water analysis sop
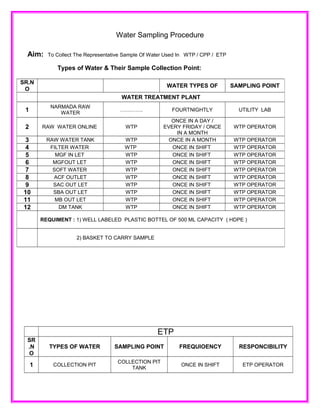
- 1. Water Sampling Procedure Aim: To Collect The Representative Sample Of Water Used In WTP / CPP / ETP Types of Water & Their Sample Collection Point: ETP SR .N O TYPES OF WATER SAMPLING POINT FREQUIOENCY RESPONCIBILITY 1 COLLECTION PIT COLLECTION PIT TANK ONCE IN SHIFT ETP OPERATOR SR.N O WATER TYPES OF SAMPLING POINT WATER TREATMENT PLANT 1 NARMADA RAW WATER …………. FOURTNIGHTLY UTILITY LAB 2 RAW WATER ONLINE WTP ONCE IN A DAY / EVERY FRIDAY / ONCE IN A MONTH WTP OPERATOR 3 RAW WATER TANK WTP ONCE IN A MONTH WTP OPERATOR 4 FILTER WATER WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 5 MGF IN LET WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 6 MGFOUT LET WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 7 SOFT WATER WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 8 ACF OUTLET WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 9 SAC OUT LET WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 10 SBA OUT LET WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 11 MB OUT LET WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR 12 DM TANK WTP ONCE IN SHIFT WTP OPERATOR REQUIMENT : 1) WELL LABELED PLASTIC BOTTEL OF 500 ML CAPACITY ( HDPE ) 2) BASKET TO CARRY SAMPLE
- 2. 2 ETP INLET HOMOGENISATION TANK ONCE IN A DAY ETP OPERATOR 3 BIOLOGICAL BIOLOGICAL TANK ONCE IN A DAY ETP OPERATOR 4 ETP OUT LET SEDIMENTATOR OUT LET ONCE IN A DAY ETP OPERATOR 5 SEWAGE SAMPLE SEWAGE TANK FOURTNIGHTLY ETP OPERATOR 6 SIZING EFFILUENT SIZING DRAIN FOURTNIGHTLY ETP OPERATOR 7 EVAPORATOR FEED TANK EVAPORATOR FEED TANK ONCE IN A DAY ETP OPERATOR 8 EVAPORATOR CIRCULATOR TANK EVAPORATOR CIRCULATOR TANK ONCE IN A DAY ETP OPERATOR REQUIMENT : 1) ) WELL LABELED PLASTIC BOTTEL OF 1000 ML CAPACITY ( HDPE ) 2) BASKET TO CARRY SAMPLE
- 3. POWER PLANT Standard Sampling Procedure SR.NO TYPES OF WATER SAMPLING POINT FREQUIOENCY RESPONCIBILITY 1 DM ONLINE Drain of line ONCE IN SHIFT BOILER FIELD OPERATOR 2 FEED WATER Sample cooler TWICE IN SHIFT BOILER FIELD OPERATOR 3 CPP DM TANK From suction of DM water pump in front of DM Storage tank ONCE IN SHIFT BOILER FIELD OPERATOR 4 SATURATED STEAM Sample cooler TWICE IN SHIFT BOILER FIELD OPERATOR 5 MAIN STEAM Sample cooler TWICE IN SHIFT BOILER FIELD OPERATOR 6 CEP Drain line of GSC discharge at G/F of STG Building TWICE IN SHIFT TURBINE FIELD OPERATOR 7 CST Drain of condensate storage tank ONCE IN SHIFT TURBINE FIELD OPERATOR 8 BOILER WATER Sample cooler TWICE IN SHIFT BOILER FIELD OPERATOR 9 COOLING WATER Sump of cooling tower/Swas panel below STG building ONCE IN SHIFT TURBINE FIELD OPERATOR REQUIMENT : 1) ) WELL LABELED PLASTIC BOTTEL OF 500 ML CAPACITY ( HDPE ) 2) BASKET TO CARRY SAMPLE
- 4. The recommended procedure for collecting water samples is as follows:- 1) The Bottle used should clean and has proper label. ensuring it is strong and durable, so that it will not break in transit and that the cap does not leak once the cap is secured. The laboratory requires a minimum of 500 mL 2) Rinse the bottle at least 4 times with the water to be sampled 3) Rinsed water should be dropped outside away from sampling point 4) Water samples can be taken directly from the main outlet on the supply line. Where the water is used for livestock. 5) Allow the water to run for sufficient time to flush out which has been in the system, then take samples at time intervals of 15 - 20 minutes, from the sample point 6) Fill the bottle to the top, leaving little or no air space and seal tightly with the cap. 7) Ensure the bottle is adequately labeled so it can be identified at all stages of the lab analytical process. 8) If water is pumped from a tank, the sample is not taken from the outlet side of the pump, take the sample from near where suction side of the pump draws water. 9) Note down time of sample received in a lab in sample receipt register ,& Any information relating to plant / field should be given to chemist & chemist should note down in sample receipt register which will assist in the interpretation of the results. 10) Care needs to be taken to ensure the sample given to lab should be in same condition as it was during sampling .Send the sample bottle as soon as possible by Courier to the laboratory. 11) All sample bottles should replace with new bottle after every three month
- 5. PURPOSE : To determine pH in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Method A: pH Meter 1. Apparatus 1.1 Digital pH meter with combined electrode and temperature compensation 2. Reagent pH buffer tablets 4.0, 7.0 & 9.2. Prepare buffer solution by dissolving 1 tablet each separately in 100 ml distilled water and store in clean glass bottles. 3. Procedure 3.1 Calibrate pH meter as per calibration procedure 3.2 Measure temperature of test solution of water/waste water and set temperature knob. Now dip the electrode in solution under test and note the pH value from display.
