Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
To investigate Fourier’s Law for the linear conduction of heat along a homoge...

To investigate Fourier’s Law for the linear conduction of heat along a homoge...
Design of machine elements - DESIGN FOR SIMPLE STRESSES

Design of machine elements - DESIGN FOR SIMPLE STRESSES
Solution of numerical problem on boiler performance - Part 2

Solution of numerical problem on boiler performance - Part 2
One dim, steady-state, heat conduction_with_heat_generation

One dim, steady-state, heat conduction_with_heat_generation
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (13)
Thermodynamic Chapter 2 Properties Of Pure Substances

Thermodynamic Chapter 2 Properties Of Pure Substances
Thermodynamic Chapter 3 First Law Of Thermodynamics

Thermodynamic Chapter 3 First Law Of Thermodynamics
Similar to MET 211 Steam tables practice_examples
Similar to MET 211 Steam tables practice_examples (20)
More from Ibrahim AboKhalil
More from Ibrahim AboKhalil (20)
MET 211 Steam tables practice_examples
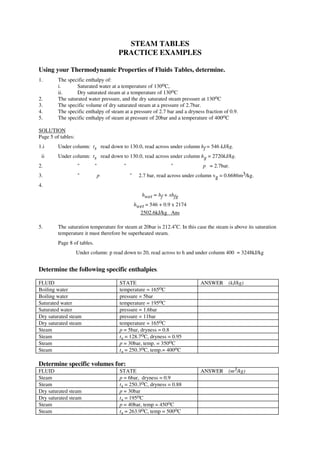
- 1. STEAM TABLES PRACTICE EXAMPLES Using your Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Tables, determine. 1. The specific enthalpy of: i. Saturated water at a temperature of 130oC, ii. Dry saturated steam at a temperature of 130oC 2. The saturated water pressure, and the dry saturated steam pressure at 130oC 3. The specific volume of dry saturated steam at a pressure of 2.7bar. 4. The specific enthalpy of steam at a pressure of 2.7 bar and a dryness fraction of 0.9. 5. The specific enthalpy of steam at pressure of 20bar and a temperature of 400oC SOLUTION Page 5 of tables: 1.i Under column: ts read down to 130.0, read across under column hf = 546 kJ/kg. ii Under column: ts read down to 130.0, read across under column hg = 2720kJ/kg. 2. " " " " p = 2.7bar. 3. " p " 2.7 bar, read across under column vg = 0.6686m3/kg. 4. hwet = hf + xhfg hwet = 546 + 0.9 x 2174 2502.6kJ/kg Ans 5. The saturation temperature for steam at 20bar is 212.4oC. In this case the steam is above its saturation temperature it must therefore be superheated steam. Page 8 of tables. Under column: p read down to 20, read across to h and under column 400 = 3248kJ/kg Determine the following specific enthalpies. FLUID STATE ANSWER (kJ/kg) Boiling water temperature = 165oC Boiling water pressure = 5bar Saturated water temperature = 195oC Saturated water pressure = 1.6bar Dry saturated steam pressure = 11bar Dry saturated steam temperature = 165oC Steam p = 5bar, dryness = 0.8 Steam ts = 128.7oC, dryness = 0.95 Steam p = 30bar, temp. = 350oC Steam ts = 250.3oC, temp.= 400oC Determine specific volumes for: FLUID STATE ANSWER (m3/kg) Steam p = 6bar, dryness = 0.9 Steam ts = 250.3oC, dryness = 0.88 Dry saturated steam p = 30bar Dry saturated steam ts = 195oC Steam p = 40bar, temp = 450oC Steam ts = 263.9oC, temp = 500oC
