Solar System Formation/Sun/Comets/Meteors
- 2. Formation of Our Solar System Formation of Our Solar System • Astronomers use Earth-based observations and data from probes to derive theories about how our solar system formed. • The significant observations related to our solar system’s formation include the shape of our solar system, the differences among the planets, and the oldest planetary surfaces, asteroids, meteorites, and comets.
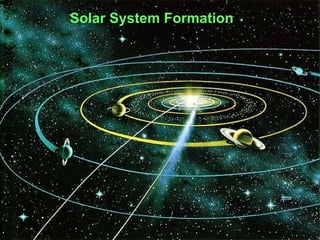
- 3. Formation of Our Solar System A Collapsing Interstellar Cloud • Stars and planets form from clouds of gas and dust, called interstellar clouds, which exist in space between the stars. • The interstellar clouds consist mostly of gas, especially hydrogen and helium that often appear as blotches of light and dark.
- 4. A Collapsing Interstellar Cloud • Our solar system may have begun when interstellar gas started to condense as a result of gravity and became concentrated enough to form the Sun and planets. – The collapse is initially slow, but it accelerates and the cloud soon becomes much denser at its center. – Rotation slows the collapse in the equatorial plane, and the cloud becomes flattened. – The cloud eventually becomes a rotating disk with a dense concentration at the center.
- 5. Sun and Planet Formation Formation of Our Solar System • The disk of dust and gas that formed the Sun and planets is known as the solar nebula. • The dense concentration of gas at the center of this rotating disk eventually became the Sun. • In the disk surrounding the Sun, the temperature varied greatly with location. • As the disk began to cool, different elements and compounds were able to condense depending on their distance from the Sun which impacted the compositions of the forming planets.
- 6. Sun and Planet Formation •Elements and compounds that were able to condense close to the Sun, where it was warm, are called refractory elements, and far from the Sun, where it was cool, volatile elements could condense. •Planets may have been formed by the Accretion Theory. •Refractory elements, such as iron, comprise the terrestrial planets, which are close to the Sun. Volatile elements, such as ices and gases like hydrogen, comprise the planets further from the Sun, where it is cool.
- 7. Our Sun
- 8. The Sun Solar Activity • The Sun’s magnetic field disturbs the solar atmosphere periodically and causes new features to appear in a process called solar activity. • Sunspots are cooler areas that form on the surface of the photosphere due to magnetic disturbances, which appear as dark spots.
- 11. The Sun Solar Activity Solar Activity Cycle – The number of sunspots changes regularly, and on average reaches a maximum number every 11.2 years. – The length of the solar activity cycle is 22.4 years. • The solar activity cycle starts with minimum spots and progresses to maximum spots. • The Sun’s magnetic field then reverses in polarity, and the spots start at a minimum number and progress to a maximum number again. • The magnetic field then switches back to the original polarity and completes the solar activity cycle.
- 12. Maximum Minimum
- 13. Solar Activity – Solar flares are violent eruptions of particles and radiation from the surface of the Sun that are associated with sunspots. – When these particles reach Earth, they can interfere with communications and damage satellites. The Sun
- 15. – A prominence, sometimes associated with flares, is an arc of gas that is ejected from the chromosphere, or gas that condenses in the inner corona and rains back to the surface.
- 18. The Sun Solar Activity Impact on Earth – Some scientists have found evidence of subtle climate variations within 11-year periods. – There were severe weather changes on Earth during the latter half of the 1600s when the solar activity cycle stopped and there were no sunspots for nearly 60 years. – Those 60 years were known as the “Little Ice Age” because the weather was very cold in Europe and North America during those years.
- 19. The Sun The Solar Interior • Fusion occurs within the core of the Sun where the pressure and temperature are extremely high. – Fusion is the combining of lightweight nuclei, such as hydrogen, into heavier nuclei. – Fission, the opposite of fusion, is the splitting of heavy atomic nuclei into smaller, lighter atomic nuclei. • In the core of the Sun, helium is a product of the process in which hydrogen nuclei fuse. • At the Sun’s rate of hydrogen fusing, it is about halfway through its lifetime, with about another 5 billion years left.