- 6. PURPOSE : To check Temperature in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Temperature Measurement 1. Apparatus Zeal make mercury in glass thermometer 2. Procedure Collect sample in a plastic bucket and dip the tip of the thermometer, and take the reading of the thermometer after sufficient time till consent reading is achieved.
- 7. PURPOSE : To determine Total Dissolved Solids in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Apparatus 1.1 Evaporation dish of porcelain or glass of capacity 25 ml to 100 ml 1.2 Drying oven capable of maintaining temperature 108 ± 2 o C 1.3 Desiccator – provide with a colour indicating desiccant 1.4 Analytical balance capable of weighing 1 mg 2. Procedure Dry the empty and clean evaporating dish in the oven at 103 o C – 105 o C for about 30 min. Cool the dish in the desiccator. Filter suitable volume of the sample through a filter paper (Whatman No. 42) and transfer 25 ml or suitable measured volume to the previous weighed evaporating dish. Evaporate to dryness first on steam bath and then further dry residue to 103 – 107 o C for one hour or till evaporation . Cool the residue in the desiccator for about 15 minutes and weigh in mg. 3. Calculation W Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), mg/l = ------- x 1000 V
- 8. Where, W= Weight in mg of residue, and V = Volume in ml of the sample taken for the test PURPOSE : To determine Total Suspended Solids in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Apparatus 1.1 Whatman filter paper no. 42 retentive for fine particles / 1.2 Drying oven capable of maintaining temperature 108 ± 2 o C 1.3 Desiccator – provide with a colour indicating desiccant 1.4 Analytical balance capable of weighing 1 mg 2. Procedure Dry the filter paper in the oven at 103 o C – 105 o C for about one hour, cool it in desiccator and weigh. 50 ml sample or aliquot is taken in a measuring cylinder and filter. Apply suction if filtration rate is slow. After filtration is over, wash the cylinder with 10 – 15 ml distilled water and filter. Wash the residue with 20 to 30 ml distilled water and filter. After filtration transfer the filter along with contents to an oven maintained at 105 ± 2 o C for at least 2 hours. Cool in a desiccator and weigh in mg. 3. Calculation W Suspended Solids (SS), mg/l = ------- x 1000 V Where,
- 9. W= Weight in mg of residue, and V = Volume in ml of the sample taken for the test PURPOSE : To determine MIX LIQUOR SUSPENDED SOLID in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Apparatus 1.5 Whatman filter paper no. 42 retentive for fine particles 1.6 Drying oven capable of maintaining temperature 108 ± 2 o C 1.7 Desiccator – provide with a colour indicating desiccant 1.8 Analytical balance capable of weighing 1 mg 2. Procedure 1) Dry the filter paper in the oven at 103 o C – 105 o C for about one hour, cool it in desiccator and weigh. 50 ml sample or aliquot is taken in a measuring cylinder and filter. Apply suction if filtration rate is slow. After filtration is over, wash the cylinder with 10 – 15 ml distilled water and filter. Wash the residue with 20 to 30 ml distilled water and filter. If necessary apply suction to remove traces of water. After filtration transfer the filter along with contents to an oven maintained at 105 ± 2 o C for at least 2 hours. Cool in a desiccator and weigh in mg. 2)Dry the empty and clean evaporating dish in the oven at 103 o C – 105 o C for about 30 min. Cool the dish in the desiccator. Filter suitable volume of the sample through a filter paper (Whatman No. 42) and transfer 25 ml or suitable measured volume to the previous weighed evaporating dish. Evaporate to dryness first on steam bath and then further dry residue to 103 – 107 o C for one hour or till evaporation . Cool the residue in the desiccator for about 15 minutes and weigh in mg.
