Assessing Grammar (Summary ch 1, 8 & 9)
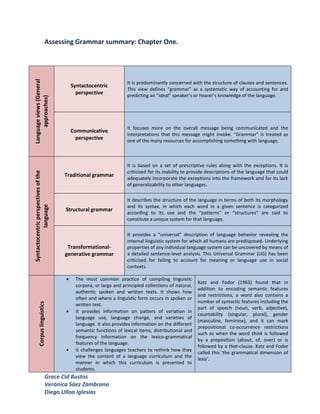
- 1. Assessing Grammar summary: Chapter One. Language views (General It is predominantly concerned with the structure of clauses and sentences. Syntactocentric This view defines “grammar” as a systematic way of accounting for and perspective predicting an “ideal” speaker’s or hearer’s knowledge of the language. approaches) It focuses more on the overall message being communicated and the Communicative interpretations that this message might invoke. “Grammar” is treated as perspective one of the many resources for accomplishing something with language. It is based on a set of prescriptive rules along with the exceptions. It is criticized for its inability to provide descriptions of the language that could Syntactocentric perspectives of the Traditional grammar adequately incorporate the exceptions into the framework and for its lack of generalizability to other languages. It describes the structure of the language in terms of both its morphology and its syntax, in which each word in a given sentence is categorized language Structural grammar according to its use and the “patterns” or “structures” are said to constitute a unique system for that language. It provides a “universal” description of language behavior revealing the internal linguistic system for which all humans are predisposed. Underlying Transformational- properties of any individual language system can be uncovered by means of generative grammar a detailed sentence-level analysis. This Universal Grammar (UG) has been criticized for failing to account for meaning or language use in social contexts. The most common practice of compiling linguistic Katz and Fodor (1963) found that in corpora, or large and principled collections of natural, addition to encoding semantic features authentic spoken and written texts. It shows how and restrictions, a word also contains a often and where a linguistic form occurs in spoken or number of syntactic features including the Corpus linguistics written text. part of speech (noun, verb, adjective), It provides information on patters of variation in countability (singular, plural), gender language use, language change, and varieties of (masculine, feminine), and it can mark language. It also provides information on the different prepositional co-occurrence restrictions semantic functions of lexical items, distributional and such as when the word think is followed frequency information on the lexico-grammatical by a preposition (about, of, over) or is features of the language. followed by a that-clause. Katz and Fodor It challenges languages teachers to rethink how they called this ‘the grammatical dimension of view the content of a language curriculum and the lexis’. manner in which this curriculum is presented to students. Grace Cid Bustos Verónica Sáez Zambrano Diego Ulloa Iglesias
- 2. Context and meaning take precedence over linguistic form. It typically describes features of grammatical form that are used to express Theories of Communication meaning beyond a single, context-free Both have had a Systemic-functional utterance. Rather, grammatical form is seen considerable impact on L2 grammar as having a symbiotic relationship with syllabus design, teaching meaning and pragmatic use, where each and testing, and are influences and shapes the other within and credited for shifting the across utterances. emphasis of language Effective communication is not simply classrooms from a formal perceived as a function of linguistic accuracy grammatical focus to a or acceptable grammar to convey literal and communication-based Speech act theory intended meaning. Communication must be one. appropriate for the context, i.e. speakers must have both ‘linguistic competence’ and ‘communicative competence’. It represents an eclectic, but principled description of the target-language forms, created for the express purpose of helping teachers understand the linguistic resources of communication. Pedagogical grammar These grammars provide information about how language is organized and offer relatively accessible ways of describing complex, linguistic phenomena for pedagogical purposes. The more L2 teachers understand how the grammatical system works, the better they will be able to tailor this information to their specific instructional contexts. Besides formal pedagogical grammars (and, of course, SLA theory), language teachers would be advised to consult language textbooks when put to the task of specifying grammatical content for instruction or assessment. These books not only provide descriptions, albeit less comprehensive, of the target grammar, but they also inform teachers of the scope with which a grammar point might be treated at a particular proficiency level or the sequence with which grammar points might be introduced. Grace Cid Bustos Verónica Sáez Zambrano Diego Ulloa Iglesias
