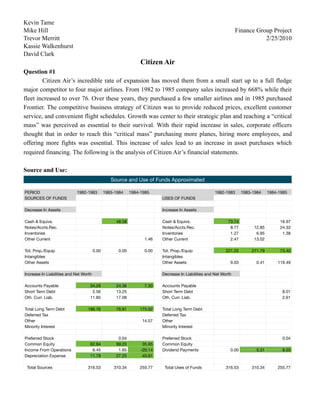
Citizen Air/People Express Final
- 1. Kevin Tame Mike Hill Finance Group Project Trevor Merritt 2/25/2010 Kassie Walkenhurst David Clark Citizen Air Question #1 Citizen Air’s incredible rate of expansion has moved them from a small start up to a full fledge major competitor to four major airlines. From 1982 to 1985 company sales increased by 668% while their fleet increased to over 76. Over these years, they purchased a few smaller airlines and in 1985 purchased Frontier. The competitive business strategy of Citizen was to provide reduced prices, excellent customer service, and convenient flight schedules. Growth was center to their strategic plan and reaching a “critical mass” was perceived as essential to their survival. With their rapid increase in sales, corporate officers thought that in order to reach this “critical mass” purchasing more planes, hiring more employees, and offering more fights was essential. This increase of sales lead to an increase in asset purchases which required financing. The following is the analysis of Citizen Air’s financial statements. Source and Use: Source and Use of Funds Approximated PERIOD 1982-1983 1983-1984 1984-1985 1982-1983 1983-1984 1984-1985 SOURCES OF FUNDS USES OF FUNDS Decrease In Assets Increase In Assets Cash & Equivs. 48.58 Cash & Equivs. 73.74 16.97 Notes/Accts.Rec. Notes/Accts.Rec. 8.77 12.85 24.33 Inventories Inventories 1.27 6.95 1.38 Other Current 1.46 Other Current 2.47 13.02 Tot. Prop./Equip 0.00 0.00 0.00 Tot. Prop./Equip 221.25 271.79 73.40 Intangibles Intangibles Other Assets Other Assets 9.03 0.41 119.49 Increase In Liabilities and Net Worth Decrease In Liabilities and Net Worth Accounts Payable 34.28 24.36 7.30 Accounts Payable Short Term Debt 2.56 13.25 Short Term Debt 8.01 Oth. Curr. Liab. 11.85 17.08 Oth. Curr. Liab. 2.61 Total Long Term Debt 186.76 78.91 175.92 Total Long Term Debt Deferred Tax Deferred Tax Other 14.57 Other Minority Interest Minority Interest Preferred Stock 0.04 Preferred Stock 0.04 Common Equity 62.84 99.23 35.85 Common Equity Income From Operations 6.45 1.65 -20.14 Dividend Payments 0.00 5.31 9.55 Depreciation Expense 11.79 27.25 40.81 Total Sources 316.53 310.34 255.77 Total Uses of Funds 316.53 310.34 255.77
- 2. According to the Source and Use statement most of Citizen’s financing was accomplished by longterm debt and the issuing of common stock. One major problem that Citizen Air faces is that by financing expansion with long term debt they are increasing their interest expense significantly while not increasing their operating income. As a result the have a negative interest burden and are paying double the amount of their operating income to pay their interest expense. On top of all their interest expense issues the company’s debt is becoming current and they have to decided to stretch out their suppliers by delaying payment to their accounts payable in order to fund their short term cash needs. Citizen Air was not always in their current financial predicament. In 1983, they had their highest percentage of cash and a high percentage of property and equipment which made them asset rich. If they had put available funds into growing the company at a moderate pace they would not be in the financial crisis they are in. Dupont Analysis: Dupont Analysis Dupont Analysis Margin X Turnover = ROI / Leverage = ROE Price of Stock NI/Sales Sales/TA NI/TA (1 - TD/TA) NI/Equity 1982 0.39% 1.09 0.42% 61.50% 1.10% 21.12499798 1983 2.25% 0.69 1.55% 75.48% 6.33% 20.87499677 1984 0.28% 0.92 0.26% 70.09% 0.86% 10.1249995 1985 -2.17% 1.10 -2.38% 