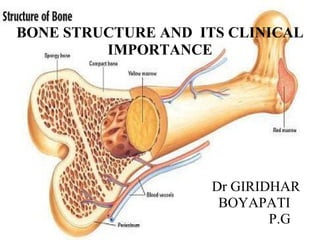
Bone structure and clinical importance
- 1. BONE STRUCTURE AND ITS CLINICAL I M P O R T A N C E Dr GIRIDHAR BOYAPATI P.G
- 2. What is Bone? – Mineralized connective tissue - constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates
- 3. Classification REGION- Axial, Appendicular SHAPE - Long bones, short bones, irregular, pneumatic, sesamoid, accessory STRUCTURE Macroscopic – Compact Spongy Microscopic – Lamellar (Secondary Bone) Woven/fibrous(Primary Bone) DEVELOPMENT – Membranous Cartilaginous Membrano-cartilaginous
- 4. ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION MESENCHYMAL CELLS CHONDROBLASTS CHONDROCYTES CARTILAGE MODEL OF FUTURE BONE OSTEOBLASTS
- 7. Endochondral Ossification Defects – AD Inheritance • Achondroplasia • Thanatophoric Dysplasia • Hypochondroplasia Mutation in FGFR 3 gene
- 9. EXAMPLES OF INTRAMEMBRANOUS OSSIFICATION 1. EMBRYONIC FLAT BONES : SKULL, PELVIS, MAXILLA, MANDIBLE, CLAVICLE 2. DISTRACTION OSTEOGENESIS 3. FRACTURE HEALING WITH RIGID FIXATION 4.BLASTEM BONE
- 10. PERIOSTEAL OSSIFICATION OSTEOGENIC CELLS FROM PERIOSTEUM LAY PARLLEL LAYERS OF COMPACT BONE
- 11. Bone cells Osteo progenitors (Pleuripotent stem cells) Osteoblasts ("bone makers") Osteocytes ("bone cells") Osteoclasts (“bone breakers”) remodeling MATRIX Ground substance Proteoglycans Glycoproteins Minerals Water Fibers
- 12. Cells of Bone (Primary/Temporary) Osteoprogenitor Osteoclast Osteoblast Osteocyte Osteoid
- 13. PERIOSTEUM MEMBRANE COVERING OUTER SURFACE OF BONE LAYERS: 1. FIBROUS LAYER 2. CAMBIUM LAYER
- 14. OSTEOGENIC CELLS
- 15. OSTEOBLAST
- 16. OSTEOCYTE
- 17. OSTEOCLAST
- 18. Osteoclast
- 19. CANALICULI
- 20. Bone cells -Function • Osteoblasts – Matrix synthesis – Osteoid, Calcification PTH receptors • Osteocyte – Maintanace of Matrix by intercellular sickling systems • Osteoclast – Digestion of collagen, dissolving hydroxyapatite * Calcitonin receptors
- 21. Bone cells- Medical application Rate of bone apposition – Bone growth Osteomalacia – Impaired mineralization Osteitis fibrosa cystica – osteoclast activity Osteopetrosis – “Marble bones” – Bone resorption defect due to osteoclastic activity Osteitis deformans (Paget’s disease) –Uncontrolled osteoclast activity followed by osteoblastic activity (incomplete)- Stops at osteoid level
- 22. BIOCHEMISTRY 1.INORGANIC 65 -70% 2.ORGANIC 30-35% ORGANIC: a. collagen 90-95% b. pps 4-5% c.Lipids 0.1% INORGANIC 90% Calcium and phosphate
- 23. BONE COLLAGEN 1.AXIAL PERIODICITY OF 640 TO 700A 2.PROTIEN COMPOSITION WITH ONE THIRD GLYCINE 3.LARGE NO. OF ALANINE RESIDUES 4.CYSTEINE IS COMPLETELY ABSENT
- 24. Matrix • Fibers – Collagen Type I- Gene mutation in alfa 1or 2 OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFACTA • Ground substance Proteoglycans – Chondroitin Sulphate, Keratan Sulphate Glycoproteins – Osteocalcin , Alkaline phosphatase
- 25. Structural regions of long bone
- 26. Gross structure of typical long bone Shaft – Thick compact bone+ medullary cavity Ends- Cancellous bone + thin compact layer Articular cartilage – No periosteum, avascular Periosteum – Fibrous + cellular Shape, nutrition, attachment fracture repair, sensitive Endosteum – Cellular -Repair and remodelling Nutrient foramen – mid shaft Bone marrow – Red, Yellow
- 27. Parts of a growing bone Epiphysis (Secondary) Epiphyseal plate Metaphysis Diaphysis (Primary)
- 29. PRESSURE region of the long bone that forms the joint is called Pressure Epiphysis ARTICULAR....WT TRANSMISSON EX: HEAD OF FEMUR AND HUMERUS TRACTION Non-articular Muscle pull Ossifies later than Pressure .EX HUMERUS G.T AND L.T FEMUR G.T AND LT
- 30. ATAVISTIC COROCOID PROCESS OF SCAPULA OS TRIGONUM ABERRANT HEAD OF 1ST METACARPEL Unusual
- 31. Epiphyseal plate
- 32. Growth Plate
- 33. ZONE 1 INJURY CAUSES CESSATION OF GROWTH ZONE 2 BONE LENGTH IS ADDED ZONE 3 WEAKEST PORTION OF GROWTH PLATE
- 34. Metaphysis Epiphyseal end of diaphysis Active growth Before fusion end arteries, hair pin bends OSTEOMYELITI S
- 35. Blood supply of bones Long Bone Nutrient artery Metaphyseal arteries Epiphyseal arteries Periosteal arteries Short Bone - Nutrient artery; Periosteal arteries Vertebra- Body, Processes Rib - Nutrient artery; Periosteal arteries
- 36. Nutrient artery Mid shaft Tortuiosity 2/3rd inner compact bone Hair pin loops Direction – away from growing end . “To the elbow I go. From the knee I flee.”
