic membrane which can rupture • Infection of nose & nasopharynx 11
- 12. • Politzer test – Done in children who are unable to perform valsalva test. – Olive shaped tip of the politzer’s bag is introduced into the patient’s nostril on the side of which the tubal function is desired to be tested – Other nostril closed & the bag compressed while at the same time the patient swallows or says “ik,ik,ik” 12
- 13. – By means of an auscultation tube a hissing sound is heard. – Compressed air can also be used instead of politzer’s bag – Test is also therapeutically used to ventilate the middle ear. 13
- 14. • Catheterisation 14
- 15. – Complications: • Injury to Eustachian tube opening • Bleeding from nose • Transmission of nasal & nasopharyngeal infection into middle ear • Rupture of atrophic area of tympanic membrane 15
- 16. • Toynbee’s test – Uses negative pressure • Tympanometry (inflation-deflation test) – +Ve & -ve pressures are created in the external ear and the patient swallows repeatedly – in patients with perforated or intact tympanic membrane • Radiological Test • Saccharine/ Methylene blue Test – Saccharine solution – Methylene blue dye – Ear drops into ear with TM perforation • Sonotubometry 16
- 17. Disorders of ET 17
- 18. Tubal Blockage ACUTE TUBAL BLOCKAGE ABSORPTION OF ME GASES -VE PRESSURE IN ME RETRACTION OF TM TRANSUDATE IN ME/HAEMORRHAGE PROLONGED TUBAL BLOCKAGE/DYSFUNCTION OME(THIN WATERY OR MUCOID DISCHARGE) ATELECTATIC EAR/PERFORATION RETRACTION POCKET/CHOLESTEATOMA EROSION OF INCUDOSTAPEDIAL JOINT 18
- 19. mechani • intrinsic cal • Extrinsic Block functional •Collapse both 19
- 20. • Symptoms of tubal occlusion – Otalgia – Hearing loss – Popping sensation – Tinnitus – Disturbances of equilibrium • Signs of tubal occlusion – Retracted TM – Congestion along the handle of malleus and pars tensa – Transudate behind TM 20
- 21. • Clinical causes of ET obstruction – Upper respiratory tract infection – Allergy – Sinusitis – Nasal polypi – DNS – Hypertrophic adenoids – Nasopharyngeal tumour/ mass – Cleft palate – Submucous cleft palate – Down’s syndrome 21
- 22. Adenoids • Adenoids cause tubal dysfunction by: – Mechanical obstruction of the tubal opening – Acting as reservoir for pathogenic organisms – Inflammatory mediators in allergy cause tubal blockage • Adenoids can cause otitis media with effusion or recurrent acute otitis media • Adenoidectomy 22
- 23. 23
- 24. large adenoid blocking left et 24
- 25. Cleft palate • Tubal dysfunction due to: – Abnormalities of torus tubaris – Tensor veli palatini doe not insert into the torus tubaris • Otitis media with effusion is common in these patients 25
- 26. Down’s syndrome • Dysfunction due to: – Poor tone of tensor veli palatini – Abnormal shape of nasopharynx 26
- 27. Retraction Pockets & ET 27
- 28. • Any obstruction in the ventilation pathway retraction pockets or atelectasis of tympanic membrane – Obstruction of Eustachian tube total atelectasis of tm – Obstruction at additus cholesterol granuloma & collection of mucoid discharge in mastoid air cells 28
- 29. 29
- 30. • Other changes – Thin atrophic TM – Cholesteatoma – Ossicular necrosis – Tympanosclerotic changes • Management – Repair of irreversible pathologic processes – Establishment of ventilation 30
- 31. 31
- 32. Patulous Eustachian Tube • ET is abnormally patent • Causes: – Idiopathic, rapid weight loss, pregnancy (esp 3rd trim) & multiple sclerosis • Chief complaints – Autophony, hearing his own breath sounds • Pressure changes in the nasopharynx are easily transmitted to the ME • Movements of the TM can be seen with inspiration & expiration 32
- 33. • Management – Acute cases Usually self-limiting – Weight gain & oral administration of KI – Long standing cases = cauterisation/ insertion of grommet 33
- 34. EXAMINATION OF EUSTACHIAN TUBE Pharyngeal end of eustachian tube :posterior rhinoscopy, rigid nasal endoscope or flexible nasopharyngoscope Tympanic end :microscope or endoscope Simple examination of TM may reveal retraction pockets or fluid in the me Movements of TM with respiration point to patulous eustachian tube 34
- 35. • Aetiologic causes of eustachian tube dysfunction assessed through: – Nasal examination – Endoscopy – Tests of allergy – CT scan of temporal bones – MRI to exclude multiple sclerosis 35
- 36. Otitis Media with Effusion 36
- 37. Serous otitis media Secretory otitis media Mucoid otitis media “Glue Ear” 37
- 38. • Insidious condition characterized by accumulation of non purulent effusion in ME cleft • Effusion is thick & viscid. • Fluid is sterile 38
- 39. Pathogenesis • Malfunctioning of Eustachian tube • Increased secretory activity of ME mucosa 39
- 40. Aetiology 1. Malfunctioning of Eustachian tube – Adenoid hyperplasia – Chronic rhinosinusitis – Chronic tonsillitis – Tumors ( to be excluded in unilateral ser. OM in adults) 2. Allergy 3. Unresolved otitis media 4. Viral infections 40
- 41. Clinical Features Symptoms : affects 5-8 yrs age gp Hearing loss Delayed & defective speech Mild earaches 41
- 42. Otoscopic Findings – Dull & opaque TM – Loss of light reflex – TM: yellow grey or bluish – Fluid level & air bubbles may be seen – Restricted mobility of tm – Thin leash of vessels along malleus handle/ periphery of TM == differentiate from acute supp. Otitis media – TM: varying degree of retraction 42
- 43. 43
- 44. 44
- 45. Hearing Tests • Tuning fork test-conductive hearing loss • Audiometry-conductive hearing loss of 20-40db • Impedance Audiometry-reduced compliance indicates presence of fluid • X-ray mastoid-clouding of air cells due to fluid. 45
- 46. Treatment Medical Surgical Decongestants Myringotomy & Aspiration Grommet Insertion Antihistaminics Tympanotomy/ cortical Steroids mastoidectomy( loculated thick fluid/ chol. granuloma) Antibiotics Surgical treatment of causative factor 46
- 47. 47
- 48. 48
- 49. Sequelae of Chronic Secretory Otitis Media • Atrophic TM & atelectasis of ME • Ossicular necrosis • Tympanosclerosis • Retraction pockets & cholesteatoma • Cholesterol granuloma 49
- 50. The above picture shows a very thin or atelectatic eardrum (tympanic membrane) 50 which is draped over the promontory and round window nitch.
- 51. Cholesterol granuloma 51
- 52. Thank You 52
