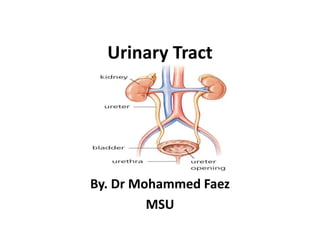
Urinary tract
- 1. Urinary Tract By. Dr Mohammed Faez MSU
- 3. Perform all functions except actual excretion.
- 4. Two Ureters
- 5. Convey urine from Kidneys to Urinary Bladder
- 7. Holds Urine until excretion
- 8. Urethra
- 10. The kidneys The right kidney lies approximately 1 cm lower than the left because of the large size of the right lobe of the liver. The lateral surface is convex and the medial surface is concave, with a vertical cleft called the renal hilusleading to the renal sinus Ureters, renal blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter and exit at thehilus
- 11. The kidneys The hilum of the kidney is situated medially and transmits from front to back the: renal vein, renal artery, ureteric pelvis as well as lymphatics and sympathetic vasomotor nerves. Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex and an inner renal medulla. The renal cortex is a continuous band of pale tissue that completely surrounds the renal medulla. Extensions of the renal cortex (the renal columns) project into the inner aspect of the kidney, dividing the renal medulla into discontinuous aggregations of triangular-shaped tissue (the renal pyramids).
- 12. The kidneys The renal pelvis divides into two or three major calices and these, in turn, divide into minor calices which receive urine from the renal pyramids by way of the papillae.
- 13. Renal Artery and Vein *usually arise at L2 Capsule Pelvis Major Calyx Cortex Ureter Medulla Minor Calyx The kidneys
- 14. The kidneys The kidneys have the following coverings : Fibrous capsule: This surrounds the kidney and is closely applied to its outer surface that prevents kidney infection. Perirenal fat: This covers the fibrous capsule that cushions the kidney. Renal fascia: This is a condensation of connective tissue that lies outside the perirenal fat and encloses the kidneys and suprarenal glands; it is continuous laterally with the fascia transversalis. Pararenal fat: This lies external to the renal fascia and is often in large quantity. It forms part of the retroperitoneal fat
- 16. Right Kidney Anatomical Relations Anteriorly: The suprarenal gland, the liver, the second part of the duodenum, and the right colic flexure Posteriorly: The diaphragm; the costodiaphragmatic recess of the pleura; the 12th rib; and the psoas, quadratuslumborum, and transversusabdominis muscles. The subcostal (T12), iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves (L1) run downward and laterally.
- 17. Left Kidney Anatomical Relations Anteriorly: The suprarenal gland, the spleen, the stomach, the pancreas, the left colic flexure, and coils of jejunum. Posteriorly: The diaphragm; the costodiaphragmatic recess of the pleura; the 11th (the left kidney is higher) and 12th ribs; and the psoas, quadratuslumborum, and transversusabdominis muscles. The subcostal (T12), iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves (L1) run downward and laterally.
- 20. Arterial Blood Supply of kidney Renal artery A single large renal artery, a lateral branch of the abdominal aorta, supplies each kidney. These vessels usually arise just inferior to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery between vertebrae L1and L2. The left renal artery usually arises a little higher than the right, and the right renal artery is longer and passes posterior to the inferior vena cava.
- 21. Arterial Blood Supply of kidney They are distributed to different segments or areas of the kidney. Lobar arteries arise from each segmental artery, one for each renal pyramid. Before entering the renal substance, each lobar artery gives off two or three interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries run toward the cortex on each side of the renal pyramid. At the junction of the cortex and the medulla, the interlobar arteries give off the arcuate arteries.
- 23. Venous drainge of kidney Renal Vein The renal vein emerges from the hilum in front of the renal artery and drains into the inferior vena cava. The left renal vein is long as it courses in front of the aorta to drain into the IVC. The right renal artery passes behind the IVC.
- 25. Lymphatic Drainage of kidney Lymph drains to the para-aortic lymph nodes.
- 26. Nerve Supply of kidney The nerve supply is the renal sympathetic plexus. The afferent fibers that travel through the renal plexus enter the spinal cord in the 10th, 11th, and 12th thoracic nerves.
- 27. The ureter The two ureters are muscular tubes that extend from the kidneys to the posterior surface of the urinary bladder . Each ureter measures about 10 in. (25 cm) long and resembles the esophagus (also 10 in. long)
- 28. The ureter The ureter has three constrictions along its course: where the renal pelvis joins the ureter, where it is kinked as it crosses the pelvic brim, where it pierces the bladder wall.
- 29. Course of the Ureter The ureter emerges from the renal pelvis at the hilum, It passes along the medial part of psoas major behind, but adherent to, the peritoneum. It then crosses the common iliac bifurcation anterior to the sacro-iliac joint and courses over the lateral wall of the pelvis to the ischial spine.
- 30. Course of the Ureter At the ischial spine the ureter passes forwards and medially to enter the bladder obliquely. The intravesical portion of the ureter is approximately 2 cm long and its passage through the bladder wall produces a sphincter-like effect. In the male the ureter is crossed superficially near its termination by the vas deferens. In the female the ureter passes above the lateral fornix of the vagina but below the broad ligament and uterine vessels.
- 31. Relations of Right Ureter Anteriorly: The duodenum, the terminal part of the ileum, the right colic and ileocolic vessels, the right testicular or ovarian vessels, and the root of the mesentery of the small intestine. Posteriorly: The right psoas muscle, which separates it from the lumbar transverse processes, and the bifurcation of the right common iliac artery
- 32. Relations of Left Ureter Anteriorly: The sigmoid colon and sigmoid mesocolon, the left colic vessels, and the left testicular or ovarian vessels. The inferior mesenteric vein lies along the medial side of the left ureter Posteriorly: The left psoas muscle, which separates it from the lumbar transverse processes, and the bifurcation of the left common iliac artery.
