Cell Structure Review
- 3. Cells
- 6. Figure 1-1d Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010)
- 7. Figure 1-1b Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010)
- 8. Figure 1-1a Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010)
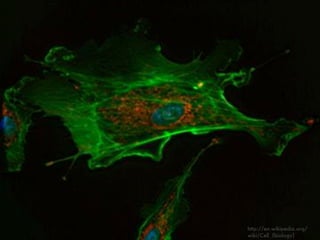
- 9. Figure 1-1c Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010)
- 10. Figure 1-1e Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010)
- 12. Number of cells in a human body
- 13. 10 - 100 trillion cells
- 14. Bright field, 400x Hematoxylin stained
- 15. Microscopes
- 18. Bright field, 1000x Hematoxylin stained
- 23. Eukaryotic Cells
- 32. Membranes
- 37. Phospholipid bilayer + membrane proteins + cholesterol
- 38. Surfaces are important! They are the parts of an object that are readily accessible by things outside the object.
- 40. Heat exchange happens via surfaces.
- 42. Gas exchange happens via surfaces.
- 56. Organelles
- 58. “...a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer.” http://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/Organelle
- 59. Table 4.2a Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. TABLE 4.2 EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS Structure Description Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins that Phospholipid encloses a cell and separates its contents from its surroundings. The bilayer results Protein from the tail-to-tail packing of the phospholipid molecules that make up the membrane. The proteins embedded in the lipid bilayer are in large part responsible for a cell’s ability to interact with its environment. Transport proteins provide channels through which molecules and ions enter and leave the cell across the plasma membrane. Receptor proteins induce changes within the cells when they come in contact with specific molecules in the environment, such as hormones, or with molecules on the surface of neighboring cells. Cholesterol Nucleus Nuclear envelope Every cell contains DNA, the hereditary material. The DNA of eukaryotes is isolated within the nucleus, a spherical organelle surrounded by a double membrane structure called the nuclear envelope. This envelope is studded with pores that control traffic into and out of the nucleus. The DNA contains the genes that code for the proteins synthesized by the cell. Stabilized by proteins, it forms chromatin, Nucleolus the major component of the nucleus. When the cell prepares to divide, the chromatin of the nucleus condenses into threadlike chromosomes. Nuclear pore The hallmark of the eukaryotic cell is compartmentalization, achieved by an extensive endomembrane system that weaves through the cell interior. The Endoplasmic Reticulum membrane network is called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The ER begins at the nuclear envelope and extends out into the cytoplasm, its sheets of membrane Rough ER weaving through the cell interior. Rough ER contains numerous ribosomes that give it a bumpy appearance. These ribosomes manufacture protein destined for the ER or for other parts of the cell. ER without these attached ribosomes is called smooth ER, which often functions to detoxify harmful substances or to aid in the synthesis of lipids. Sugar side chains are added to molecules as they pass through the ER. Delivery of molecules to other parts of the cell is via vesicles that pinch off from the borders of the rough ER. Ribosome Smooth ER Golgi Complex Transport vesicles At various locations within the cytoplasm flattened stacks of membranes occur. Animal cells may contain 20, plant cells several hundred. Collectively, they are Lysosome referred to as the Golgi complex. Molecules manufactured in the ER pass to the Golgi complex within vesicles. The Golgi sorts and packages these molecules and also synthesizes carbohydrates. The Golgi adds sugar side chains to molecules as they pass through the stacks of membranes. The Golgi then directs the molecules to lysosomes, secretory vesicles, or the plasma memrane. Secretory vesicles
- 60. Table 4.2b Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Structure Description Mitochondrion Mitochondria are bacteria-like organelles that are responsible for extracting most Of the energy a cell derives from the food molecules it consumes. Two membranes Intermembrane space Outer Encase each mitochondrion, separated by an intermembrane space. The key membrane energy-harvesting chemical reactions occur within the interior matrix. The energy is Used to pump protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space; their return Across this membrane drives the synthesis of ATP, the energy currency of the cell. Inner membrane Matrix The green color of plants and algae results from cell organelles called chloroplasts Chloroplast rich in the photosynthetic green pigment chlorophyll. Photosynthesis is the sunlight-powered process at converts CO2 in the air to the organic molecules Outer membrane of which all living things are composed. Chloroplasts, like mitochondria, are composed of two membranes separated by an intermembrane space. In a chloroplast, the inner membrane pinches into a series of sacs called thylakoids, Inner membrane which pile up in columns called grana. The chlorophyll-facilitated light reactions of photosynthesis take place within the thylakoids. These are suspended in a Granum semiliquid substance called the stroma. Thylakoid Stroma The cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells is crisscrossed by a network of protein fibers Cytoskeleton called the cytoskeleton that supports the shape of the cell and anchors organelles Actin filament to fixed locations. The cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure, composed of three kinds of fibers. Long actin filaments are responsible for cellular movements such as contraction, crawling, and the “pinching” that occurs as cells divide. Hollow microtubule tubes, constantly forming and disassembling, facilitate cellular movements an are responsible for moving materials within the cell. Special motor proteins move organelles around the cell on microtubular “tracks.” Durable Microtubule intermediate filaments provide the cell with structural stability. Intermediate filament Centrioles Centrioles are barrel-shaped organelles found in the cells of animals and most protists. They occur in pairs, usually located at right angles to each other near the nucleus. Centrioles help assemble the animal cell’s microtubules, playing a key role in producing the microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division. Centrioles are also involved in the formation of cilia and flagella, which are composed of sets of microtubules. Cells of plants and fungi lack centrioles, and cell biologists are still in the process of characterizing their microtubule-organizing centers. Microtubule triplet
- 61. Why is having organelles advantageous?
- 67. Nuclear Envelope Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Vesicles Cell Membrane http://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/Endomembrane_system
- 68. “...the set of membranes that form a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected together directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport.” http://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/Endomembrane_system
- 70. Endoplasmic Reticulum where proteins are made and processed
- 72. Lots of surface area!
- 74. Vesicles containers for storage, transport and digestion
- 75. The Golgi Complex where proteins are processed, sorted and packaged
- 78. Mitochondria
- 82. Cytoskeleton
- 97. Movement into and out of the cell
- 98. Diffusion
- 99. The wandering around of molecules
- 100. wandering The of around molecules
- 101. The wandering molecules around of
- 103. Fig. 4.21 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solution Solution Solution Human Red Blood Cells Shriveled cells Normal cells Cells swell and eventually burst 0.55 µm 0.55 µm 0.55 µm Plant Cells Cell body shrinks Flaccid cell Normal turgid cell from cell wall (all): © David M. Phillips/Visuals Unlimited
- 104. Endocytosis
- 107. Exocytosis
- 115. In 1951, an African-American woman named Henrietta Lacks was diagnosed with terminal cervical cancer. She was treated at Johns Hopkins University, where a doctor named George Gey snipped cells from her cervix without telling her. Gey discovered that Lacks' cells could not only be kept alive, but would also grow indefinitely. For the past 60 years Lacks' cells have been cultured and used in experiments ranging from determining the long-term effects of radiation to testing the live polio vaccine. Her cells were commercialized and have generated millions of dollars in profit for the medical researchers who patented her tissue. Lacks' family, however, didn't know the cell cultures existed until more than 20 years after her death. Medical writer Rebecca Skloot examines the legacy of Lacks' contribution to science — and effect that has had on her family — in her new book, The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks. Skloot is a freelance science writer and a contributing editor at Popular Science. She has written feature stories for The New York Times, Discover Magazine, and RadioLab. http://www.npr.org/ 2011/03/18/134622044/tracing- the-immortal-cells-of-henrietta-lacks
