Presentasi ca mammae
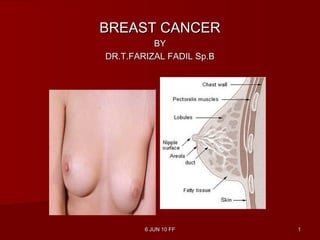
- 1. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 11 BREAST CANCERBREAST CANCER BYBY DR.T.FARIZAL FADIL Sp.BDR.T.FARIZAL FADIL Sp.B
- 2. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 22 Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth ofBreast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of breast cells or breast tissue, which canbreast cells or breast tissue, which can occur in both women and men. Worldwide,occur in both women and men. Worldwide, breast cancerbreast cancer is the fifth most commonis the fifth most common cause of cancer death (after lung cancer,cause of cancer death (after lung cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, and colonstomach cancer, liver cancer, and colon cancer)cancer)
- 3. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 33 Breast CancerBreast Cancer Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of breast cells or breast tissue,Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of breast cells or breast tissue, which can occur in both women and men. Worldwide,which can occur in both women and men. Worldwide, breast cancerbreast cancer is theis the fifth most common cause of cancer death (after lung cancer, stomachfifth most common cause of cancer death (after lung cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, and colon cancer).cancer, liver cancer, and colon cancer). No one knows why some women get breast cancer, but Breast cancer theNo one knows why some women get breast cancer, but Breast cancer the most common cause by :most common cause by : Age, the chance ofAge, the chance of getting breast cancergetting breast cancer rises as a woman gets olderrises as a woman gets older Genes, there are two genes, BRCA1 and BRCA2, that greatly increase theGenes, there are two genes, BRCA1 and BRCA2, that greatly increase the risk. Having one close relative (mother or sister) with breast cancer doublesrisk. Having one close relative (mother or sister) with breast cancer doubles your risk of getting breast canceryour risk of getting breast cancer Certain Medications, Taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) drugsCertain Medications, Taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) drugs after menopause may increase your chance of getting breast cancer.after menopause may increase your chance of getting breast cancer. Personal factors, beginning periods before age 12 or going throughPersonal factors, beginning periods before age 12 or going through menopause after agemenopause after age
- 4. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 44 Symptoms & DiagnosisSymptoms & Diagnosis :: If you discover a persistent lump in your breastIf you discover a persistent lump in your breast or any changes in breast tissue, it is veryor any changes in breast tissue, it is very important that you see a physician immediately.important that you see a physician immediately. Other thing that you should See your healthOther thing that you should See your health professional if :professional if : - A new lump in the breast- A new lump in the breast - A lump that has changed- A lump that has changed - change in the size or shape of the breast- change in the size or shape of the breast - Pain in the breast or nipple that does not go- Pain in the breast or nipple that does not go awayaway - Skin anywhere on the breast that is flaky, red,- Skin anywhere on the breast that is flaky, red, or swollenor swollen - A nipple that is very tender or that suddenly- A nipple that is very tender or that suddenly turns inwardturns inward - Fluid coming from the nipple when not nursing- Fluid coming from the nipple when not nursing a babya baby
- 5. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 55 The most important method used toThe most important method used to diagnose breast cancer is by taking adiagnose breast cancer is by taking a biopsy (abiopsy (a tissue sampletissue sample), The shape and), The shape and appearance of the cells in the tissueappearance of the cells in the tissue sample reveals whether the lump issample reveals whether the lump is benign, which is true of the vast majority,benign, which is true of the vast majority, or if it is cancerous.or if it is cancerous.
- 6. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 66 Type of Breast Cancer :Type of Breast Cancer : Ductal carcinoma in situ, is an early breast cancer in theDuctal carcinoma in situ, is an early breast cancer in the milk ducts. It can be detected by mammograms and ismilk ducts. It can be detected by mammograms and is normally easy to cure.normally easy to cure. Lobular carcinoma in situ, this is not considered to beLobular carcinoma in situ, this is not considered to be breast cancer but a pre-cancerous condition. They justbreast cancer but a pre-cancerous condition. They just have an increasedhave an increased risk of breast cancerrisk of breast cancer, so they are, so they are given frequent checkups.given frequent checkups. Invasive lobular carcinoma, is a breast cancer that startsInvasive lobular carcinoma, is a breast cancer that starts in the lobules and has spread. It's may difficult toin the lobules and has spread. It's may difficult to diagnose because they do not always form a lump ordiagnose because they do not always form a lump or show up on mammograms.show up on mammograms.
