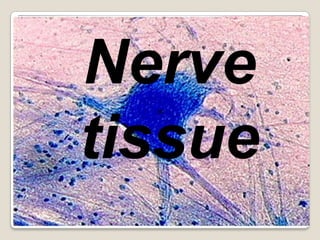
Nerve tissues (mic ana lec)
- 1. Nerve tissue
- 2. Function: reception of information from the external and internal environment, (2) integration and analysis of the incoming information, (3) generation of new signals, (4) conduction of these neural messages to special responding tissue (effectors).
- 3. Divisions of the nervous system 1. Central nervous system - The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. 2. Peripheral nervous system - The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nervous tissue lying outside the brain and spinal cord. It consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. This PNS is further divided into the somatic nervous system, which supplies motor fibers to skeletal muscles that are under conscious control, and the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which supplies motor fibers to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. The ANS consists of the sympathetic (thoracolumbar) nervous system and the parasympathetic (craniosacral) nervous system.
- 4. Classification of Neurons On the basis of their structure, neurons can also be classified into three main types: UnipolarNeurons.Sensory neurons have only a single process or fibre which divides close to the cell body into two main branches (axon and dendrite). Because of their structure they are often referred to as unipolar neurons. MultipolarNeurons.Motor neurons, which have numerous cell processes (an axon and many dendrites) are often referred to as multipolar neurons. Interneurons are also multipolar. Bipolar Neurons.Bipolar neurons are spindle-shaped, with a dendrite at one end and an axon at the other . An example can be found in the light-sensitive retina of the eye.
- 6. Parts of a neuron:
- 7. A motor neuron has many processes (cytoplasmic extensions), called dendtrites, which enter a large, grey cell body at one end. A single process, the axon, leaves at the other end, extending towards the dendrites of the next neuron or to form a motor endplate in a muscle. Dendrites are usually short and divided while the axons are very long and does not branched freely. The impulses are transmitted through the motor neuron in one direction, i.e. into the cell body by the dendrites and away from the cell body by the axon
- 8. . The cell body is enclosed by a cell (plasma) membrane and has a central nucleus. Granules, called Nissl, bodies are found in the cytoplasm of the cell body. Within the cell body, extremely fine neurofibrils extend from the dendrites into the axon. The axon is surrounded by the myelin sheath, which forms a whitish, non-cellular, fatty layer around the axon. Outside the myelin sheath is a cellular layer called the neurilemma or sheath of Schwann cells. The myelin sheath together with the neurilemma is also known as the medullary sheath. This medullary sheath is interrupted at intervals by the nodes of Ranvier.
- 9. Structures seen in PERIKARYON: A Nissl body (or Nissl granule or tigroid body) is a large granular body found in neurons. These granules are rough endoplasmic reticulum (with free ribosomes) and are the site of protein synthesis. Nissl body
- 10. Perikaryon or soma is the bulbous end of a neuron, containing the cell nucleus. The soma contains many organelles, including granules called Nissl granules, which are composed largely of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free polyribosomes
- 11. dendrites Most nerve cells have several dendrites. These increase the receptive area of the neuron. Dendrites do not maintain a constant diameter (unlike axons) and transmit impulses to the cell body decrementally (unlike axons. The regions of the dendrites closest to the perikaryon are usually larger, than those farther away. Typically dendrites have large numbers of thorny spines, which are now known to be areas of synaptic contact.
- 12. axon An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma. An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type beingdendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them).
- 13. nucleus a nucleus is a brain structure consisting of a relatively compact cluster of neurons. It is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter.
- 14. Golgi apparatus is an organellefound in most eukaryotic cells. It processes and packages proteins after their synthesis and before they make their way to their destination; it is particularly important in the processing of proteins for secretion. The Golgi apparatus forms a part of the cellularendomembrane system.
- 15. is a membrane-enclosed organellefound in most eukaryotic cellsthey generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source ofchemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in a range of other processes, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, cell death, as well as the control of the cell cycle and cell growth Mitochondrion
- 16. centrosome is an organelle that serves as the mainmicrotubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression.Centrosomes are composed of two orthogonally arranged centriolessurrounded by an amorphous mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring[7] including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based on a nine tripletmicrotubule assembled in a cartwheel structure, and contains centrin,cenexin and tektin.
- 17. III. According to functional roles: 1.motor-(efferent) neurons – control organs such as muscle fibers ,exocrine and endocrine glands. .2.sensory (afferent) neurons – involved in the reception of sensory stimuli from the environment and from within the body. 3.Interneurons – establish interrelationships among other neurons, forming complex functional chains or circuits.
- 18. synapse the junction between the processes of two neurons or between a neuron and an effector organ, where neural impulses are transmitted by chemical means. The impulse causes the release of a neurotransmitter (e.g. acetylcholine or norepinephrine) from the presynaptic membrane of the axon terminal. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft, bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, causing depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell.
