Lecture 7.2- Ionic Compounds
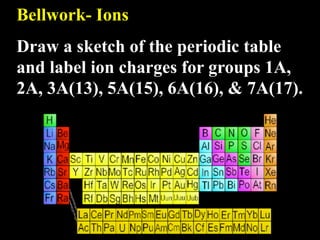
- 1. Bellwork- Ions Draw a sketch of the periodic table and label ion charges for groups 1A, 2A, 3A(13), 5A(15), 6A(16), & 7A(17).
- 2. Lecture 7.2- Ionic Compounds
- 3. Compounds composed of cations and anions are called ionic compounds.
- 4. Compounds composed of cations and anions are called ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are electrically neutral. (positive charges always equal the negative charges)
- 5. Aluminum metal and the nonmetal bromine react to form an ionic solid, aluminum bromide.
- 6. The electrostatic forces that hold ions together in ionic compounds are called ionic bonds.
- 7. An ionic compound is also called a salt.
- 8. An ionic compound is also called a salt. Salts contain positive and negative ions that alternate in a perfect 3D pattern called a crystal lattice.
- 9. The transfer of an electron from Na Na Cl to Cl creates an anion and a cation. Na+ Cl-
- 10. The transfer of an electron from Na Na Cl to Cl creates an anion and a cation. Na+ Cl-
- 11. The transfer of an Their electron opposite from Na charges Na Cl to Cl attract creates them to an each anion other. and a cation. Na+ Cl-
- 12. Take an atomic-level look at the formation of KCl.
- 13. •A chemical formula shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in the smallest representative unit of a substance.
- 14. •A chemical formula shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in the smallest representative unit of a substance. •A formula unit is the lowest whole-number ratio of ions in an ionic compound.
- 15. NaCl is the chemical formula for sodium chloride.
- 16. NaCl is the chemical formula for sodium chloride.
- 17. NaCl is the chemical formula for sodium chloride.
- 18. NaCl is the chemical formula for sodium chloride.
- 19. Determining formulas for ionic compounds
- 20. Determining formulas for ionic compounds The positive charges must equal the negative charges, because the compound is neutral.
- 21. Determining formulas for ionic compounds The positive charges must equal the negative charges, because the compound is neutral. Mg2+ and Cl- make MgCl2 because you need 2 Cl- to cancel the 2+ charge on Mg
- 22. What is the formula of a compound containing ions of Al and O?
- 23. What is the formula of a compound containing ions of Al and O? Al3+ O2-
- 24. What is the formula of a compound containing ions of Al and O? Al3+ O2- Find the least common multiple! 3+ x 2 = 6+ 2- x 3 = 6-
- 25. What is the formula of a compound containing ions of Al and O? Al3+ O2- Find the least common multiple! 3+ x 2 = 6+ 2- x 3 = 6- So you need 2 Al3+ and 3 O2- Al2O3
- 26. What is the formula of a compound containing ions of Al and O? Al 3+ O2- Al2O3 The charge on one ion becomes the subscript for the other ion!
- 31. Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature.
- 32. Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. Ionic compounds have high melting points.
- 33. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 34. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 35. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 36. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 37. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 38. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 39. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 40. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 41. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 42. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 43. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 44. The orderly arrangement of component ions produces the beauty of crystalline solids.
- 45. Simulation 5 Simulate the formation of ionic compounds at the atomic level. Simulation 5
- 46. • The coordination number of an ion is the number of ions of opposite charge that surround the ion in a crystal. • In NaCl, each ion has a coordination number of 6.
- 47. • In CsCl, each ion has a coordination number of 8. • In TiO2, each Ti4+ ion has a coordination number of 6, while each O2- ion has a coordination number of 3.
- 48. Electricity is the directed movement of charged particles. To conduct electricity, a substance or mixture must contain positive or negative charges that can move freely.
- 49. Ionic compounds can conduct an electric current when melted or dissolved in water.
- 50. Ionic compounds can conduct an electric current when melted or dissolved in water.
- 51. 7.2 Section Quiz. 1. Which chemical formula is incorrect? a. KF2 b. CaS c. MgO d. NaBr
- 52. 7.2 Section Quiz. 1. Which chemical formula is incorrect? a. KF2 b. CaS c. MgO d. NaBr
- 53. 2. Ionic compounds can conduct an electric current a. only when melted. b. when melted or dissolved in water. c. only when dissolved in water. d. when solid or melted.
- 54. 2. Ionic compounds can conduct an electric current a. only when melted. b. when melted or dissolved in water. c. only when dissolved in water. d. when solid or melted.
- 55. 3. At room temperature, most ionic compounds are a. crystalline solids. b. liquids. c. gases. d. soft, low melting-point solids.
- 56. 3. At room temperature, most ionic compounds are a. crystalline solids. b. liquids. c. gases. d. soft, low melting-point solids.