- 10. 3. Calculation Mass of residue in mg MLSS, mg/l = ----------------------------------- x 1000 Volume in ml of sample MLSS = TOTAL SOLID – TOTAL DISSOLVED SOLID PURPOSE : To determine Settled Sludge Volume SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Apparatus 1.1 Liter graduated cylinder 1.2 Stop watch 2. Procedure Collect little more than 1 lit of mixed suspended solids from aeration tank and pour in the cylinder and fill up to 1 lit mark. Note the time. After ½ hour note down the volume of sludge in the cylinder. 3. Calculation Volume settled sludge x 100 % Settled sludge = ------------------------------------------ 1000
- 11. PURPOSE : To determine Dissolved Oxygen SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Outline of the method O2 present in sample oxidizes the divalent manganous to its higher valency which precipitates as brown hydrate oxide after addition of NaOH & KI. Upon acidification manganese reverts to the divalent state & librates I2 from KI equivalent to DO content in sample. Librated I2 is titrated aga 2. Reagents 2.1 MnSO4 91 gm MnSO4 H2O in 250 ml distilled water. 2.2 Alkali Iodide Azide Solution 125 gm NaOH + 37.5 gm KI + 250 ml DM Water + 2.5 gm NaN3 dissolved in 10ml DM Water 2.3 Conc H2SO4 2.4 Starch Solution Paste 0.5 gm starch in distilled water, pure 100 ml boiling water, stirr and cool. 2.5 Sodium Thioulphate 0.1 N (Stock Solution)
- 12. Dissolve 12.41 gm Na2S2O3 in boiled cooled distilled water, dilute to 500 ml with distilled water. 2.6 Standard Sodium Thiosulphate Solution Dilute 125 ml stock solution to 500 ml with freshly boiled cooled water. 3. Procedure 3.1 Collect sample in BOD bottles. 3.2 Add 2 ml MnSo4+ 2 ml (NaOH+KI+NaN3) solution. It is to be noted that the tip of pipette should be below the liquid level while adding these reagents. Insert stopper immediately. 3.3 Mix well by inverting bottles 2-3 times allow ppt to settled down. 3.4 Add 2 ml Conc. H2SO4, mix well, ppt dissolved. 3.5 Take 100 ml and titrate against std. Na2S2O3 using starch as an indicator.. 4. Calculation 1 Lit 1N (Na2S2O3) = 8 g O2 1 ml 1N (Na2S2O3) = 8 mg O2 1 ml of 0.1N (Na2S2O3) = 0.8 mg O2 1 ml of 0.025 N (Na2S2O3) = 0.2 mg O2 ml of thiosulphate x 0.2 x 1000 DO in mg/l = ---------------------------------------------- ml of sample ml of thiosulphate x 0.2 x 1000 = ---------------------------------------------- 100 = ml of thiosulphate x 2
- 13. PURPOSE : To determine total BOD in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Outline of the method BOD is defined as the amount of oxygen required by microorganism while stabilizing biologically decomposable organic matter in a waste under aerobic conditions. Strong wastes are always diluted, so that demand does not exceed available oxygen Following dilutions are recommended: 0.1 to 1% : Strong trade waste (untreated effluent) 1 to 5% : Raw or settled sewage 5 to 25 % : Secondary treated effluent 25 to 25% : Tertiary treated effluent / Borewell / River water 2. Reagents 2.1 Phosphate buffer 0.85 gm KH2PO4+2.175 gm K2HPO4+3.34 gm Na2HPO47H2O+0.17 gm NH4Cl in 100 ml distilled water . 2.2 Magnesium sulphate 2.25 gm MgSO47H2O in 100 ml distilled water.
- 14. 2.3 Calcium chloride 2.75 gm anhydrous CaCl2 in 100 ml distilled water. 2.4 Ferric Chloride 0.025 gm Fecl36H2O in 100 ml distilled water 2.5 Sodium Sulphate (0.025 N) 0.3938 gm Na2SO3 in 250 ml distilled water. The solution should be prepared freshly before use. 3. Procedure 3.1 Preparation of dilution water 3.1.1 Aerate sufficient water by air pump for 4-6 hrs to attain dissolve oxygen saturation. 3.1.2 Add 1 each ml of Phosphate buffer, Magnesium sulphate, Calcium chloride & ferric chloride for each litre of dilution water 3.1.3 If sufficient bacteria are not present in waste water add seed water to the dilution water generally 2 ml settled sewage is considered sufficient for 1000 ml dilution water. 3.2 Dilution of sample 3.2.1 If required neutralize sample to 7.0 ± 1.0 pH. 3.2.2 Remove residual chlorine if any by Na2SO3 solution as follows : To 50 ml sample add 10 ml 1:1 acetic acid, add 1 g KI. Titrate with 0.025 N Na2SO3 using starch indicator. Calculate the volume of Na2SO3 required per ml of sample to remove residual chlorine and add accordingly to the sample. 3.2.4 Make two dilutions, take test solution accordingly in BOD bottles and fill with dilution water. 3.2.5 Keep 1 bottle for determination of initial DO and incubate 2 bottles. Observe the bottles have a water seal. Incubate at 20 o C for 5 days or at 27 o C in a BOD incubator or in a plastic bucket filled with water 3.2.6 Determine DO in the sample and in the blank on initial day and after 3 days. 4. Calculation Dilution – 1 :
- 15. [DO, sample (1st day- 5th day) – DO, Blank (1st day- 5th day) BOD mg/l = --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- x 100 .. ….A % Dilution Dilution – 2 : [DO, sample (1st day- 5th day) – DO, Blank (1st day- 5th day) BOD mg/l = --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- x 100 .. ….B % Dilution A + B BOD mg/l = --------------- 2 PURPOSE : To determine COD in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Outline of the method COD test determines the oxygen required for chemical oxidation of organic matter with the help of strong chemical oxidant (K2Cr2O7 in presence of H2SO4 to produce CO2+H2O). Excess dichromate remaining after reaction is titrated with ferrous ammonium sulphate. The dichromate consumed gives the O2 required for oxidation of organic matter. 2. Interference HgSO4 added is complexes with chloride to avoid interference of chloride. 3. Reagents 3.1 Standard Potassium Dichromate 0.25 (N) 12.259 gm in 1 lit, add 0.12 gm sulphamic acid. 3.2 H2SO4 Reagent 10.0 gm Ag2SO4 in 1 lit, H2SO4, keep overnight 3.3 Standard Ferrous Ammonium Sulphate 0.1 (n) Dissolve 39.2 gm in 800 ml distilled water, add 20 ml H2SO4 and makeup 1 litre. 3.4 Standardization
