Kingdom Protista: Diverse Eukaryotes Beyond Plants, Animals, Fungi
- 2. Protists, What are they? Protists are defined by what they are NOT… Eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi Scientists believe they were the “1st eukaryotic organisms” Most are unicellular (algae exception) Many are “aquatic” Very diverse kingdom
- 3. Protists and the Evolutionary Tree
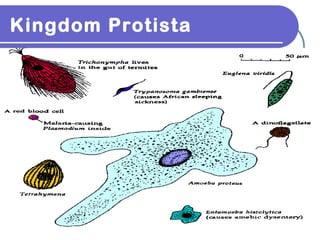
- 4. Animal-like Protist Heterotrophic organisms Distinguished by how they move : 1) flagella: long “tail-like” structure 2) pseudopods: “false feet” extensions of cytoplasm 3) cilia: tiny “hair-like” structures beat in unison 4) some immobile
- 5. Sarcodines Animallike protists use pseudopods for feeding and moving Ex) Amoeba Food
- 6. Ciliates Animallike protists use cilia for feeding and movement Ex) Paramecium
- 7. Zooflagellates Animallike protists swim using flagella Trypanosoma protist spread by the bite of tsetse fly causes African Sleeping Sickness Giardia can contaminate water and cause digestive problems Trichonympha lives in mutualistic relationship with termites
- 8. Sporozoans Animallike protists that do not move on their own and are parasitic Plasmodium sporozoan causes malaria Sporozoan parasite is carried by female Anopheles mosquito
- 9. Plasmodium Life Cycle Mosquito bites human parasite injected • Parasites invade liver reproduce and develop • Liver cells burst and parasites move red blood cells • RBC burst person experiences anemia, fever, chills, may result in death • Parasites may then move into other RBC or are picked up by mosquito and transferred to another person
- 10. Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae Photoautotrophs- contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis Often called “phytoplankton”- small photosynthetic organisms near the surface of ocean Phytoplankton carries out photosynthesis releasing oxygen into the atmosphere Phytoplankton important food source for many “filter feeders”
- 11. Euglenophytes Plantlikeprotists that have flagella chloroplast, but no cell wall. Ex) Euglena
- 12. Diatoms Produce thin, delicate cell walls made of silicon Used in toothpaste, paints on license plates, dynamite
- 13. Plantlike Protists: Algae Red Algae- mostly multicellular algae contains special pigments that allows it to live deep areas of water Brown Algae- all multicellular and most are found in marine environments (ex: Kelp)
- 14. Plantlike Protists: Algae Green Algae- some are unicellular, some form colonies, few are multicellular Volvox Chlamydomona s Sea Lettuce
- 15. Humans and Algae • Humans understand many beneficial uses of algae: 1) Used to make nutrient agar 2) Used as ingredient in ice cream, pudding, salad dressing, syrups 3) Food source – humans and other animals 4) Releases oxygen from photosynthesis • Algae causes harm in “algal blooms” – depletes water of nutrients and oxygen
- 16. Funguslike Protists Heterotrophic protists that absorb nutrients, but lack cell walls with chitin Ex) Slime molds- found near moist, rotting logs and composts Ex) Water molds – can be parasitic and cause “ick” in fish