Molecular Aspects Of Drug Action
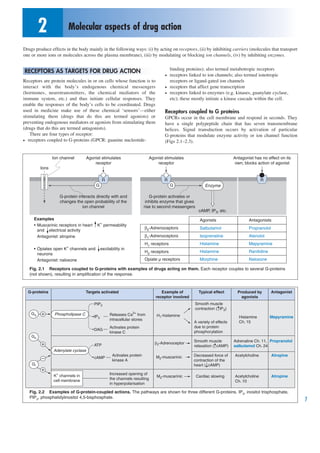
- 1. 2 Molecular aspects of drug action Drugs produce effects in the body mainly in the following ways: (i) by acting on receptors, (ii) by inhibiting carriers (molecules that transport one or more ions or molecules across the plasma membrane), (iii) by modulating or blocking ion channels, (iv) by inhibiting enzymes. binding proteins); also termed metabotropic receptors RECEPTORS AS TARGETS FOR DRUG ACTION • receptors linked to ion channels; also termed ionotropic Receptors are protein molecules in or on cells whose function is to receptors or ligand-gated ion channels interact with the body’s endogenous chemical messengers • receptors that affect gene transcription (hormones, neurotransmitters, the chemical mediators of the • receptors linked to enzymes (e.g. kinases, guanylate cyclase, immune system, etc.) and thus initiate cellular responses. They etc); these mostly initiate a kinase cascade within the cell. enable the responses of the body’s cells to be coordinated. Drugs used in medicine make use of these chemical ‘sensors’—either Receptors coupled to G proteins stimulating them (drugs that do this are termed agonists) or GPCRs occur in the cell membrane and respond in seconds. They preventing endogenous mediators or agonists from stimulating them have a single polypeptide chain that has seven transmembrane (drugs that do this are termed antagonists). helices. Signal transduction occurs by activation of particular There are four types of receptor: G-proteins that modulate enzyme activity or ion channel function • receptors coupled to G-proteins (GPCR: guanine nucleotide- (Figs 2.1–2.3). Ion channel Agonist stimulates Agonist stimulates Antagonist has no effect on its receptor receptor own; blocks action of agonist Ions R R R G G Enzyme G-protein interacts directly with and G-protein activates or changes the open probability of the inhibits enzyme that gives ion channel rise to second messengers cAMP, IP3, etc. Examples Agonists Antagonists • Muscarinic receptors in heart K+ permeability β2-Adrenoceptors Salbutamol Propranolol and electrical activity Antagonist: atropine β1-Adrenoceptors Isoprenaline Atenolol H1 receptors Histamine Mepyramine • Opiates open K+ channels and excitability in H2 receptors Histamine Ranitidine neurons Antagonist: naloxone Opiate µ receptors Morphine Naloxone Fig. 2.1 Receptors coupled to G-proteins with examples of drugs acting on them. Each receptor couples to several G-proteins (not shown), resulting in amplification of the response. G-proteins Targets activated Example of Typical effect Produced by Antagonist receptor involved agonists PIP2 Smooth muscle contraction ( IP3) Gq Phospholipase C IP3 Releases Ca2+ from H1-histamine Histamine Mepyramine intracellular stores A variety of effects Ch. 15 Activates protein due to protein DAG kinase C phosphorylation Gs Smooth muscle Adrenaline Ch. 11, Propranolol ATP >2-Adrenoceptor relaxation ( cAMP) salbutamol Ch. 24 Adenylate cyclase Activates protein M2-muscarinic Decreased force of Acetylcholine Atropine cAMP kinase A contraction of the Gi heart ( cAMP) K+ channels in Increased opening of M2-muscarinic Cardiac slowing Acetylcholine Atropine cell membrane the channels resulting Ch. 10 in hyperpolarisation Fig. 2.2 Examples of G-protein-coupled actions. The pathways are shown for three different G-proteins. IP3, inositol trisphosphate, PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. 7
- 2. 2 MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DRUG ACTION G-proteins are attached to the membrane and consist of 3 subunits a, b and g, the last two being closely associated: In the free G protein, GDP occupies the binding site on the a-subunit. The a subunit and the b/g complex can each activate intracellular targets. Subtypes of all 3 subunits exist; the particular subunit determines which targets are activated R R R a a E1 bg E1 bg E1 bg E2 GDP a GDP GDP P 1. Agonist interacts with receptor 6. The a-subunit + GDP re-associates with 5. GTP is hydrolysed by the GTPase of the the bg-subunits, to be back where we a-subunit. The agonist dissociates from started the receptor R R R a a a E1 GDP bg E1 bg E1 GTP bg E2 GTP GDP 2. The a-subunit (+ GDP) interacts with the 3. GTP replaces GDP 4. The a-subunit + GTP interacts with the receptor enzyme, activating it. The b/g complex also activates a target enzyme Fig. 2.3 The mechanism of the G-protein transduction process. Activated enzyme indicated by a blue box. Receptors linked to ion channels (i.e. ionotropic receptors) Receptors linked to ion channels are located in the cell membrane and respond in milliseconds. The channel forms part of the receptor. The nicotinic receptor for acetylcholine (see Ch. 10) is an example (Fig. 2.4). Receptor with Agonist Channel Antagonist The nicotinic receptor has 5 subunits (3 shown). 