- 20. The “Little Pieces” Asteroids and Comets Gaspra is an irregular body with dimensions of about 20 x 12 x 11 km (12.5 x 7.5 x 7 miles). Its surface reflects approximately 20 percent of the sunlight striking it. Gaspra is composed of metal-rich silicates and perhaps blocks of pure metal.
- 21. Comet Hale-Bopp Earth Closest Approach: March 22, 1997 Last seen by Tycho Brahe (1577)
- 22. Formation of Our Solar System I. Asteroids • Asteroids comprise the thousands and thousands of bodies that orbit the Sun within the planetary orbits that are leftovers from the formation of the solar system. • Asteroids range from a few kilometers to about 1000 km in diameter and have pitted, irregular surfaces. • Most asteroids are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter within the asteroid belt.
- 23. Formation of Our Solar System I. Asteroids Pieces of Asteroids – As the asteroids orbit, they occasionally collide and break into fragments. • A meteoroid is a asteroid fragment or any other interplanetary material that falls toward Earth and enters Earth’s atmosphere.
- 24. • A meteor is the streak of light produced when a meteoroid burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. In the early morning of the 3rd of november 2007 a meteor hit Eslöv, known as the most boring town of Sweden. It was an unexpected event that was witnessed only by a few.
- 25. • A meteorite is part of a meteoroid, that does not completely burn up, that collides with the ground.
- 26. Look! Meteorites! Mr. Bantay at Washington DC’s Smithsonian Museum of Natural Sciences.
- 27. Proposed site of the Impact Crater that hit 65 million years ago.
- 28. Asteroid Impact Crater below the Chesapeake Bay.
- 29. Great Meteor Crater, Arizona.
- 31. Distribution of Impact Craters on Earth
- 32. Russian Meteor - 02/15/2013
- 33. II. Comets Formation of Our Solar System • Comets are small, icy bodies that have highly eccentric orbits around the Sun and are remnants from solar system formation. • Comets are made of ice and rock, and they range from 1 to 10 km in diameter. • There are two clusters, or clouds, of comets: the Kuiper belt and the Oort cloud. • Occasionally, a comet is disturbed by the gravity of another object and is thrown into the inner solar system from one of these clusters.
- 35. November 4, 2010: NASA’s EPOXI mission passed within 435 miles of Comet Hartley 1 on Nov. 4. This image, one of the closest taken of comet Hartley 2 by NASA's EPOXI mission, shows jets from the comet's surface. Analysis shows that dry ice sublimating from the comet causes the fuzzy appearance.
- 36. Formation of Our Solar System Comets The Orbits of Comets – When a comet nears the sun in its highly eccentric orbit, it begins to evaporate and form a head and one or more tails. – The coma is an extended volume of glowing gas flowing from a comet’s head. – The nucleus of a comet is the small solid core that releases gases and dust particles that form the coma and tails when it is heated.
- 37. Changes to a comet: 1a. Seen as a star 1b. Coma grows 1c. Tail grows & ALWAYS faces AWAY from the sun. 1d. Tail fades 1e. Coma shrinks 1f. Coma vanished.
- 38. Comets Formation of Our Solar System Periodic Comets – Comets that repeatedly orbit into the inner solar system are known as periodic comets. – Meteor showers occur when Earth intersects a cometary orbit and numerous particles from the comet burn up upon entering Earth’s upper atmosphere. – Most meteors are caused by dust particles from comets, while most meteorites, the solid chunks of rock or metal that Leo reach Earth’s surface, are fragments of asteroids. Leonids
- 39. Comets and Meteors ( 4 min)
- 40. Solar Storm Alert 2012 - Discovery Channel: 19 minutes