75.05% -9.55% 9.125 Tax Interest Burden Burden Margin Turnover Leverage ROE NI/EBT EBT/EBIT EBIT/Sales Sales/TA TA/Equity 1982 53.99% 8.17% 8.83% 1.09 2.60 1.10% 1983 58.92% 49.04% 7.79% 0.69 4.08 6.33% 1984 -13.14% -45.90% 4.66% 0.92 3.34 0.86% 1985 99.60% -49.34% 4.42% 1.10 4.01 -9.55% The Dupont Analysis shows that the margin has decreased to -2.17% even though sales have increased by 668%. This is a bad sign and much of the companies problems in this area can be attributed to the interest burden that they are facing. Turnover on the other hand has fluctuating slightly but for the most part has stayed fairly consistent. This is due to the fact that sales are increasing at a fairly even rate compared to the company’s assets. The ROI is taking a hit because Net Income is suffering drastically because the operating income cannot cover the interest expense the firm is incurring. The company is highly leveraged and as a result interest expense is high. In the end the ROE has decreased from a high of 6.33% to -9.55%. The firm is loosing money and has no return on equity and the stock price is starting to show signs of weakness. The decrease in stock price from 1983-1984 is a result of the stock being split but the overall trend in price is still down.
- 3. Altman Test: Altman Test Ratios 1982 1983 1984 1985 Liquidity -0.0093 0.1055 -0.0637 0.0151 Cummulative Profitability -0.2183 -0.1005 -0.0880 -0.0926 Earning Power of Assets 0.3177 0.1773 0.1413 0.1600 Leverage 1.3021 0.7965 0.2888 0.2105 Activity 1.0888 0.6887 0.9184 1.0963 Z Value (weighted sum) 2.4810 1.6675 1.1968 1.3893 The major benefit to the Altman test is its ability to show the likelihood of a firm to go bankrupt. If a firm has a “Z” score to 3.0, or greater, it is almost certain to be in the non-bankrupt category. If the score is below 2.0 then it has a very high probability of becoming bankrupt. Between 2.0 and 3.0 firms may go either way. The “Z” score for Citizen Air decreases over the years and falls way below what is acceptable. This analysis shows that Citizen is most likely going to go bankrupt. Internal and External Growth: Growth Rates 4 Year Weighted 1982 1983 1984 1985 Average Internal Growth Rate 0.40% 1.60% -0.60% -3.40% -0.10% Sustainable Growth 1.10% 6.80% -1.90% -12.30% -0.50% The internal growth rate and sustainable growth rate of the firm has drastically decreased from 1982-1985. The problem with sustainable growth is a direct result of a decrease in ROE and an increase in dividend payout. Since the plowback ratio is increasing and ROE is dropping below zero the sustainable growth of the firm is -12.3% in 1985. This is the same case with the internal growth. ROI is decreasing below zero and the plowback is increasing. Paying a dividend with a negative ROI and ROE is going to yield a non sustainable company. Question #2 The initial growth the Citizen Air saw was a result of carefully selecting routes that were not main stream. It was not until Citizen grew so rapidly that they were forced to compete with the large companies on routes that had been flown by them for over 20 years. Airlines, such as Northwest with deep pockets, cut cost and increased the number of available flights in order to protect their stake in their bread and butter routes. This made it hard for Citizen to compete in the highly successful areas. Citizen still hung strong to the belief that they needed to expand but was not in any position to continue their growth at that time. On top of pressure from other competitors, American Airlines eventually announced it’s Ultimate
