Ic fab
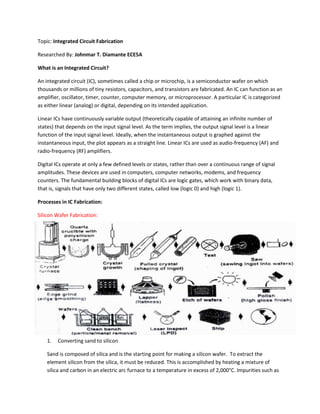
- 1. Topic: Integrated Circuit Fabrication Researched By: Johnmar T. Diamante ECE5A What is an Integrated Circuit? An integrated circuit (IC), sometimes called a chip or microchip, is a semiconductor wafer on which thousands or millions of tiny resistors, capacitors, and transistors are fabricated. An IC can function as an amplifier, oscillator, timer, counter, computer memory, or microprocessor. A particular IC is categorized as either linear (analog) or digital, depending on its intended application. Linear ICs have continuously variable output (theoretically capable of attaining an infinite number of states) that depends on the input signal level. As the term implies, the output signal level is a linear function of the input signal level. Ideally, when the instantaneous output is graphed against the instantaneous input, the plot appears as a straight line. Linear ICs are used as audio-frequency (AF) and radio-frequency (RF) amplifiers. Digital ICs operate at only a few defined levels or states, rather than over a continuous range of signal amplitudes. These devices are used in computers, computer networks, modems, and frequency counters. The fundamental building blocks of digital ICs are logic gates, which work with binary data, that is, signals that have only two different states, called low (logic 0) and high (logic 1). Processes in IC Fabrication: Silicon Wafer Fabrication: 1. Converting sand to silicon Sand is composed of silica and is the starting point for making a silicon wafer. To extract the element silicon from the silica, it must be reduced. This is accomplished by heating a mixture of silica and carbon in an electric arc furnace to a temperature in excess of 2,000°C. Impurities such as
- 2. iron, aluminum, boron and phosphorous also react to give their chlorides, which are then removed by fractional distillation. During the reaction, silicon is deposited on the surface of an electrically heated ultra-pure silicon rod to produce a silicon ingot. 2. Creating a cylindrical crystal To turn it into a usable material, the silicon must be turned into single crystals that have a regular atomic structure. This transformation is achieved through the Czochralski Process. Electronic-grade silicon is melted in a rotating quartz crucible and held at just above its melting point of 1,414°C. 3. Slicing the crystal into wafers Integrated circuits are approximately linear, which is to say that they're formed on the surface of the silicon. To maximize the surface area of silicon available for making chips, the silicon ingot is sliced up into discs called wafers. The wafers are just thick enough to allow them to be handled safely during semiconductor fabrication. 300mm wafers are typically 0.775mm thick. Sawing is carried out using a wire saw that cuts multiple slices simultaneously, in the same way that some kitchen gadgets cut an egg into several slices in a single operation. 4. Making a patterned oxide layer The wafer is heated to a high temperature in a furnace. The wafer is spun in a vacuum so that the photoresist spreads out evenly over the surface before being baked dry. The wafer is exposed to ultraviolet light through a photographic mask or film. The next stage is to develop the latent circuit image. The photoresist isn't sufficiently durable to withstand the hot gasses used in some steps, but it is able to withstand hydrofluoric acid, which is now used to dissolve those parts of the silicon oxide layer where the photoresist has been washed away. Finally, a solvent is used to remove the remaining photoresist, leaving a patterned oxide layer in the shape of the required circuit features. Wafer Testing: Wafer testing is a step performed during semiconductor device fabrication. During this step, performed before a wafer is sent to die preparation, all individual integrated circuits that are present on the wafer are tested for functional defects by applying special test patterns to them. The wafer testing is performed by a piece of test equipment called a wafer prober. Wafer Mounting: To facilitate the processing of the wafer at wafer saw, support is provided to the wafer by mounting the wafer on dicing tape. The dicing tape is a PVC sheet typically 3 mm in thickness with synthetic adhesive on one side to hold both the wafer frame and the wafer.
