Dna replication
- 1. Describe the role of DNA in relation to gene expression DNA Replication
- 2. Contents Why replicate? The basics The enzymes Okazaki fragments Fixing errors Review Questions
- 3. Why replicate? DNA replicates before it forms a chromatid. I.e. when it still looks like… Over an organisms life the DNA in the zygote is copied trillions of times with minimal error. Error rates are generally 1 in 50 million Stuff that any respectful Bio student really should know… Mitosis and Meiosis What are they and where they happen! Meiosis Revision exercise When we copy this 100,000,000,000,000 times it turns into this
- 4. Why replicate? www.cellsalive.com Each new cell must have a copy of the entire DNA genome. Some of the DNA released from a single human chromosome
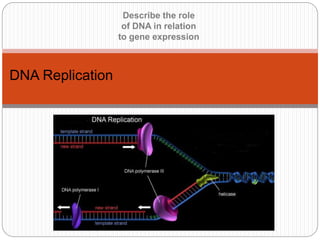
- 5. DNA Replication - the very basics The basics of DNA REPLICATION Unwind – Unzip – Add nucleotides – wind it all back up. If only it could be that simple Two things make it a little more fiddly DNA is a VERY LONG double helix chemical molecule It has a anti-parallel structure
- 6. • DNA Synthesis The DNA bases on each strand act as a template to synthesize a complementary strand • Recall that Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C) The process is semiconservative because each new double-stranded DNA contains one old strand (template) and one newly-synthesized complementary strand DNA Replication A G C T G T C G A C A G C T G T C G A C A G C T G T C G A C A G C T G T C G A C T C G A C A G C T G
- 7. Anti-parallel structure of DNA It’s a long Double Helix
- 8. 8 DNA Replication Begins at origins of replication Two strands open forming Replication Forks (Y-shaped region) New strands grow at the forks Replication Fork Parental DNA Molecule 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ copyright cmassengale
- 9. DNA replication forks Because the DNA chromosome is so long it needs multiple replication forks working at the same time.
- 10. Anti-parallel structure (DNA) This diagram shows a lot of stuff not yet discussed. What you need to understand at this point When the enzyme travels along a strand of DNA it travels in the 3’ to 5’ direction of the original strand DNA Polymerase travels 3’ to 5’ on original/template strand
- 11. 3’ end has a free deoxyribose 5’ end has a free phosphate The enzyme: can only build the new strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction Thus scans the template strand in 3’ to 5’ direction DNA Replication
- 13. Okazaki Fragments An Okazaki fragment is a relatively short fragment of DNA created on the lagging strand. Each Okazaki fragment is joined together by DNA ligase after the primers have been removed. http://www.youtube.com/ Replication animation http://www.youtube.com/ crash course in DNA (summary)
- 14. Semi-conservative replication A simple idea really… S.C.R is simply the formation of two double helix molecules where each molecule contains one of the original strands and one new strand of nucleotides (daughter strand). This helps to minimise the errors made in replication as each molecule contains a copy of the original nucleotide sequence.
- 15. Checking for errors In general, enzymes (DNA polymerases) are extremely accurate. Even so, some DNA polymerases also have proofreading ability; they can remove nucleotides from the end of a strand in order to correct mismatched bases. You don’t need to know the detail in this box. But read it cause it is interesting ;-)
- 16. Review Questions ENZYME FUNCTION Helicase DNA Polymerase III DNA Polymerase I RNA Primase DNA Ligase http://www.biologycorner.com DNA Quizs
- 17. Review Question 2011 NCEA exam – Q1 (b) When DNA is replicated, each of the parent strands acts as a template. Explain why there is a difference in the way in which the parallel strands of DNA are replicated. You may use a labelled diagram to support your answer.
- 18. Review Question What words are hidden under the yellow boxes? Click to show answer Click to show answer Click to show answer Click to show answer
- 19. Review Question Add the 3’ and 5’ labels to the diagram Click for answers
- 20. Review Question – taken from 2008 NCEA Paper