12 Appendicular Muscles
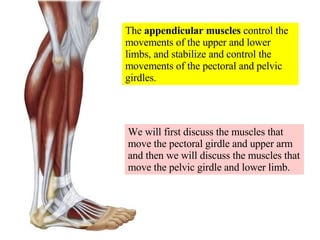
- 1. The appendicular muscles control the movements of the upper and lower limbs, and stabilize and control the movements of the pectoral and pelvic girdles. We will first discuss the muscles that move the pectoral girdle and upper arm and then we will discuss the muscles that move the pelvic girdle and lower limb.
- 2. There are many muscles that act on the pectoral girdle to help it in its activities. Remember that the only bone which connects your shoulder to the rest of your skeleton is the delicate clavicle.
- 3. The muscles of the pectoral girdle originate on the axial skeleton and insert on the clavicle and scapula. These muscles are classified depending on their location on the anterior or posterior of the thorax.
- 4. The pectoralis minor muscle is an anterior thoracic muscle and is NOT visible on the surface as it is deep to the pectoralis major. It is synergistic to the serratus anterior muscles.
- 5. The serratus anterior muscle (an anterior thoracic muscle) originates on the lateral surface of upper ribs, passes deep to the medial border of the scapula and protracts and depresses the scapula, stabilizes the scapula, and superiorly rotates the scapula.
- 6. Serratus anterior muscles with the scapula tilted up for a better view of the insertion on the medial (vertebral) border of the scapula and anterior surface of scapula. Anterior view
- 8. Deltoid Biceps brachii Read about damage to the long thoracic nerve and paralysis of the serratus anterior in the clinical view in the text.
- 9. Both the rhomboid major and the rhomboid minor are located deep to the trapezius, and thus are not visible on the surface. The rhomboids adduct the scapula, elevate the scapula, and inferiorly rotate the scapula.
- 10. The rhomboid major muscle and the rhomboid minor muscle adduct, elevate and inferiorly rotate the scapulae. They are antagonistic to the serratus anterior and pectoralis minor muscles. Severe lateral abducting movements stress the rhomboids
- 11. Inform your partner of the location of the rhomboids (between the scapulae and deep to the trapezius) so these stressed muscles can be properly massaged at the end of a long day (“rub my rhomboids”).
- 12. External view of the trapezius muscle .
- 13. The trapezius muscle elevates the scapula, draws the head back, and adducts (retracts) the scapulae. Note that its most superior attachment is the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
- 14. The trapezius muscle, along with the splenius capitis and semispinalis capitis, extends the head and hyperextend the neck . All three insert on the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone. Now do you know why there is so much stress on the back of your head?
- 15. WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS SYNERGISTIC TO THE PECTORALIS MINOR? A TRAPEZIUS B SERRATUS ANTERIOR C RHOMBOID MAJOR AND MINOR D DELTOID E LATISSIMUS DORSI
- 16. The muscles that move the glenohumeral joint are classified according to those that originate on the axial skeleton (i.e.-latissimus dorsi) and those that originate on the scapula (i.e.- deltoid)
- 17. Latissimus dorsi muscles getting a work-out doing the “butterfly stroke” while swimming.
- 18. The latissimus dorsi inserts on the intertubercular groove of the proximal humerus. This muscle extends the arm at the shoulder joint and draws the arm downward and backwards while it rotates the arm medially (swimmer’s muscle).
- 19. Resistance while adducting the arm and flexing the shoulder can strengthen the pectoralis major muscles
- 20. The pectoralis major muscle flexes, adducts, and rotates the arm medially at the glenohumeral joint.
- 21. Rupture of the pectoralis major insertion on the greater tubercle of the humerus
- 22. Incision sites commonly used for insertion of breast implants. Such implants can be used simply for cosmetic reasons or for reconstruction following cancer surgery.
- 23. Silicon or saline-filled breast implants can be used cosmetically or for reconstruction.
- 24. Plastic surgeons have told me that breast implants are best positioned in a pouch within or under the pectoralis major muscle to prevent displacement Most stable location Less stable location
- 25. The deltoid muscles getting a work-out while abducting the arm at the glenohumeral joint. This is an excellent example of a third class lever system.
- 26. The deltoid muscles are a good site for performing intramuscular (IM) injections of medication.
- 27. The deltoid muscle abducts the arm, rotates the arm, and extends the humerus at the glenohumeral joint. It inserts on the deltoid tuberosity on the lateral midregion of the humerus
- 28. The corocobrachialis is synergistic to the pectoralis major in flexing and adducting the arm. Its origin is the coracoid process of the scapula and it inserts on the middle shaft of the humerus.
- 29. The teres major works synergistically with the latissimus dorsi by extending, adducting, and medially rotating the arm. It originates on the inferior border and angle of scapula and inserts on the lesser tubercle and intertubercular groove at lateral proximal end of humerus.