- 4. Super Saver plan and put even greater strain on Citizen Air. At that point management felt they only had two options to battle their decreasing loss of market share. One possibility was to develop new hubs, thereby finally achieving a competitive nationally comprehensive route system, or by buying another airline. The second option was to break off the battle, sell aircraft to raise cash, and invest in the further development of the Newark hub, build a computerized reservation system and create a yield management system. Since growth is center to their philosophical business strategy, Citizen Air did not like the idea of downsizing and choose the option to purchase Frontier Airlines. They felt that they could successfully integrate the service of Frontier into their own. However, the purchase of Frontier only added to their problems. First of all, Citizen Air was structured as a single ticket option at a low cost where Frontier was a traditional airline with business class and varied ticket price. This established system that Frontier had is in contradiction with Citizen Air’s business structure. For one thing Frontier is highly unionized while Citizen Air is not. Problems also arose with culture integration and general operations, and Frontier eventually became a drain on Citizen Air’s funds. With growth comes many benefits and so comes its costs. For Citizen Air, their employees were overworked and were starting to have family problems, become ill, and feel burned out. On top that Customers were starting to become frustrated with Citizen Air’s facilities, and the problem of overbooking. Citizen was trying to fit 1,000,000 people a month into a facility that could only handle 100,000. As a result, flights were cancelled, delayed and customers had to wait for hours in uncomfortable conditions. The fact is that Citizen Air could not expand and needed to focus on the problems it already had such as facilities, customer dissatisfaction, and high amounts of debt. However, they choose to purchase Frontier. This combination of a highly volatile financial situation, customer decline, and a threat of competitors ultimately will be the destruction of Citizen Air. At this point, they need significant financing in order to continue growth. It is difficult to imagine where this financing will come from. If they take out any more loans their interest expense will skyrocket even more then it already is. They cannot turn to stretching their suppliers anymore because they are most likely already upset. The use of accounts payable to fiance growth is a short term and dangerous approach. The truth is market share has already been lost and is going to continue to be lost. Citizen’s sustainability is now the real question at hand. They should not be concerned about losing their market share but should be concerned about survival. Question #3 (see also Decision tree on next page) The first step in improving the situation would be to stop any dividends payments. Next, selling of Frontier, if at all possible, will alleviate the financial and cultural strain that is causes. This was a poor purchase to begin with and if it can be sold quickly then their might be a chance of potential turn around. Next, making overall operations more efficient would help lower cost. The problem of over booking and unsatisfied customers will eventually lead to failure. Finally, the last step is downsizing. Slow down the growth and let the company get back on its feet. Ultimately, these solutions are not guaranteed and Citizen Air’s situation might be beyond the point of no return.
