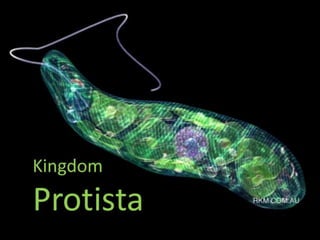
Kingdom Protista
- 2. CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTISTS Simplest eukaryotes Ernest Haeckel coined the term protista in 1886 mostly unicellular, some are multicellular can be heterotrophic or autotrophic microscopic or macroscopic most live in water (though some live in moist soil or even the human body) ALL are eukaryotic (have a nucleus) A protist is any organism that is not a plant, animal or fungus.
- 3. Plantlike Protists The algae, euglena, and dinoflagellates are representatives of the plantlike protists. Live in the aquatic environment (fresh and salt water). ALGAE Algae is multicellular or unicellular, but the single celled type can’t be seen without a microscope. Thrive in aquatic environment They mostly use photosynthesis, but some eat other protists or absorb nutrients for food Described as thallus body. They are known as algae. (Alga- singular) Macroscopic algae are referred to as seaweeds.
- 4. Euglena Live mostly in fresh water Have plant and animal characteristics Use photosynthesis, but when there’s not enough light, they are consumers Some don’t use photosynthesis at all because they don’t have chloroplast. Instead, they just eat other protists or take in nutrients Move by using flagella to push them through the water
- 5. Dinoflagellates Live mostly in salt water, but some are found in fresh water and snow. Have flagella that make the protists spin Most use photosynthesis, but some get food as consumers, decomposers, or parasites They are sometimes red and produce a strong poison When they produce very fast, they cause red tide, where the water turns red and the shellfish eat it, making the shellfish poisonous to all vertebrates.
- 6. Animal-like protists: Protozoans they are heterotrophs and can move around. They are multicellular. Their means of movement are through their flagella and cilia. Amoeba- moves using pseudopodia ( “false feet” ), which are like extensions of the cytoplasm. Ingests food by surrounding and engulfing food (endocytosis) Reproducing by binary fission (mitosis) can cause amebic dysentery in humans – diarrhea and stomach upset from drinking contaminated water
- 7. Animal-like protists: Protozoans PARAMECIUM move using cilia exhibits avoidance behavior reproduces asexually (binary fission) or sexually (conjugation) outer membrane pellicle- is rigid and paramecia are always the same shape, like a shoe
- 8. Animal-like protists: Protozoans Trypanosoma group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. cause various diseases, including the fatal human diseases sleeping sickness
- 9. Funguslike protists Thrive in moist, damp places where there is a lot of rotting organic matter. Fungus-like protists are heterotrophs with cell walls. All fungus-like protists are able to move at some point in their lives. There are essentially three types of fungus-like protists: water molds, downy mildews, and slime molds. Often brightly colored Change form during life cycle Tend to live in damp locations