- 3. Assessing Grammar summary: Chapter Nine. Defining grammatical At the moment of assessing grammatical form and meaning in communicative ability language testing, it is relevant to provide teachers and learners with a more complete assessment, taking into account the grammatical ability of the test takers than just Challenge 1 providing information about the form or the meaning. Theoretical challenges It is concerned to language educators who need to make comprehensible distinctions about the definition of between the form and meaning components of grammatical knowledge in terms of grammatical the test purpose in order to integrate these distinctions in construct definition. knowledge Scoring grammatical It is related to scoring form, meaning and grammar assessments and also how ability language teachers need to adapt their scoring procedures to reflect the two dimensions of grammatical knowledge. It requires the use of measurement models to contain dichotomous and partial- credit data in analyzing test scores. In scoring extended-production tasks descriptors, rubrics must be adapted to grade Challenge 2 performance in form and meaning more noticeably. Advantages and “The advantage of using complex performance tasks that are highly authentic is the disadvantages generalizability of the inferences these tasks allow us to make about grammatical ability”.(p.259) The disadvantages are related to the lack of accuracy with which teachers are able to infer what students or test takers know about grammar, taking into other constructs that could be intended or no measured in such tasks by raters. Assessing meanings It is concerned about the meaning and how meaning in a model of communicative language ability can be defined and assessed. The assessment of The primary goal in grammar assessment is to notice if students are able to Challenge 3 meaning in terms of use forms to acquire their basic point across correctly and significantly. If grammatical meaning is construct-relevant, as a result communicative meaningfulness should be scored. meaning and Pragmatic meaning involves an amount of implied meanings that originate pragmatic meaning from context relating to the interpersonal relationship of the interlocutors. The distinctions between grammatical meaning and pragmatic meanings are observable when L2 students fail at the moment of understanding how meanings could be extended or intentionally confusing. Grace Cid Bustos Verónica Sáez Zambrano Diego Ulloa Iglesias
- 4. Reconsidering To design tasks that are authentic and engaging measures of performance, it is grammar-test tasks necessary to consider: It is related to the The assessment purpose and the construct that is going to be measure. design of test tasks To consider the kinds of grammatical performance required in order to Challenge 4 provide evidence in support of the inferences. that are able to After the inferences are specified, it is required to support these claims to measure grammatical design test tasks to measure what students know about grammar or how ability and provide they are able to use grammatical resources to accomplish a wide range of authentic and engage activities in the target language. measures of grammatical performance. Assessing the Ellis (2001) states that grammar scores should be calculated to provide a measure of development of grammatical accuracy and the underlying acquisitional development of L2 students. grammatical ability With limited or extended production tasks. Teachers can give learners credit for and feedback by judging performance on these tasks by means of “The challenge for analytic rating scales. Challenge 5 language testers is to design, score and Rating scales need to be based on construct and task based methods in interpret grammar which the different level of grammatical abilities can be described assessments with a completely. consideration for developmental proficiency” (Pupura, 2005; p. 273) Grace Cid Bustos Verónica Sáez Zambrano Diego Ulloa Iglesias
- 5. Learning-oriented assessment of grammatical ability: Chapter Eight. What is learning-oriented assessment of grammar? In the context of learning grammar learning-oriented assessment of grammar, is believed among the educational assessment experts, that student learning would improve if assessment, curriculum and instruction were more connected. In reaction to conventional test, many experts have been working in new assessments techniques that better elicit students’ outcome and that better connect to classroom goals, curricula and instruction. In this process we find alternative, authentic and performance assessment, all of them seems to be the same, but they have slightly differences. According to Purpura (2004) Alternative assessment encourage assessments in which students are asked to perform or produce meaningful tasks that need both higher level thinking and real world implication. Authentic assessment requires knowledge and skills where can be observed some real life or authentic tasks, to perform these tasks students need some complex and extended production, self-assessment is an important component of these tasks. Performance assessment refers to the evaluation of outcome, which is derived from the observation of more complex tasks that implicates real life situation. Self-assessment is required by making explicit scoring in a rubric. The objective of learning-oriented assessment of grammar is to provide information about the grammar students know, understand or are able to use in different contexts, and the repercussion that this information might have for grammar processing; moreover, teachers can be provided with information about what students feel about learning grammar and about themselves as learners. In terms of method, learning-oriented assessment of grammar believe that assessment must be open to all task types, and this include the use of