- 16. 10 ml K2Cr2O7 in 100 ml distilled water + 30 ml Conc H2SO4 & titrate with ferrous ammonium sulphate using ferroin indicator – calculate normality Volume of K2Cr2O7 FAS (N) = ----------------------------------------------- Volume of ferrous ammonium sulphate 3.5 Ferroin indicator 1.485 gm O phenanthroline, monohydrate and 695 mg FeSO4.7H2O and dilute to 100 ml. 3.6 HgSO4 : AR Grade 4. Procedure Place 0.4 gm HgSO4 in reflex flask. Add 20 ml or aliquot of sample, dilute to 20 ml with distilled water and mix. Add glass beds and 10 ml standard K2Cr2O7. add slowly 30 ml H2SO4 reagent containing Ag2SO4 with swirling. If color is green, take lesser aliquot. Connect condenser and reflux for 2 hours. Cool, wash down condenser. Dilute to 150 ml cool, titrate ferrous ammonium sulfate using ferroin indicator. End point is sharp color change form blue green to wine red. Run blank using distilled water. 5. Calculation (a-b) x N x 8000 COD mg/l = --------------------------- ml of sample Where, a = ml ferrous ammonium sulfate for blank b = ml ferrous ammonium sulfate for sample N = Normality of ferrous ammonium sulfate
- 17. PURPOSE : To determine Chlorides of water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Apparatus a. Glass Burette – 50 ml capacity b. Glass Pipette, Volumetric – 2 ml c. Glass Cylinder, Graduate – 50 ml capacity d. Conical Flask – 250 ml capacity 2. Reagents a. AgNo3 0.0141 N = 1.1975 gm in 500 ml water. b. 0.0141 N NaCl = 0.412 gm in 500 ml water c. Potassium chromate = 5% (W/V) Standardization of AgNo3 Acidify 10 ml 0.0141 N NaCl with dil. H2SO4 solution. Add 4 to 5 drop potassium chromate & titrate against 0.0141 N AgNo3. For 10 ml 0.0141 N NaCl, V2 ml of AgNo3 required. Calculate strength of AgNo3 solution using N1V1 = N2V2 3. Procedure
- 18. Take 50 ml sample, if the pH of solution is beyond 7-8, neutral with dilute solution of sulphuric acid or sodium hydroxide as require. Add 4 to 5 drops potassium chromate. Titrate against 0.0141 N AgNo3. Colour change from yellow to Brick Red. 4. Calculation B.R.x N of AgNo3 x35.46 x 1000 Chloride as (Cl) ppm = -------------------------------------------- Volume of sample Chloride as (CaCO3) ppm = Volume of AgNo3 x 14.1 PURPOSE : To Determine Oil & grease in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. OUTLINE OF METHOD: The determination of oil & grease includes all the substances that are extractable by specified solvent and the results obtained indicates only nonvolatile fraction of these material. Oil, grease and other extractable matters are dissolved in a suitable solvent and separated from the aqueous phase. The solvent layer is then evaporated and residue is weighed as oil & grease. 2. Reagent a. Sulfuric Acid : 1+1 : Add carefully 250 ml conc. H2SO4 to 250 distilled water and cool. b. Petroleum ether / Chloroform: Boiling point 25 to 60 o C. c. Sodium sulfate : Crystal, anhydrous
- 19. 3. Procedure a. Take 250 ml well mixed sample in a measuring cylinder and transfer the sample in a separating funnel. b. Add 1.5 ml sulfuric acid. c. Rinse the empty sample cylinder with 15 ml petroleum ether and add the rinsing to the separating funnel. Add further 25 ml ether to the funnel and shake vigorously for 2 minutes. d. Draw the aqueous phase in to a clear container. e. Filter the ether layer through a filter paper (Whatman No 42) containing sodium sulfate in its core and moistened with petroleum ether, into a treated beaker. f. Continue the extraction of the aqueous layer twice and add the ether extracts to the breaker after passing through sodium sulfate in the filter. g. Evaporate the ether in the beaker on water bath. Dry in oven at 105±2 o C. h. Cool in desiccators and weigh. 4. Calculation mg residue in the beaker Oil & Grease mg/l = --------------------------------------------------- x 100 ml of sample taken for determination
- 20. PURPOSE : To determine Total hardness of water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Apparatus a. Glass Burette – 50 ml capacity b. Glass Pipette, Volumetric – 2 ml c. Glass Cylinder, Graduate – 50 ml capacity d. Conical Flask – 250 ml capacity 2. Reagents a. Buffer Solution : Ammonia buffer solution b. EDTA (0.02N) : 3.72 gm in 1 liter distilled water c. EBT : Pinch of EBT
- 21. 3. Procedure In Conical flask take 50 ml water +1 to 2 ml buffer solution. Add pinch of EBT & Titrate with EDTA (0.02N) normal solution, color changes from red to blue, if the color before titration is blue, titration is not necessary. 4. Calculation Total Hardness (CaCo3) ppm = TV x 20 PURPOSE : To determine Calcium Hardness of water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1. Apparatus A Glass Burette – 50 ml capacity B Glass Pipette, Volumetric – 2 ml C Glass Cylinder, Graduate – 50 ml capacity D Conical Flask – 250 ml capacity 2. Reagents A Indicator : Murexide B EDTA (0.02N) : 3.72 gm in 1 liter distilled water C 1 N Sodium Hydroxide : 40 GM in 100 ml 3. Procedure