- 6. Ratios Based On Year End Data Period 1982 1983 1984 1985 4 Year DuPont Ratios Return On Investment 0.40% 1.60% 0.30% -2.40% -0.50% Return On Equity 1.10% 6.30% 0.90% -9.50% -2.20% Profit Margin 0.40% 2.30% 0.30% -2.20% -0.30% Total Asset Turnover 1.09 0.69 0.92 1.10 96.20% Leverage Ratio (TD/TA) 61.50% 75.50% 70.10% 75.10% 72.30% Income Ratios Tax Burden 54.00% 58.90% -13.10% 99.60% 53.10% Interest Burden 8.20% 49.00% -45.90% -49.30% -22.90% Degree of Fin Leverage 12.24 2.04 -2.18 -2.03 16.80% Operating Margin 8.80% 7.80% 4.70% 4.40% 5.60% Cash Flow To Common Eq. 0.16 0.18 0.12 0.07 11.80% Interest Coverage 1.09 1.96 0.69 0.67 97.50% Total Dividend Payout 0.00% 0.00% 322.40% -47.40% 77.70% Common Dividend Payout 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% -19.40% -7.80% Effective Tax Rate 46.00% 41.10% -2.00% 0.40% 12.40% Asset Ratios Fixed Asset Turnover 1.28 0.95 1.09 1.58 1.28 Degree of Op Leverage 1.70 0.05 1.78 1.07 Acc. Depr As % Gross Plant 7.89% 6.54% 7.91% 12.40% 9.43% Acc Depr/Depr Exp (Asset Age) 1.26 1.79 1.70 2.03 1.81 Current Asset Turnover 7.92 2.76 6.67 7.18 6.22 Current Ratio 0.95 1.54 0.72 1.09 1.06 Ouick Ratio 0.91 1.52 0.65 1.00 0.99 Accounts Recievable Turnover 48.08 24.58 23.95 19.00 24.51 Accounts Recievable Collection 7.59 14.85 15.24 19.21 15.99 Inventory Turnover (Sales) 229.52 153.01 66.50 90.91 109.87 Inventory Turnover (COGS) 159.13 105.86 48.67 65.49 77.88 Cash Turnover 31.65 109.25 23.14 21.31 40.48 Working Cap Turnover 309.25 286.84 113.58 131.23 174.86 Leverage Ratios Assets to Equity 2.60 4.08 3.34 4.01 3.68 Current Debt To Total Debt 23.64% 21.42% 27.25% 18.69% 22.30% A/P Turnover (COGS) 25.34 75.40 55.52 39.66 50.13 A/P Turnover (Purchases) 74.92 54.63 39.57 47.20 LTD to Assets 47.00% 59.30% 51.00% 61.00% 56.27% Net Debt Repay Ability (Yrs) 8.33 12.50 14.20 28.08 18.83 Funded Debt to Capital 55.00% 70.80% 63.00% 71.00% 66.95% Preferred to Capital 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Common Eq. To Capital 45.00% 29.20% 37.00% 29.00% 33.05% LTD To Equity 1.22 2.42 1.71 2.45 2.10 Altman Ratios Working Capital/T. Assets -0.78% 8.79% -5.31% 1.26% 0.59% RE/TA -15.60% -7.18% -6.28% -6.61% -7.53% EBIT/TA 9.63% 5.37% 4.28% 4.85% 5.26% Mkt Value Eq/Book Value TD 217.02% 132.75% 48.13% 35.09% 76.73% Sales/TA 108.99% 68.94% 91.93% 109.74% 96.16%
- 7. Common Size Income and Balance Sheet (as a percent of Sales) INCOME STATEMENT 4 Year PERIOD 1982 1983 1984 1985 Weighted Fiscal Year Ends Average Sales 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% Cost of Goods Sold 69.30% 69.20% 73.20% 72.00% 71.50% Gross Margin 30.70% 30.80% 26.80% 28.00% 28.50% Sell./Gen./Admin. 17.80% 19.90% 18.70% 20.00% 19.40% Depreciation and Amort 5.30% 4.10% 4.60% 4.40% 4.50% Total Expenses 23.10% 24.00% 23.40% 24.40% 23.90% Operating Income 7.53% 6.85% 3.44% 3.60% 4.60% Other Income 1.30% 0.90% 1.20% 0.80% 1.00% Interest Expense 8.10% 4.00% 6.80% 6.60% 6.30% EBIT 0.70% 3.80% -2.10% -2.20% -0.70% Minortity Interest 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Income Taxes 0.30% 1.60% 0.00% 0.00% 0.40% Special Inc or Exp 0.00% 0.00% 2.50% 0.00% 0.70% Net Income 0.40% 2.30% 0.30% -2.20% -1.80% Extra Ordinary Income 0.30% 1.40% 0.00% 0.00% 0.30% Total Income 0.70% 3.60% 0.30% -2.20% -1.50% Cash Dividends (% Income) 0.00% 0.00% 322.40% -47.40% 77.70% BALANCE SHEET (as percent of Sales) 4 Year Weighted PERIOD 1982 1983 1984 1985 Average ASSETS: Cash & Equivs. 