- 30. There are four rotator cuff muscles to provide strength and stability for the glenohumeral joint: subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor.
- 31. The subscapularis is located on the anterior surface of the scapula. Its action is to medially rotate the arm , like when you wind up to pitch a baseball
- 33. The supraspinatus abducts the arm, as when you start to execute a pitch of a baseball with your arm fully extended.
- 35. The infraspinatus originates on the infraspinous fossa, inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus, and adducts and laterally rotates the arm, like when you slow down your arm after pitching a baseball.
- 37. The teres minor originates on the lateral border of the scapula, inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus, and is synergistic to the infraspinatus.
- 38. are synergistic
- 39. Clavicle Coracoid process Head of humerus Acromion Read the clinical view in the text about rotator cuff injuries
- 40. WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING MEDIALLY ROTATES THE ARM , LIKE WHEN YOU WIND UP TO PITCH A BASEBALL? A MUSCLE THAT INSERTS ON THE GREATER TUBERCLE OF THE HUMERUS B MUSCLE BETWEEN THE THORACIC CAGE AND SHOULDER BLADE C INFRASPINATUS D SUPRASPINATUS E TERES MINOR
- 41. There are several muscles that move the elbow joint/forearm . In the interest of simplicity I will limit our discussion only to the biceps brachii and triceps brachii .
- 42. Deep fascia divides the muscles of the brachium into an anterior compartment (which contains the biceps brachii) and a posterior compartment (which contains the triceps brachii).
- 43. The biceps brachii muscle flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm and hand at the elbow joint.
- 44. The biceps brachii muscles getting a work-out . This is an excellent example of a third class lever system.
- 46. The triceps brachii muscle extends the arm at the elbow joint. This is a good example of a first class lever system.
- 47. The triceps brachii muscles getting a work-out while doing push-ups.
- 48. Most of the muscles in the forearm move the hand and wrist and/or the fingers . Palpate the bellies of these muscles near your elbow and the tendons near your wrist.
- 49. Note that there are no muscles located within your digits . The fingers are moved by the pulling action of tendons from muscles located in the antebrachium.
- 50. Most of the anterior compartment muscles are flexors of the wrist and fingers. Most of the posterior compartment muscles are extensors of the wrist and fingers.
- 51. Lateral epicondyle (extensors) Read about tennis elbow in the clinical view in the text
- 52. On the palmar (anterior) surface of the wrist there is a strong fascial structure called the flexor retinaculum that hold the tendons close and prevents them from “bowstringing” outward. Flexor tendons leading to the digits and the median nerve pass through the tight space ( carpal tunnel ) between the flexor retinacula and the underlying bones.
- 53. Read about carpal tunnel syndrome in the clinical view in the text
- 54. The anterior compartment contains either extensors of the knee or flexors of the thigh. The medial compartment contains adductors of the thigh The posterior compartment contains flexors of the knee and extensors of the thigh. The lateral compartment contains a single abductor of the thigh
- 55. Most of the muscles that act on the thigh originate on the os coxae and insert on the femur. These muscles stabilize the highly moveable coxal joint (acetabulofemoral joint) and support the body during standing and walking. We will discuss only a few of these muscles in this introductory class.
- 56. The sartorius muscle (“tailor’s muscle”) is the longest muscle in the body and it is in the anterior compartment. It flexes the leg and thigh, and after it’s flexed, medially rotates the lower leg. This is the muscles that helps you cross your legs. It is easily visualized externally.
- 57. The sartorius muscle helps you position your legs to cross them. This muscle also helps you sit “Indian style” on the floor with legs crossed in front.
- 58. The sartorius muscle , like other major muscles of the thigh, is easily visible on the surface when it is tensed.
- 59. The gracilis muscle , a medial compartment muscle, is one of several groin muscles. The gracilis, since it is on the medial side of the thigh, adducts the thigh at the hip joint and flexes the leg at the knee joint.
- 60. The tensor fasciae latae is the only muscle in the lateral compartment. This muscle abducts and medially rotates the thigh. It attaches to the iliotibial tract (IT band ), which extends from the liliac crest to the lateral condyle of the tibia.
- 61. One of several maladies that can afflict runners is “IT band syndrome ”.
- 62. Friction of IT band over lateral side of femoral condyle
- 63. Site of pain with IT band syndrome on lateral side of knee
- 64. In my professional opinion, more attention is paid to the rectus abdominis and gluteus maximus muscles than is warranted. They are JUST MUSCLES and do not indicate the intrinsic worth of a person! Ask someone who has been married for more than 10 years how important superficialities are in the long term.
- 65. Head turner?