- 22. In Conical flask take 50 ml water Add 0.1 to0.2 mg of the Mureoxide indicator and add 2 ml of 1N NaOH Immediately titrate with EDTA (0.02N) normal solution, colour changes from red to blue, if the colour before titration is blue, titration is not necessary. 4. Calculation B.R. X N OF E.D.T.A.X EQ WT OF CaCO3 (50) X 1000 Calcium as PPM CaCO3 = ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ML. OF SAMPLE Magnesium Hardness = Total Hardness – Ca Hardness PURPOSE : To determine Conductivity of water SCOPE : All types water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows PRINCIPAL OF CONDUCTIVITY MEASUREMENT: - A conductivity cell dipped in a measuring solution placed in the inverting input path of an “Operational Amplifier” (Op. Amp.) when an external. Voltage of fixed amplitude and suitable frequency is applied to the system, then for a given feedback resistance, the output voltage is linearly proportional to the conductance of the solution. OPERATING PROCEDURE: - An accurate conductivity measurement is possible with the help of Conductivity meter. A general procedure for an accurate Conductivity measurement is possible with the help of conductivity Meter. A general Procedure for conductivity measurement using any Standard conductivity meter is as follows: 1) Switch on & allow the instrument to warm up. 2) If the instrument is equipped with a manual temperature control, take the temperature of the solution &set the temp. Control to this value. If automatic temp. Compensation probe is available, and then dip the temp. Probe & The conductivity electrode assembly in a water sample contained in a small beaker. 3) Ensure that the conductivity meter is calibrated using buffer solution prior to the conductivity measurement 4) .Read the conductivity of the solution & note down the conductivity reading along with its temp. 5) Remove the electrode etc., rinse in distilled water, & leave standing in distilled water.
- 23. PURPOSE : To determine Silica of water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows SUMMARY OF TEST METHOD: - This test method is based on the reaction of the soluble silica with molybdate ion to from a greenish yellow complex, which in turn is converted to a blue complex by reduction with 1-amino-2-naphthol-1-sulfonic acid. APPARATUS: - Spectrophotometer: - To obtain maximum sensitivity and reproducibility, a spectrophotometer suitable for measurement at 820 nm is required. Measurement may be made at 640 nm with a spectrophotometer. Sample Cell: - The cell size to be used depends on the range covered and the particular instrument used. The higher concentration range should be attainable with 10-mm path length cell. Longer path length cell (40 to50 nm) are recommended for concentration below 0.1 mg/l. REAGENTS: - 1. Amino Napthnol Slulfonilic Acid Solution: - Dissolve 0.5gm of 1-Amino-2-Naphthol-4- Sulfonic acid in 50ml of a solution containing 1gm of Sodium sulfite. (Na2So3) After dissolving, add the solution to100ml of containing 30gm of Sodium Hydrogen Sulfite. Make up to 200ml and store in a dark, plastic bottle. Shelf life of this reagent may be extended by refrigeration.
- 24. Solution should be adjusted to room temperature 25 ± 5ºC, before use. Discard when the Colour darkens or a precipitate forms. 2. Ammonium Molybdate Solution (75gm/L): - Dissolve 75gm of Ammonium Molybdate in 500 ml of distilled water.To 322 ml 10 N sulphuric acid the molybdate solution added gradually with constant stirring The Solution is made upto 1liter 3. Oxalic acid solution (100gm/L): - Dissolve 10gm of Oxalic Acid in 100ml of water. 4. Silica solution standard (1ml = 0.1 mg SiO2): - dissolve 0.473gm of Sodium Metasilicate in water and dilute to 1 liter. PREPARATION OF CALIBRATION CURVE: - 1. Prepare a series of at least four standards covering the concentration range by proper dilution of the standard silica solution. Treat 50ml aliquots of the standard. Prepare a blank using a 50ml aliquot of water that has been similarly treated. 2. Prepare a calibration curve for lower silica(0.02-0.14) measurement at 815 nm by plotting absorbance versus ppm SiO2 on linear graph paper. For higher silica (0.5-2.5) measurements at 640 nm, plot absorbance versus ppm SiO2. PROCEDURE: - 1. Prepare calibration standards by diluting appropriate aliquots of Silica standard stock sol. of 100 ppm, Add 0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0 & 2.5ml. of standard Silica sol. Into 100 ml. volumetric flask and make up to 100ml by DM water. This series of sol. Corresponds contains 0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0 & 2.5 ppm of Silica respectively. 2. Transfer quantitavely 25 ml (or an aliquot dilute to 25 ml) of the sample/standard to a polyethylene or other suitable plastic container and add, in quick succession, 1 ml of the Ammonium Molybdate solution. Mix well. 3. After exactly 5 minutes, add 2 ml of Oxalic acid solution and again mix well. 4. After 1minutes, add 1 ml of Amino-Naphthol-Sufonic Acid Solution. Mix well and allow standing for 10 minutes. 5. Prepare a reagent blank by treating a 25 ml aliquot of water as directed in 1to3. 6. Measure the absorbance of the sample at 820 nm against the reagent blank (or at 640 nm for higher concentration). CALCULATION: - Silica concentration in ppm SiO2 may be read directly from calibration curve at 815 nm. For higher silica measurements made at 640 nm, silica concentration may be read directly in ppm as SiO2 from the calibration curve.