- 37. Nutrient Artery 1.Enters into the diaphysis of long bones through an oblique canal 2.direction of canal is determined by relative amount of growth that has occurred at proximal and distal ends of the bone; 3.does not branch within the cortex, divides after reaching the medullary cavity, 4. direction of blood flow is centrifugal;
- 38. Disruption of Nutrient Artery causes 1. In growing bone can result in necrosis of large portion of marrow & of inner two thirds of cortex 2. This cortical death does not occur in adult bone because combined epiphyseal-metaphyseal collateral circulation is developed enough to maintain these areas; 3.loss of circulation in terminal vessels of nutrient artery of growing bone will interfere with enchondral ossification;
- 39. Epiphyseal arteries In femoral and radial heads, which are almost entirely covered by cartilage vessels enter in region between articular cartilage & growth-plate cartilage In other regions, the epiphysis has openings that permit passage of large number of vessels into and out of the ossification centers
- 40. Obliteration of epiphyseal blood supply causes 1.necrosis of epiphysis 2. longitudinal growth ceases 3. permanent closure of epiphyseal plate
- 41. METAPHYSIAL ARTERIES BRANCHES OF SYSTEMIC VESSELS Epiphyseal vessels are responsible for permitting longitudinal growth to occur, whereas metaphyseal vessels nourish osteoprogenitor cells, which lay down bone on cartilage matrix;
- 42. PERIOSTEAL ARTERIES Periosteal vessels send small branches thru minute channels in cortex to supply about outer 1/3 of cortex Extensive network of vessels covers entire length of the bone shaft Anastomoses with adjacent skeletal muscles so in cases in which the nutrient artery of muscle has been damaged, then periosteal vessels may temporarily serve as the primary blood supply;
- 44. BLOOD SUPPLY OF GROWTH PLATE growth plate itself is avascular & receives nutrition from 2 sources 1.epiphyseal vessels that supply germinal, proliferating, and upper hypertrophic cell layers by diffusion 2 .metaphyseal vessels that supply zone of provisional calcification
- 45. In a young child, epiphyseal vessels are separated from metaphyseal vessels, but following growth arrest of the cartilage plate, there is an extensive anastomoses between epiphyseal vessels, metaphyseal vessels, & terminal branches of Nutrient Artery;
- 46. VENOUS DRAINAGE TRANSVERSE VENOUS CHANNELS CENTRAL VENOUS SINUS NUTRIENT VEIN -ONLY 5-10% OF VENOUS DRINAGE IS THROUGH NUTRIENT VEIN -REMAINING IS THROUGH PERIOSTEAL VENOUS DRINAGE
- 47. Circulatory disturbances PHYSIS AND EPIPHYSIS 1.Legg–Calve–Perthes Disease: Circulatory disturbance to the capital femoral epiphysis 2.Physeal Trauma METAPHYSIS 1.Haematogenous Osteomyelitis 2.Metastasis. DIAPHYSIS 1.Intramedullary Reaming 2.Fracture Healing PERIOSTEAL BLOOD SUPPLY 1.Paralytic conditions
- 48. Spongy bone 1. loose network of bone trabecule 2. interconnected 3. arranged along lines of maximum stress
- 49. Spongy Bone Superimposed lamllae No Haversian system Lamellated trabeculae Red marrow
- 50. Spongy Bone- No HS
- 51. Osteon (Haversian system) Central canal (Haversian or osteonal canal) Transverse (Volkmann) canals Lacuna Canaliculi ("tiny canals") Lamellae Concentric,Intersititial, Circumferential
- 52. Compact bone
- 53. COMPACT BONE
- 54. Sharpey’s fibers Connective tissue matrix Bundles of collagen fibers Connect Perisoteum to Bone Fibrous layer of Periosteum to outer circumferential and interstitial lamellae
- 55. Growing Bone BONE GROWTH 1. Appositional 2. Endochondral
- 56. Factors affecting growth of a bone Nutritional Vit. A - Co-ordination of osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity Vit.C – Synthesis of organic matrix Vit.D – Absorption of Ca, P Rickets, Osteomalacia (Calcification deficiency) Calcium – Decalcification of bone
- 58. Factors affecting growth of a bone Hormonal – • Pituitary - GH- Dwarfism; Gigantism, Acromegaly • Thyroid - Calcitonin Parathyroid – PTH Decalcification Sex Hormones - Androgens, estrogens - Stimulators Mechanical factors Tensile forces – Bone formation Compressive forces – Bone resorption
- 60. Rules of Ossification Primary centers - before birth except carpal and tarsal (except calcaneus, talus, cuboid) Secondary centers - after birth except lower end of femur, upper end of tibia, humerus Center which appears first unites last except lower end of FIBULA
- 61. Rules of Ossification Center which appears later unites first except upper end of fibula Direction of nutrient artery - away from growing end except fibula Growing end is one where center appears first and unites last except fibula
- 62. Fracture Healing 1. Hematoma formation Macrophages Osteoclasts 2. Fibrocartilaginous callus formation Periosteum Endosteum 3. Bony callus formation Ossification (EC & IM) 4. Remodeling Sec.bone formation