- 67. The gluteus maximus extends and rotates the thigh laterally at the hip joint while the tensor fasciae latae abducts the thigh at the hip joint. They both insert on the iliotibial tract (IT band) which attaches to the lateral tibial condyle.
- 68. The iliotibial tract extends down the lateral thigh and is easily palpated. It inserts on the lateral tibial condyle. Where it passes over the lateral femoral condyle it can cause friction and pain (IT band syndrome ) in runners.
- 69. An overly tight piriformis muscle can put pressure on the underlying sciatic nerve (piriformis syndrome).
- 70. An overly tight piriformis muscle can cause pressure on the sciatic nerve, resulting in pain or numbness in the leg (piriformis syndrome).
- 71. IF YOU WERE GOING TO PERFORM AN ALLOGRAFT REPLACEMENT OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT, WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING WOULD YOU USE? A SUPERFICIAL FASCIA B EPIMYSIUM C DEEP FASCIA D INSERTION OF TENSOR FASCIA LATAE E PIRIFORMIS
- 72. Most of the massive muscles that move the thigh originate on the pelvic girdle and insert on various places on the femur.
- 73. Chyna , a professional female wrestler, has significant thigh muscles! The anterior thigh muscles shown are the quadriceps femoris muscles.
- 74. The quadriceps femoris muscles act synergistically to extend the leg at the knee (tibiofemoral joint).
- 75. Three of the quadriceps femoris muscles are easily visible on the surface: vastus lateralis, rectus femoris (which runs straight up the middle), and the vastus medialis. Note the qudriceps femoris tendon above the patella and the patellar ligament below the patella.
- 76. The vastus lateralis is a good site for intramuscular (IM) injection of medications.
- 77. Visible on the surface Deep and not visible on surface The quadriceps muscles are actually four muscles that all share a common insertion via the quadriceps femoris tendon onto the patella. This tendinous structure then becomes the patellar ligament
- 78. The vastus intermedius muscle is deep to the other quadriceps muscles and is NOT visible on the surface.
- 79. Rectus femoris muscle Visible muscles and knee structures
- 80. Charles Barkley , a famous basketball player, was forced to end his career when he tore his quadriceps femoris tendon.
- 84. The three major posterior muscles of the thigh help flex the knee and are antagonistic to the quads. They are collectively referred to as the hamstring muscles because of the butcher’s practice of using the tendons of insertion of these muscles to help hang hams on hooks for smoking and curing. All three have same origin.
- 85. Hams being hung via hamstring muscle tendons for smoking and curing
- 86. The biceps femoris muscle has its origin on the ischial tuberosity and linea aspera of femur and inserts on the head of the tibia. It flexes the leg at knee joint and extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint. The tendon of insertion forms the lateral margin of the popliteal fossa .
- 87. #2 is iliotibial tract (IT band) while #1 is the biceps femoris tendon of insertion. This tendon forms the lateral margin of the popliteal fossa. Lateral view of leg at knee
- 88. Both the semitendinosus and the semimembranosus muscles originate on the ishial tuberosity. The semitendinosus inserts on the proximal medial surface of the tibia while the semitendinosus inserts on the medial condyle of the tibia. They both flex the leg at the knee joint and extend and medially rotate the thigh at the hip joint. The tendons of insertion form the medial boundary of the popliteal fossa (the semitendinosus is more superficial).
- 89. semitendinosus semimembranosus The semitendinosus is more superficial Medial view of leg at knee
- 90. The Mongol Hordes would cut the hamstring tendons of their fleeing enemies and then return later to kill them.
- 91. Read clinical view on lower limb muscle injuries in text
- 92. Muscles are found anteriolaterally No muscles are found anteriomedially Leg (crural) muscles
- 93. The deep fascia of the crural region partitions the leg musculature into three compartments (anterior, lateral, and posterior), each with its own nerve and blood supply. Note none anteriorlaterally None anteriorlaterally
- 94. The tibialis anterior muscle originates on lateral condyle and proximal shaft of tibia. The insertion is over the top of the foot onto the first metatarsal and a tarsal bone (cuneiform). The action is to dorsiflex the ankle and invert the foot at the ankle . I had a temporary nerve disorder that prevented me from using this important muscle! Anterior view
- 95. The peroneus (fibularis) longus muscle is located laterally, has its origin on the lateral condyle of the tibia and head and shaft of the fibula, and inserts under the arch of the foot on the first metatarsal and a tarsal bone (cuneiform) to plantar flex and evert the foot at the ankle. It is antagonistic to tibialis anterior. Lateral view
- 96. Note that when Mike Bond inverted his ankle he not only injured his ankle ligaments, he also injured his peroneus longus muscle. He then proceeded to bleed superiorly within the fascial compartment of his peroneus longus muscle!