selected-response, limited-production and complex production tasks that may not involve real-life implication. Finally, learning-oriented assessment is designed to be an integral part of instruction, it can occur at formal or informal situation, at any stage of the learning process. The data can be collected at one point in time or over a period of time. Implementing learning-oriented assessment of grammar. Considerations from grammar testing theory. For implementing learning-oriented assessment of grammar some implications must be consider as design and operationalization, and also test developers need to plan for and specify how assessment will be used to promote further leaning. . Implications for test design: First consideration: in the design stage of a test construction, classrooms teacher need to specify whom we are doing the assignment for, why assessment information is needed and what kind of information (essential information to specify assessment purpose). Second consideration: construct definition. Learning-oriented assessment aims to measure simple or complex constructs depending on both the claim that the assessment is designed to make and the feedback that can result from observation of performance. Third consideration: the need to measure the students’ explicit as well as their implicit knowledge of grammar, but also the students’ implicit or internalized knowledge of the grammar. Implications for operationalization: The learning mandates will affect the specification of test task so can be better to align some characteristics with instructional goals. Learning oriented-assessment of grammar promotes the collection of data on students’ ability and methods in classroom, and also collects information about students’ attitudes and Grace Cid Bustos Verónica Sáez Zambrano Diego Ulloa Iglesias
- 6. feeling toward learning grammar. This data collection can be taken one point in time or accumulated over a period of time. In classroom assessment design, the scoring process results in a written or oral evaluation of candidate responses. At the same time, this provides learners with summative or formative evaluation as for example feedback. Therefore, scoring process allows test-takers to discover themselves, positive and negative evidence on their grammatical ability. The information resulting from achievements test can provide much more meaningful and constructive guidance on what to notice and how to improve. Feedback and scoring method can involve students; this can develop their capacity for self-assessment, and also develop the responsibility of their own learning. Planning for further learning: The test blueprint should include explicit information on how the assessment plans to satisfy the learning mandate. Teachers have many options for presenting assessment results to students. They could present student with feedback, a score for each test component, scoring rubrics, narrative summary of teachers’ observation, etc. Consideration from L2 learning theory In implementing learning-oriented assessment of grammar, teachers need to consider how assessment relates to and can help promote grammar acquisition. This will affect not only what is and how is assessed, but also when in the lesson grammar knowledge are best assessed, and what the results mean for learners to improve. SLA processes – briefly revisited: Research in SLA suggests that learning an L2 involves three simultaneously process: Input processing: relates to how the learner understands the meaning of a new grammatical feature or how form-meaning connections are made. System change: refers to how learners accommodate new grammatical forms to their interlanguage and how this change helps restructure their interlanguage. Output processing: relates to how learners access or make use of implicit grammatical knowledge to produce utterances spontaneously in real time. Assessing for intake: This process is described as the first critical stage of acquisition, as the process of converting input into intake. Students are given a communicative language classroom and are encouraged to use tasks in which they must use language meaningfully and use comprehensible input as an essential component of instruction. Assessing for intake requires learners understand the target forms, but do not produce them themselves. This can be achieved by selected-response and limited-production tasks in which learners need to make form-meaning connections. Assessing to push restructuring: Once input has been converted into intake, the new grammatical feature is ready to be accommodated into the learners’ developing linguistic system. To initiate this process, teaches provide them with tasks that enable them to use the new grammatical forms in decreasingly controlled situations. By attending to grammatical input and by getting feedback learners are able to accommodate the differences between their interlanguage and the target language. Assessing for output processing: Even though learners have showed explicit knowledge of form and meaning of new grammatical points, it does not mean they can access this knowledge automatically in spontaneous communication. Learners need to be able to produce unplanned, meaningful output in real time showing that the grammatical knowledge is already unconscious part of their developing system of language knowledge. Grace Cid Bustos Verónica Sáez Zambrano Diego Ulloa Iglesias