- 19. Forms of synapse
- 20. Synapses are specialized areas of contact between neurons. Various categories of synapses are found including: axo-dendritic axo-somatic dendro-dendritic axo-axonic
- 21. axoaxonic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron. axodendritic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another. axodendrosomatic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites and body of another. axosomatic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the body of another. dendrodendritic synapse one from a dendrite of one cell to a dendrite of another. electrotonic synapse a special type of gap junction found in tissue such as the myocardium.
- 22. Neuroglia Neuroglia or glial cells are protective and supportive structures of nervous tissue. They are found in bunches surrounding the neurons and have the ability to regenerate in case of injury. Neuroglia provide nutrition and immune protection to the neurons. In addition, they are responsible for the formation of myelin sheath and maintaining homeostasis inside the neurons. Some of the forms of neuroglia are astrocytes (provide metabolic support to nervous tissue) and oligodendrocytes (support axons), microglia (repair the damage of neurons).
- 23. Types of neuroglia Astrocytes also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.
- 24. protoplasmic astrocytes and fibrous astrocytes
- 25. are a type of brain cell. They are a variety of neuroglia. Their main function is the insulation of axons (the long projection of nerve cells) in the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) of some vertebrates. (The same function is performed bySchwann cells in the peripheral nervous system). A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping around approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only 1 axon. oligodendrocytes
- 26. Microglia These are small cells, with elongated bodies, elongated nuclei with dense chromatin and relatively few processes. They are found in both the gray and white matter of the CNS and are thought to function as macrophages. There is some evidence that they are in fact of mesenchymal origin and derived from blood-borne monocytes.
- 27. Ependymal cells The ependyma is composed of neuroglia that line the internal cavities (ventricles) of the brain and spinal cord (central canal). They are similar in appearance to a stratified columnar epithelium. The ependymal cells are bathed in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Modified ependymal cells of the choroid plexuses of the brain ventricles are the main source of the CSF.
- 28. Nerve fibers
- 29. A nerve fiber is a threadlike extension of a nerve cell and consists of an axon and myelin sheath (if present) in the nervous system. There are nerve fibers in the central nervous systemand peripheral nervous system. A nerve fiber may be myelinated and/or unmyelinated. In the central nervous system (CNS), myelin is produced by oligodendroglia cells. Schwann cells form myelin in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Schwann cells can also make a thin covering for an axon which does not consist of myelin (in the PNS). A peripheral nerve fiber consists of an axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells and its endoneurium. There are no endoneurium and Schwann cells in the central nervous system.
- 30. Two coverings of nerve fibers 1.Myelin sheath the myelin sheath, usually around only the axon of aneuron. It is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Myelin is an outgrowth of a type of glial cell. The production of the myelin sheath is called myelination.
- 31. is the outermost nucleated cytoplasmic layer of Schwann cells that surrounds the axon of the neuron. It forms the outermost layer of the nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system. The neurolemma is underlain by the basal lamina (referred to as the medullary sheath in the included illustrations). In CNS, axons are myelinated by oligodendrocytes, thus lack neurolemma. 2. neurolemma
- 32. Peripheral nervous system: - consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. -main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the limbs and organs *The peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system
- 33. Somatic nervous system -associated with the voluntary control of body movements via skeletal muscles.
- 34. autonomic nervous system - is the part of theperipheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions.
- 35. Subsystems of autonomic nervous system: *Parasympathetic nervous system-The parasympathetic system specifically is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" activities that occur when the body is at rest, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination,digestion and defecation. *Sympathetic nervous system -along with the enteric and parasympathetic systems. Its general action is to mobilize the body's nervous system fight-or-flight response. It is, however, constantly active at a basal level to maintain homeostasis
- 36. White matter - is one of the two components of the central nervous system and consists mostly of myelinated axons. White matter tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined withcapillaries. Its white color is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde.
- 37. Gray matter consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and both unmyelinated axons andmyelinated axons), glial cells (astroglia and oligodendrocytes) and capillaries. Grey matter contains neural cell bodies, in contrast to white matter, which does not and mostly contains myelinated axon tracts
- 38. Spinal cord:
- 39. -The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain (the medulla oblongata specifically). The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system.
- 40. Cerebellum -is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It is also involved in some cognitive functions such as attention andlanguage, and probably in some emotional functions such as regulating fear andpleasure responses.
- 41. Cerebrum The cerebrum or telencephalon, together with the diencephalon, constitutes the forebrain. The cerebrum is the most anterior (or, in humans, most superior) region of the vertebrate central nervous system. Telencephalon refers to the embryonic structure, from which the mature cerebrum develops. In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetricleft and right cerebral hemispheres. the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the body.
- 42. Meninges: is the system of membraneswhich envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: thedura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.
- 43. Dura mater-is the outermost of the three layers of themeninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is derived from Mesoderm Arachnoidmater- delicate, spiderweb-like attached to the inside of the dura, surrounds the brain and spinal cord but does not line the brain down into itssulci (folds). Piamater-delicate innermost layer of themeninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Pia mater is a thin fibrous tissue that is impermeable to fluid. This allows the pia mater to enclosecerebrospinal fluid. By containing this fluid the pia mater works with the other meningeal layers to protect and cushion the brain. The pia mater allows blood vessels to pass through and nourish the brain.
- 44. Thank you!