8.70% 29.90% 6.30% 5.80% 11.10% Accts.Rec. 2.10% 4.10% 4.20% 5.30% 4.40% Inventories 0.40% 0.70% 1.50% 1.10% 1.10% Other Current Assets 1.40% 1.60% 3.00% 1.70% 2.00% Total Current Assets 12.60% 36.20% 15.00% 13.90% 18.60% Tot. Prop./Equip 85.10% 112.70% 99.90% 72.10% 89.90% Depreciation 6.70% 7.40% 7.90% 8.90% 8.10% Net Prop./Equip 78.40% 105.40% 92.00% 63.20% 81.80% Intangibles 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Other Assets 0.70% 3.50% 1.80% 14.00% 6.90% Total Assets 91.80% 145.10% 108.80% 91.10% 107.30% LIABILITIES: Accounts Payable 4.80% 14.30% 11.10% 7.80% 9.80% Short Term Debt 5.10% 3.40% 3.90% 1.60% 3.00% Other Current Liab 3.40% 5.80% 5.70% 3.30% 4.60% Total Current Liabs 13.30% 23.50% 20.80% 12.80% 17.40% Total Long Term Debt 43.10% 86.00% 55.50% 54.00% 59.80% Deferred Tax 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Other 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 1.60% 0.60% Minority Interest 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Total Long Term 43.10% 86.00% 55.50% 55.60% 60.40% Total Liabilities 56.40% 109.50% 76.20% 68.40% 77.80% Preferred Stock 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Common Stock 49.60% 46.00% 39.40% 28.80% 37.50% Retained Erngs. -14.30% -10.40% -6.80% -6.00% -8.00% Treasury Stock 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Total Equity 35.30% 35.60% 32.50% 22.70% 29.50% Total Liab. And Equity 91.80% 145.10% 108.80% 91.10% 107.30%
- 8. Common Size Balance Sheet (as percent of Assets) BALANCE SHEET (as percent of Assets) 4 Year Weighted PERIOD 1982 1983 1984 1985 Average ASSETS: Cash & Equivs. 9.50% 20.60% 5.80% 6.40% 9.40% Accts.Rec. 2.30% 2.80% 3.80% 5.80% 4.20% Inventories 0.50% 0.50% 1.40% 1.20% 1.00% Other Current Assets 1.60% 1.10% 2.70% 1.90% 2.00% Total Current Assets 13.80% 25.00% 13.80% 15.30% 16.60% Tot. Prop./Equip 92.80% 77.70% 91.80% 79.20% 84.00% Depreciation 7.30% 5.10% 7.30% 9.80% 7.90% Net Prop./Equip 85.50% 72.60% 84.60% 69.30% 76.20% Intangibles 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Other Assets 0.80% 2.40% 1.60% 15.40% 7.20% Total Assets 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% LIABILITIES: Accounts Payable 5.25% 9.85% 10.23% 8.59% 9.00% Short Term Debt 5.56% 2.32% 3.59% 1.76% 2.80% Other Current Liab 3.73% 3.99% 5.28% 3.68% 4.20% Total Current Liabs 14.54% 16.17% 19.10% 14.03% 16.00% Total Long Term Debt 46.96% 59.31% 50.99% 59.30% 55.60% Deferred Tax 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Other 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 1.72% 0.70% Minority Interest 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Total Long Term 46.96% 59.31% 50.99% 61.03% 56.30% Total Liabilities 61.50% 75.48% 70.09% 75.05% 72.30% Preferred Stock 0.00% 0.00% 0.01% 0.00% 0.00% Common Stock 54.09% 31.69% 36.19% 31.56% 35.20% Retained Erngs. -15.60% -7.18% -6.28% -6.61% -7.50% Treasury Stock 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Total Equity 38.50% 24.52% 29.91% 24.95% 27.70% Total Liab. And Equity 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% List of Key take aways: Interest Coverage Ratio is on avg 97% and declining over last 2 years. This may be a factor in taking out new loans. Acquiring companies with contradictory cultures. (purchasing a highly unionized company when they are not unionized) • Initial growth because CA was careful in rout selection and stayed away from routs occupied by the larger airlines ◦ In attempts to reach "critical mass" they would try to start competing head to head with the giants but would be unable to offer the heavy discounts their airline was based around
- 9. • Their strategic model was lost as they moved into direct competition with the majors. ◦ debt from excessive growth caused them to abandon their key philosophies