- 25. PURPOSE : To determine P and M Alkalinity of water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows APPARATUS: - Conical flask 250ml., Measuring cylinder 100ml. REAGENTS: - 1. STANDARD H2SO4 0.02N: - Prepare 0.1N H2SO4 by add 2.75ml. Of conc. H2SO4 in little dm water and make up volume to 1 liter with dm water. Take 20ml. 0.1N H2SO4 & dilute to 1000ml. with DM water to prepare standard 0.02N H2SO4. METHOD OF STANDARDIZATION: - Weigh exactly 0.02-1.0gm of dried Sodium Carbonate in a conical flask and dissolve it in little DM water and add 2-3 drops of mixed indicator and titrate with H2SO4 solution to be standardized for the Colour change green to red. Normality of H2SO4 = (Wt. of Na2CO3 * 1000)/vol. of H2SO4 * 53
- 26. PHYNOLPHTHELEIN INDICATOR: - Dissolve 2.5gm of Phenolphthalein in 100ml. Ethyl Alcohol and dilute with DM water to 250ml. Add drop wise 0.02N NaOH till faint pink Colour appears. METHYL ORANGE INDICATOR: - Dissolve 1.0gm Methyl orange indicator in DM water and dilute it to 1.0 liter with Dm water and filter out the undissoved portion. MIXED INDICATOR: - Dissolved 0.3gm Bromocresol Green and 0.2gm Methyl Red indicator in 400ml. Methanol. PROCEDURE: - 1. Take 50 ml sample. 2. Add 2-3 drops of Phenolphthalein indicator. 3. If pink Colour develops titrate with 0.02N H2SO4 Till it disappear B.R. X N OF H2SO4 X EQ WT OF CaCO3 (50) X 1000 P Alkalinity (ppm) as CaCO3 = ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ML. OF SAMPLE . 4. Add 2-3 drops Methyl Orange to the same flask and titrate with 0.02N H2SO4 till it Yellow Colour changes to Orange. B.R. X N OF H2SO4 X EQ WT OF CaCO3 (50) X 1000 M Alkalinity (ppm) as CaCO3 = ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ML. OF SAMPLE
- 27. PURPOSE : To determine Phosphate in Boiler water SCOPE : Boiler water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows PRINCIPAL: - Ammonium molybdate react with phosphate to from molybdophosphoric acid, which is reduced to blue coloured complex ‘molybdenum blue’ by the addition of stannous chloride . REAGENTS: - 1. Ammonium Molybdate Solution: - (a) Dissolve 25gm Ammonium Molybdate in about 175 ml distilled water. (b) Add carefully 310 ml conc. Sulphuric acid to 400ml distilled water and cool. Add (a) & (b) and dilute to 1000ml. 2. Stannous Chloride Solution: - Dissolve 2.5gm – fresh Stannous Chloride in 100ml glycerol and heat in a water bath. Mix by stirring with a glass rod. This reagent is stable and requires no special storage.