2 binding sites (ACh) opens inhibits Stimulation by agonist opens the ion channel for ACh binds binding of and lets cations through Ions agonist Other examples: • GABAA receptor: a ligand-gated Cl– channel (Ch. 32) • ionotropic glutamate receptor: a cation channel (Ch. 32) • 5-HT3 receptor: a ligand-gated cation channel (Ch. 12) Fig. 2.4 Examples of receptors linked to ion channels (ionotropic receptors). ACh, acetylcholine. Receptors linked to gene transcription receptors activate Jak kinases, which, in turn, activate Stat The receptors that regulate gene transcription are called nuclear transcription factors and these activate gene transcription (Fig. 2.6). receptors although some are located in the cytosol (e.g. glucocorticoid receptors) and migrate to the nucleus after binding a ligand (Fig. 2.5). CARRIERS AS TARGETS FOR DRUG ACTION Receptors linked to enzymes The classification of membrane transport proteins varies between These receptors are transmembrane proteins with a large authorities, but in essence there are two main types: extracellular portion that contains the binding sites for ligands (e.g. • ATP-powered ion pumps growth factors, cytokines) and an intracellular portion that has • transporters (Table 3.1) integral enzyme activity—usually tyrosine kinase activity (Fig. 2.6). Activation initiates an intracellular pathway involving cytosolic and Both are transmembrane proteins. In Rang et al. Pharmacology, 8 nuclear transducers and eventually gene transcription. Cytokine these are termed ‘carriers’.
- 3. MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DRUG ACTION 2 Gc Plasma Examples are members of the steroid superfamily of receptors; • corticosteroid receptors Gc Gc Gc • oestrogen and progestogen receptors R R R Receptor changes • thyroid hormone receptors conformation • Vitamin D3 receptors Nucleus Gc The Gc/receptor complexes form dimers before entering the nucleus Complex interacts with R (not shown) DNA and alters gene expression Transcription Translation mRNA Mediator Mediator Transcribed genes induce Cytoplasm proteins proteins synthesis of some in plasma mediator proteins and inhibit synthesis of others Fig. 2.5 Mechanism of action of a receptor linked to gene transcription. Gc, glucocorticoid; R, receptor. ATP-powered ion pumps The K+ concentration is 140 mmol/l inside cells and 5 mmol/l The three principal ion pumps are the sodium pump (the Na /K + + outside. For each molecule of ATP hydrolysed, the sodium pump ATPase), the calcium pump, and the Na+/H+ pump in the pumps 3Na+ out of the cell and 2K+ in against their chemical gastric parietal cell, which is the target for the proton pump gradients. (The pump in Fig. 2.7 has simplified stoichiometry.) inhibitor omeprazole. Here we will concentrate on the sodium pump. This is important in maintaining cellular osmotic Transporters balance and cell volume and in maintaining the membrane The main transporters involved in drug action are symporters and potential. In many cells (e.g. in the myocardium, the nephron) antiporters (exchangers) (see Fig. 2.7). it is the primary mechanism for transporting Na+ out of the Symporters These use the electrochemical gradient of one ion cell (Fig. 2.7). (usually Na+) to carry another ion (or molecule or several ions) A B C Growth factors Adapter proteins Plasma membrane Growth factor receptors P P P SH2 Tyrosine kinases GTP Kinase 1 Nucleus Kinase 2 Cytoplasm Kinase 3 Gene transcription Agonist binding to 2 SH2-containing ‘adapter’ proteins bind to the receptors leads to phosphorylated residues in the receptors and activate a coupling (dimerisation). pathway consisting of Ras, which becomes activated after The TKs in each receptor exchange of GDP for GTP; this, in turn, activates a cascade phosphorylate the other of three kinases. The last kinase phosphorylates various member of the dimer transcription factors, thus activating transcription of the genes for proliferation and differentiation Fig. 2.6 Receptors linked to tyrosine kinases, e.g. growth factor receptor. 9