- 3. Dicing or Wafer Sawing: Wafer saw follows wafer mounting and is the step that actually cuts the wafer into individual dice for assembly in IC packages. The wafer saw process consists of the following steps: 1. The frame-mounted wafer is automatically aligned into position for cutting; 2. The wafer is then cut thru its thickness according to the programmed die dimensions using a resin-bonded diamond wheel rotating at a very high rpm; 3. The wafer goes through a cleaning process using high pressure DI water sprayed on the rotating wafer and then dried by air-blowing. Die Bonding or Die Attach: Die Bonding is the process of attaching the silicon chip to the die pad or die cavity of the support structure of the semiconductor package. These are the two common die attach processes: 1. Adhesive Die Attach - uses adhesives such as polyimide, epoxy and silver-filled glass as die attach material to mount the die on the die pad or cavity. The adhesive is first dispensed in controlled amounts on the die pad or cavity. The die for mounting is then ejected from the wafer by one or more ejector needles. While being ejected, a pick-and-place tool commonly known as a 'collet' then retrieves the die from the wafer tape and positions it on the adhesive. 2. Eutectic Die Attach - is commonly employed in hermetic packages, uses a eutectic alloy to attach the die to the cavity. A eutectic alloy is an alloy with the lowest melting point possible for the metals combined in the alloy. The Au-Si eutectic alloy is the most commonly used die attach alloy in semiconductor packaging. Wire Bonding: Wire bonding is the process of providing electrical connection between the silicon chip and the external leads of the semiconductor device using very fine bonding wires. The wire used in wire bonding is usually made either of gold (Au) or aluminum (Al), although Cu wire bonding is starting to gain a foothold in the semiconductor manufacturing industry. These are the two common wire bonding processes: 1. Gold ball wire bonding - a gold ball is first formed by melting the end of the wire through electronic flame-off (EFO). The free-air ball is then brought into contact with the bond pad. Adequate amounts of pressure, heat, and ultrasonic forces are then applied to the ball for a specific amount of time, forming the initial metallurgical weld between the ball and the
- 4. bond pad as well as deforming the ball bond itself into its final shape. The wire is then run to the corresponding finger of the lead frame, forming a gradual arc or "loop" between the bond pad and the lead finger. Pressure and ultrasonic forces are applied to the wire to form the second bond, this time with the lead finger. 2. Aluminum wedge wire bonding - a clamped aluminum wire is brought in contact with the aluminum bond pad. Ultrasonic energy is then applied to the wire for a specific duration while being held down by a specific amount of force, forming the first wedge bond between the wire and the bond pad. The wire is then run to the corresponding lead finger, against which it is again pressed. The second bond is again formed by applying ultrasonic energy to the wire. The wire is then broken off by clamping and movement of the wire. Molding or IC encapsulation: Molding is the process of encapsulating the device in plastic material. Transfer molding is one of the most widely used molding processes in the semiconductor industry because of its capability to mold small parts with complex features. In this process, the molding compound is first preheated prior to its loading into the molding chamber. After pre-heating, the molding compound is forced by a hydraulic plunger into the pot where it reaches melting temperature and becomes fluid. The plunger then continues to force the fluid molding compound into the runners of the mold chase. These runners serve as canals where the fluid molding compound travels until it reaches the cavities, which contain the lead frames for encapsulation. Plating or Lead Finish: Plating or Lead Finish is the process of applying a coat of metal over the leads of an IC to protect the leads against corrosion, protect the leads against abrasion, improve the solderability of the leads and improve the appearance of the leads. These are the two widely used lead finish techniques in the semiconductor industry: 1. Tin plating - is a form of pure metal electroplating, which is the process of depositing a coating of metal on a surface by passing a current through a conductive medium, or electrolyte. 2. Solder plating - is a form of alloy plating. An alloy is composed of at least two elements, at least one of which is a metal. An alloy has better properties than its component metals: it is harder, more corrosion-resistant, has better solderability and better appearance.
- 5. Marking: Marking is the process of putting identification, traceability, and distinguishing marks on the package of an IC. The device name, company logo, date code, and lot id are examples of information commonly marked on the IC's package. Some marks are put on the package during Assembly and some marks are put on the package during Test. These are the two common marking processes: 1. Laser marking - as the name implies, refers to the process of engraving marks on the marking surface using a laser beam. There are many types of lasers, but the ones used or in use in the semiconductor industry include the CO2 laser, the YAG laser, and diode lasers. 2. Ink marking - consists of transferring an ink pattern from the plate, which is a flat block with pattern depressions that are filled with ink, to the package, using a silicone rubber stamp pad. Silicone rubber repels ink, making the transfer of the ink pattern clean and efficient. It is also resilient and elastic, making it possible to print even on uneven surfaces. Deflash/ Trim & Form /IC Singulation: Deflash - removal of flashes from the package of the newly molded parts.. Flashes are the excess plastic material sticking out of the package edges right after molding. Trim - cutting of the dambars that short the leads together. Form - forming of the leads into the correct shape and position. Singulation - cutting of the tie bars that attach the individual units to the lead frame, resulting in the individual separation of each unit from the lead frame. IC testing: In this process, the IC’s are checked by an IC tester for physical and electrical defects. Defective IC’s are retested by the previous processes to ascertain the cause of the defects.