- 28. 3. Phosphate Stock Solution (50 ppm): - Dissolve 0.716gm anhydrous Potassium di Hydrogen Phosphate in distilled water and make up to 1000ml in a volumetric flask. Dilute 100ml of solution to 1 litre. 1ml of this solution = 0.05mg of phosphate (as PO4) PROCEDURE: - Important Note: Do not use synthetic detergents containing Phosphate for cleaning of the glassware’s. Use only acid solutions. 1. To the blank, standard and sample add 4.0ml ammonium molybdate solution and 0.5ml stannous chloride solution, mixing after each addition. 2. After 10 minutes but before 12 minutes, measure the Colour using a spectrophotometer at 690nm. (730nm) PURPOSE : To determine Sulfate in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows EDTA METHOD A measured excess of standard barium chloride solution is added to the sample & the excess barium chloride estimated by titration against standard EDTA solution. REAGENTS 1. Approx. 1N nitric acid 2. Standard barium chloride solution 3. pH – 10 buffer solution 4. EBT indicator 5. 0.01 M EDTA solution PROCEDURE
- 29. Neutralize 100 ml of the sample with dilute nitric acid , adding a slight excess, and boil off to expel carbon dioxide. Add 10 ml or more if required, of standard barium chloride solution to boiling solution & allow it to cool. Dilute to 200 ml . mix and allow precipitate to settle. Withdraw 50 ml of the supertant liquid , add 0.5 ml to 1.0 ml of buffer & several drops of indicator solution. Titrate with standard EDTA solution to a blue color which does not change on addition of further drops of EDTA solution. CALCULATION Sulphates, as SO4,mg/l = 9.6 ( 0.1 A + B - 4C ) Where A = Total hardness of sample (as CaCo3 mg/l) B = Volume in ml of standard barium chloride solution added C = Volume in ml of standard EDTA solution required for titration It is very difficult to judge the end point of titration of barium against EDTA using EBT as indicator. It is preferable to use standard MgCl2 solution along with BaCl2 for BaCl2 standardization ( or use a mixture of BaCl2 + MgCl2 solutions, instead of BaCl2 solution for precipitate of sulphate ion). It is also desirable to add MgCl2 solution, whenever sample is low in mg ions as in the case of decationized water. PURPOSE : To determine FMA in SAC outlet SCOPE : SAC outlet RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Determination of Free Mineral Acidity (FMA): - Apparatus: - Burette for standard sodium hydroxide. Conical flask. 100 ml. Graduated cylinder. Reagents: - 0.02N Sodium hydroxide sol.: - Dissolved 4 GMS. AR NaOH pellets in 1 lit. DM water & mix 0.02N (N/50) sodium hydroxide sol.: - Take exactly 200 ml. of 0.1 N NaOH sol.
- 30. & dilute it to lit. by DM water. Screened Methyl orange indicator (SMO) : - Dissolve 0.2 GM. of crystalline methyl orange in a mix. Of 25 ml. Methylated spirits 25-ml. Deionised water. Dissolve 0.28 gm. Xylene cyanol in a mix. Of 25 ml. Metylated spirits 25 ml Deionised water. .Method: - 1. Measure out 50 ml.of the sample & pour into the flask. 2. Add 3 drops of SMO Ind. The sample turns red. 3. Run in 0.02 N NaOH sol. A few drops at a time until the sample turn yellow. FMA (PPM as CaCO3) = Burette reading * 20 CONDUCTIVITY STANDARD SOLUTIONS CONCENTRATION OF POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (KCl) NEEDED TO GIVE REQUIRED CONDUCTIVITY VALUE KCl G/L ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY AT 25 DEG C uS KCl G/L ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY AT 25 DEG C uS 0.0051 10 1.3707 2500 0.0075 15 1.492 2767 0.0373 75 2.789 5000 0.0524 100 4.5848 8000 0.0746 147 5.704 10000 0.0769 150 8.6478 15000 0.1279 250 11.85 20000 0.1543 300 15.7005 25000 0.2591 500 19.055 30000 0.3728 718 25.779 40000
- 31. 0.5331 1000 31.9117 50000 0.7456 1400 49.2096 75000 0.8106 1500 66.5025 100000 1.0663 2000 PREPARATION: KCl WEIGHED ON ANALYTICAL BALANCE AND DISSOLVED IN A VOLUMETRIC FLASK USING DEIONISED WATER PURPOSE : To determine Silica content SCOPE : All type of boiler water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1.0 Determination of Silica Content : REAGENT REQURIED 1) Ammonium molybdate solution for silica estimation : 75 gm of ammonium molybdate is dissolved in 500ml. Of distilled water. To 322ml of 10N sulphuric acid the molybdate solution added gradually with constant stirring. The solution is made upto 1 liter. 2) OXALIC ACID SOLUTION ( 10 % )
- 32. Dissolve 100 gm. Oxalic Acid in 1000 ml by DM Water. 3) AMINO NAPHTHOL SULPHONIC ACID SOLUTION ( ANSA) Dissolve 0.5gm of 1 amino-2napthol-4sulphuric acid and 1 gm sodium sulphite (Na2So3) in 50ml. Distilled water, with gentle warming if necessary, add this to a solution of 30gm sodium metabisulphite (NaHSo3) in 150ml. Distilled water. Filter into plastic bottle. Discard the solution when it becomes dark. Prolong reagent life by storing in a refrigerator. Testing in Spectrophotometer. Sio2 Test: Take 25 ml Sample of water. Add 1 ml Ammonium Molybdate after 5 min add 2 ml Oxalic acid and after 5 min add 1 ml ANSA . After 10 min test in Spectrophotometer. CALIBRATION AND STANDARDIZATION: ALL above solution calibrate & Standardized with MERCK SILICA KIT Take DM water sample and test with Merck Silica Kit & same DM water sample analyzed with newly prepaired silica solution result between deviations should not more than 0.005 PPM Procedure For Merck Kit: 1) Take 10 ml sample in test tube add Reagent si-1 six drops and mix leave it for 3 Min. then add Reagent si-2 six drops add Reagent si-3 1 ml with pipette and mix leave to stand for 10 min ( Reaction time) Then fill the sample into cell and measure in the photometer.