- 4. 2 MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DRUG ACTION 1. The sodium pump is 2. The conformation 3. Sodium binds 4. ATP binds to and 5. This conformation shown with the shown below phosphorylates has a low affinity binding sites (3 for (sites facing the the cytoplasmic which causes a for Na+ and a high Na+, 2 for K+) facing cytoplasm) has surface of the change in the affinity for K+ the cytoplasmic high affinity for pump conformation of surface of the Na+ and lower the ATPase (see 5) plasma membrane affinity for K+ so that the binding sites now face outward Plasma membrane ATP P Cytoplasm + Na and we're Digitalis glycosides inhibit the back where pump by binding to a K+ site we started K + P P P P 11. Potassium 10. The sites now 9. Dephosphorylation 7,8. Potassium binds 6. Sodium is is released face inwards. occurs, changing released There is now the ATPase and... lower affinity conformation for K+ than Na+ Fig. 2.7 The action of the sodium pump. across a cell membrane. Drugs can modify this action by occupying Ca2+ exchanger, which exchanges 3Na+ for 1Ca2+ (Fig. 2.8). Note a binding site (e.g. the action of furosemide (frusemide) on the that this calcium exchanger should be distinguished from the ATP- Na+/K+/2Cl– symport in the nephron (Fig. 2.8). Similarly, thiazide driven calcium pump and the ligand-gated and voltage-gated Ca2+ diuretics bind to and inhibit the Na+/Cl– symporter in the distal channels (see Fig. 4.1 in Rang et al.). The calcium exchanger is tubule. crucial in the maintenance of the Ca2+ concentration in blood vessel Antiporters These use the electrochemical gradient of one ion smooth muscle and cardiac muscle (see Ch. 20). Another example is (usually Na+) to drive another ion (or molecule) across the the uptake carrier in the noradrenergic varicosity, which transports membrane in the opposite direction. An important example is the noradrenaline into the cell (see Ch. 11). A B Electrochemical + Ions bind Transporter gradient of Na+ K changes conformation; Cl− Na+ binds ions releasd in + the cell Na Transporter Membrane Cell interior Ca2+ binds Change of conformation Ions ) inhibits by binding to a Cl− site released Furosemide ( Fig. 2.8 Examples of (A) a symporter, and (B) an antiporter. 10
- 5. MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DRUG ACTION 2 ION CHANNELS AS TARGETS FOR DRUG ACTION Some drugs produce their actions by directly interacting with ion channels. Three examples are given in Figure 2.9. Note that these ion channels transport ions across the plasma membrane. They are not receptors and should be distinguished from ion channels that function as ionotropic receptors (see above). Voltage-gated Na+ channels 2+ Voltage-gated L-type Ca channels ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the in sensory neurons consist in cardiac myocytes consist of several insulin-secreting pancreatic B cell of 4 subunits (not shown). subunits (not shown). The channels have binding sites for Local anaesthetics (LAs) can be blocked by the dihydropyridine sulfonylureas, which are used to block the channel, stopping calcium antagonists, which bind to a treat non-insulin-dependent action potential generation site on an =-subunit diabetes (Ch. 27) KATP channel Sulfonylurea (e.g. Uncharged LAs reach Calcium (opens when the glibenclamide) blocking site from antagonist, cytosolic ATP acts on binding outside of membrane e.g. nifedipine concentration falls) site, blocks Binding site channel, + 2+ Na Ca depolarises cell... Plasma membrane Cytoplasm ...and causes K+ insulin secretion Charged LAs reach blocking site from inside of membrane Fig. 2.9 Examples of drugs acting directly on ion channels. ENZYMES AS TARGETS FOR DRUG ACTION Drugs can produce effects on enzyme reactions by substrate competition or by reversibly or irreversibly modifying the enzyme. Some examples are given in Table 2.1. Table 2.1 Drugs acting through alteration of enzyme reactions Enzyme Enzyme Substrate Products Inhibitor ? Substrate Substrate Enzyme Products Inhibitor Uses Acetylcholine Acetylcholine esterase Choline; acetate Neostigmine Myasthenia gravis and to reverse neuromuscular block Arachidonate Cyclooxygenase Prostanoids Aspirin Heart disease and inflammation Angiotensin (AT)I AT converting enzyme AT II Captopril Hypertension, heart failure, post-infarct Hypoxanthine Xanthine oxidase Uric acid Allopurinol Gout HMG-CoA HMG-CoA reductase Mevalonic acid Simvastatin To lower blood cholesterol Folate Dihydrofolate reductase Tetrahydrofolate Trimethoprim With cotrimoxazole as antibacterial Thymidine Viral reverse transcriptase Zidovudine HIV infection Deoxyribonucleotides DNA polymerase DNA Cytarabine Anticancer drug 11