- 34. Blood supply of Ureter Upper end receives blood supply from the renal arteries, The middle part may receive branches from the abdominal aorta, the testicular or ovarian arteries, and the common iliac arteries, In the pelvic cavity, the ureters are supplied by one or more arteries from branches of the internal iliac arteries and inferior vesical arteries.
- 35. Lymphatic Drainage of The Ureters Lymphatic drainage of the ureters follows a pattern similar to that of the arterial supply: The upper part of each ureter drains to the lumbar nodes; The middle part of each ureter drains to lymph nodes associated with the common iliac vessels; The inferior part of each ureter drains to lymph nodes associated with the external and internal iliac vessels.
- 36. Uretericinnervation Uretericinnervation is from the renal, aortic, superior hypogastric, and inferior hypogastric plexuses through nerves that follow the blood vessels. Visceral efferent fibers come from both sympathetic and parasympathetic sources, while visceral afferent fibers return to T11 to L2 spinal cord levels.
- 37. Urinary Bladder Urinary bladder is a musculomembranous sac which acts as a reservoir for the urine. The bladder is the most anterior element of the pelvic viscera. It is entirely situated in the pelvic cavity when empty, it expands superiorly into the abdomen when full.
- 38. Urinary Bladder The empty bladder is shaped like a three-sided pyramid. It has an apex, a base, a superior surface, and two inferolateral surfaces.
- 39. Urinary Bladder The apex of the bladder is directed toward the top of the pubic symphysis; a structure known as the median umbilical ligament (a remnant of the embryologic urachus that contributes to the formation of the bladder) continues from it superiorly up the anterior abdominal wall to the umbilicus.
- 40. Urinary Bladder The base of the bladder is shaped like an inverted triangle and faces posteroinferiorly. The two ureters enter the bladder at each of the upper corners of the base, and the urethra drains inferiorly from the lower corner of the base. The smooth triangular area between the openings of the ureters and urethra on the inside of the bladder is known as the trigone
- 41. Urinary Bladder The inferolateral surfacesof the bladder are cradled between the levatorani muscles of the pelvic diaphragm and the adjacent obturatorinternus muscles above the attachment of the pelvic diaphragm. The superior surface is slightly domed when the bladder is empty. It balloons upward as the bladder fills.
- 42. Neck of bladder The neck of the bladder surrounds the origin of the urethra at the point where the two inferolateral surfaces and the base intersect. The neck is the most inferior part of the bladder and also the most 'fixed' part.
- 43. Urinary Bladder: Location Posterior to pubic symphysis In females is anterior to vagina & inferior to uterus
- 44. Urinary Bladder: Location Posterior to pubic symphysis In males lies anterior to rectum
- 45. Blood Supply of Urinary Bladder Its blood supply from the superior and inferior vesicular arteries. These arteries are tributaries of the internal iliac arteries.
- 46. Innervations of Urinary Bladder The pelvic plexus is supplying the urinary bladder with autonomic nerves. The sympathetic innervation is directed to the blood vessels, urethral openings, and the trigone. The last thoracic and L1,2 nerves create the necessary innervation to the bladder. Parasympathetic innervation is derived from S2,3 and 4 nerves. These are aimed at serving the detrusor muscle. The pelvic spinal nerves are responsible for responding to the sensory response of a full bladder, which responds to the impulses sent via the central nervous system.
- 48. Urethra The urethra begins at the base of the bladder and ends with an external opening in the perineum. The urethra differs significantly in women and men.
- 49. Urethra In women The urethra is short, being about 4 cm long. It travels a slightly curved course as it passes inferiorly through the pelvic floor into the perineum, where it passes through the deep perineal pouch and perineal membrane before opening in the vestibule that lies between the labia minora.
- 50. Urethra In men The urethra is long, about 20 cm, and bends twice along its course. Beginning at the base of the bladder and passing inferiorly through the prostate, it passes through the deep perineal pouch and perineal membrane and immediately enters the root of the penis. The urethra exits the deep perineal pouch, it bends forward to course anteriorly in the root of the penis. When the penis is flaccid, the urethra makes another bend, this time inferiorly, when passing from the root to the body of the penis. During erection, the bend between the root and body of the penis disappears.
- 51. Urethra The urethra in men is divided into: preprostatic, prostatic, membranous, and spongy (penile) parts.
- 52. Parts of the Urethra Preprostatic part The preprostatic part of the urethra is about 1 cm long. It extends from the base of the bladder to the prostate, and is associated with a circular cuff of smooth muscle fibers (the internal urethral sphincter). Contraction of this sphincter prevents retrograde movement of semen into the bladder during ejaculation. Prostatic part The prostatic part of the urethra is 3-4 cm long and is surrounded by the prostate. In this region, the lumen of the urethra is marked by a longitudinal midline fold of mucosa (the urethral crest). (Read more)
- 53. Parts of the Urethra Membranous part The membranous part of the urethra is narrow and passes through the deep perineal pouch. During its transit through this pouch, the urethra, in both men and women, is surrounded by skeletal muscle of the external urethral sphincter. Spongy (Penile) urethra The spongy urethra is surrounded by erectile tissue (the corpus spongiosum) of the penis. It is enlarged to form a bulb at the base of the penis and again at the end of the penis to form the navicularfossa). The external urethral orifice is the sagittal slit at the end of the penis.