- 33. PURPOSE : To determine IRON by Test Kit SCOPE : All type of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows 1) Take 10 ml Sample in test tube add 6 drops of Reagent Fe – 1 & mix it well 2) Leave the test to stand for 3 min as its reaction time 3) Measure in 50 mm cell in spectrophotometer
- 34. PURPOSE : To determine Turbidity by turbidity meter SCOPE : All type of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Measurement Procedure 1) Place turbidity meter on a flat surface. 2) Place the sample vial inside the sample well and align the vial’s index mark with the meter’s index 3) Push the vial until it is fully snapped in 4) Cover the vial with the light shield cap. 5) Turn on the meter by pressing the ON / OFF key 6) After the power up sequence, the meter goes to measurement mode and the display blinks “—RD—“ for about 10 times
- 35. 7) The measured reading appears in the display 8) If necessary, place the second sample vial into the sample well.Remember to align the marks with the meter’s index mark 9) Press READ/ENTER key. The display blinks “—RD—“ for several times and measured reading appears 10) Repeat steps 2 through 9 for all of your samples. Calibration Procedure :- 1) Place turbidity meter on a flat surface. 2) Insert the CAL 1 standard ( 800 NTU )into the sample well. Aligning the mark on the vial with the mark on the meter . 3) Cover the vial with the light shield cap. PURPOSE : To determine Free Carbon-dioxide SCOPE : All type of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Free carbon dioxide is term used to designate uncombined dissolved gas in water. This terms differentiates the carbon dioxide present in the form of carbonate and bicarbonate ions. Method The method consists of titrating a freshly drawn sample to phenolphthalein indicator end point with standard alkali. Apparatus required 1. Burette 25 – 50ml 2. Graduated Cylinder 100ml 3. Stirrer
- 36. Reagents 1. Standard 0.02N NaOH. 2. Phenolphthalein indicator. Procedure Step 1: Collect the water sample in a glass bottle by allowing the water to flow from bottom Through a rubber tube connected to the source. Step 2: Allow the water to flow to over flow 2 to 3 times the capacity of the bottle and close Immediately without allowing air to enter. Step 3: Siphon sample is graduated cylinder and allow some over flow and quickly adjust the Sample to 100ml volume. Step 4: Add 0.25 to 0.5 ml of indicator solution i.e. 5 to 10 drops. Step 5: Titrate with standard solution of NaOH while stirring with rod until the color persists For five minutes Calculation : V X N X 44000 Free Carbon dioxide = ------------------------------ V = Vol of NaOH (as CO2) Vol .Of Sample N = Normality of NaOH PURPOSE : To determine Free Residual Chlorine in Water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Reagents: TestCHLOR sol. Procedure: In a Nessler tube take 5 ml. of Testchlor sol. & 45 ml. of Water sample under test. Mix quickly & thoroughly & wait for 1 min. & compare the colour with the colour indication marked on the TestCHLOR bottle
- 37. PURPOSE : To determine Sodium (Na) in water SCOPE : All types of water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows REAGENTS: 1) Standard Sodium sol. 2) Sodium / Potassium free water (Distilled or MB water) PROCEDURAL DETAILS: Principle :
- 38. Flame photometry is concerned with the emission of characteristic radiation in flames by individual elements & the co- relation of the emission intensity with the conc. Of the elements. A small volume of the sol. Of the sample is placed in a cup of atomizer. Air & a combustible gas are fed to the atomizer at controlled rates of flow & the sol. is vaporized in a special burner. At the high temp. Of flame, the salts vaporize & dissociate into the constituent atoms or radicals. The vapors of the metal atoms are then exited by thermal energy of the flame. The thermally exited atoms radiate their characteristics special color, the intensity of which is a relative measure of the metal in sol. Suitable instruments measure this intensity. 1) Adjust the sensitivity control to the desired sensitivity. 2)Turn the compressor ON, then turn the gas supply ON & light the gas at the burner. 3)Adjust the air supply till a blue flame is obtained. 4)Charge the small sample in beaker with sodium free water & place it in position. MB water is sodium free water. 5) Do fine adjustment of air supply so that the blue conc. of the flame just forms separate cones, one to each burner hole 6) Calibrate flame photometer using lower and higher standard solutions. First take higher std. Solution place it in position and follow the instructions displayed on LCD panel. Remove the std solution and place the MB water for cleaning of the capillary. Then place lower std. (eg. 1 ppm Na). Remove the std solution and place the MB water for cleaning of the capillary. System is now calibrated and ready for measurement. 7) After calibration, Place the sample sol. & note the reading on display PURPOSE : To determine Residual Hydrazine in water SCOPE : Feed water RESPONSIBILITY : Chemist cum Attendant DESCRIPTION : As follows Reagent Required 1) 1 : 9 HCl : - 10 ml HCl in Volumetric Flask and make up with DM Water. 2) 1,4 dimethyl amino Benzaldehyde Solution A :- 45 ml HCl dissolve in 100 ml DM Water i.e. 145 ml
- 39. Solution B :- 7.5 gm 4 dimethyl amino Benzaldehyde dissolve In 250 ml DM Water . Then ADD Sol A + Sol B Procedure :- Take 50 ml Sample add 5 ml HCl (1:9) , 5 ml dimethyl amino Benzaldehyde and Mix well and put stand for 10 min ( Reaction time ) Note down the absorbance on 450 nm in 10 mm cuvette Calculation :- PPM = ABS x FACTOR