- 97. The gastrocnemius muscle forms the major portion of the calf of the leg. Its origin is on the non-articular portions of the lateral and medial epicondyles of the femur and it inserts onto the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon. It plantar flexes the foot at the ankle and flexes the knee joint.
- 98. Posterior view The soleus muscle is deeper than the gastrocnemius. It has its origin on the proximal shaft of the fibula and medial border of tibia. Its insertion is the same as the gastrocnemius. Its action is to simply plantar flex the foot at the ankle.
- 99. Gastrocnemius muscle Soleus muscle Achilles tendon The gastrocnemius and soleus are collectively known as the triceps surae.
- 100. Achilles being dipped in the River Styx by his mother, Thetis, to make him invulnerable . Unfortunately, he was still not protected where she had held him by the heel. Later he was killed in battle by an arrow that struck him in the vulnerable heel. This gave rise to describing any area of weakness as an “Achilles heel”.
- 104. Repair of ruptured Achilles tendon
- 105. WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING FLEXES THE TIBIOFEMORAL JOINT? A MUSCLE THAT INSERTS ON CALCANEUS B MUSCLE THAT CREATES LATERAL BORDER OF POPLITEAL FOSSA C MUSCLE THAT CREATES MEDIAL BORDER OF POPLITEAL FOSSA D MUSCLE THAT ORIGINATES ON THE ISCHIAL TUBEROSITY E ALL OF THE ABOVE
- 106. Compartment syndrome can occur with any skeletal muscle when pressure builds up inside its fascial sheath (compartment) because of bleeding or inflammation. The pressure will then compress blood vessels and the entire muscle will die for a lack of oxygen and a lack of energy. The leg shown was kicked in a soccer game. Read the clinical view in the text . Swollen leg Normal leg
- 107. Measuring internal pressure in patient with compartment syndrome
- 108. Decompression fasciotomy is the treatment
- 109. Decompression fasciotomy to treat compartment syndrome
- 110. Delayed closure and skin grafting may be required
- 111. RICE = rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
- 112. The intrinsic muscles of the foot originate and insert within the foot. They support the arches and move the toes to aid locomotion. As was true in the upper extremity, there are no muscles in the digits.
- 113. The plantar surface of the foot is supported by the plantar aponeurosis formed from the deep fascia of the foot. This aponeurosis extends between the phalanges of the toes and the calcaneus.
- 114. Read the clinical view about plantar fasciitis in text
- 116. Muscle fatigue is typically caused by a build-up of lactic acid.
- 117. Muscle strains are usually caused by insufficient warm-up before competing
- 118. Atrophy is the wasting away of muscles that can result from nerve damage, disease, or lack of use. Bone loss will also occur.
- 119. Hypertrophy is an increase in the size of muscle cells, not an increase in the number of cells. It is caused by exercise and conditioning. Increased bone mass also occurs.
- 120. A cramp (Charley horse) is a prolonged and painful involuntary muscle contraction. Typically caused by lactic acid build-up, calcium deficiency, or oxygen deficiency. [It is occasionally called a “Charley horse” in association with a baseball player in the 1800’s who often suffered from muscle cramps.]
- 121. Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disease characterized by gradual atrophy and weakening of the muscles.
- 122. Muscular dystrophy is poorly understood and most children die before the age of 20.
- 231. Decompression fasciotomy of medial compartment in leg
- 270. Posterior view of shoulder
- 274. Plantar fasciitis
- 276. Skeletal muscles attach to the skeleton and use the bones as levers and the joints as fulcra (pivots) so as to accomplish the work of moving against the resistance of gravity.
- 278. Both arms at rest Both arms pushing against a wall
- 281. Figure 12.02
- 284. The teres major is synergistic to the latissimus dorsi muscle while the teres minor is synergistic to the infraspinatus.
- 291. Note that there is fascial compartmentalization of the muscles in the brachium.
- 292. Rupture of the long head of the biceps brachii
- 293. Figure 12.04aa
- 296. Figure 12.07b
- 297. Figure 12.08b
- 298. Figure 12.09
- 299. Figure 12.11b
- 300. Figure 12.11c
- 301. Figure 12.13aa
- 302. Figure 12.p371b
- 303. Figure 12.07a
- 304. Figure 12.07a
- 305. Figure 12.08a
- 306. Figure 12.08a
- 308. Indentation caused by complete rupture of the Achilles tendon
- 311. Figure 13.p411
- 312. Figure 12.17aa
- 313. Figure 12.17b
- 314. Figure 12.18a
- 315. Figure 12.18a
- 316. Figure 12.18b
- 317. Figure 12.20aa
- 318. Figure 12.20b
- 319. Figure 12.21aa
- 320. Figure 12.21b
- 321. Figure 12.22a
- 322. Figure 12.15cb