- 7. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 77 Types of Breast CancerTypes of Breast Cancer Ductal carcinomaDuctal carcinoma is the most common form of breast cancer.is the most common form of breast cancer. Tumors form in the cells of the milk ducts, which convey milk to theTumors form in the cells of the milk ducts, which convey milk to the nipples. Ductal carcinoma can either be invasive, with the potentialnipples. Ductal carcinoma can either be invasive, with the potential to spread, or non-invasive.to spread, or non-invasive. Lobular carcinomaLobular carcinoma occurs in the lobules, which are the milk-occurs in the lobules, which are the milk- producing glands. Lobular carcinoma can be invasive, with aproducing glands. Lobular carcinoma can be invasive, with a tendency to spread, or non-invasive.tendency to spread, or non-invasive. Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare, aggressive form ofis a rare, aggressive form of breast cancer that affects the dermal lymphatic system. Rather thanbreast cancer that affects the dermal lymphatic system. Rather than forming a lump, IBC tumors grow in flat sheets that cannot be felt informing a lump, IBC tumors grow in flat sheets that cannot be felt in a breast exam.a breast exam. Read more about IBCRead more about IBC Recurrent breast cancerRecurrent breast cancer means that the cancer has returnedmeans that the cancer has returned after being undetected for a time. Recurrent cancer can occur in theafter being undetected for a time. Recurrent cancer can occur in the remaining breast tissue, and also at other sites such as the lungs,remaining breast tissue, and also at other sites such as the lungs, liver, bones or brain. Even though these tumors are in a newliver, bones or brain. Even though these tumors are in a new location, they are still called breast cancer.location, they are still called breast cancer.
- 8. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 88 Symptoms include:Symptoms include: Lump or mass in your breastLump or mass in your breast Enlarged lymph nodes in the armpitEnlarged lymph nodes in the armpit Changes in breast size, shape, skin texture or colorChanges in breast size, shape, skin texture or color Skin rednessSkin redness Dimpling or puckeringDimpling or puckering Nipple changes or dischargeNipple changes or discharge ScalinessScaliness Nipple pulling to one side or a change in directionNipple pulling to one side or a change in direction Many breast changes – including lumps – are not cancer,Many breast changes – including lumps – are not cancer, but if you notice one or more of these symptoms forbut if you notice one or more of these symptoms for more than two weeks, see your doctor.more than two weeks, see your doctor.
- 9. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 99 Symptoms includeSymptoms include •• lump or mass in your breastlump or mass in your breast •• enlarged lymph nodes in the armpitenlarged lymph nodes in the armpit •• changes in breast size, shape, skinchanges in breast size, shape, skin texture or colortexture or color •• skin rednessskin redness •• dimpling or puckeringdimpling or puckering •• nipple changes or dischargenipple changes or discharge •• scalinessscaliness •• nipple pulling to one side or a change innipple pulling to one side or a change in directiondirection
- 10. 6 JUN 10 FF 10 • age Most cases occur in women 50 or older; it is less • common in women 35 or younger. Age is the most • influential risk factor. • • family history Your risk is higher with a family history • (especially mother, sister, daughter) of breast and/or • ovarian cancer. • • hormones / childbirth Your risk is higher if you had • your first period before age 12, began menopause after • age 55, never had children or had your first child after • age 30. Postmenopausal use of hormonal therapy • increases your risk of developing breast cancer. • • previous biopsy If you’ve had abnormal breast biopsy • results or benign breast diseases requiring biopsies, you • may be at increased risk. Other breast diseases such as • atypical hyperplasia, lobular or ductal carcinoma in situ • are risk factors, too. • • education / socioeconomic status Women with a • higher socioeconomic status and/or education tend to • have fewer children and start childbearing after age 30 – • both of which put them at higher risk. • • weight Obesity or weight gain after menopause are risk • factors. • • genetic alterations Inherited alterations in the genes, • called BRCA1 and BRCA2, account for about five to 10 • percent of all breast cancer cases. • Other risk factors include: • • oral contraceptive use • • a diet high in saturated fats • • physical inactivity • • alcohol (more than one alcoholic drink a day)
- 11. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 1111 ScreeningScreening Cancer screening exams are medical tests that are performed whenCancer screening exams are medical tests that are performed when a person has no symptoms.a person has no symptoms. All women should be familiar with their breasts so that they willAll women should be familiar with their breasts so that they will notice any changes and reportnotice any changes and report them to their doctor without delay. M. D. Anderson alsothem to their doctor without delay. M. D. Anderson also recommends the following:recommends the following: •• Clinical breast exams every one to three years beginning at ageClinical breast exams every one to three years beginning at age 20.20. •• Yearly mammograms and clinical breast exams beginning at ageYearly mammograms and clinical breast exams beginning at age 40 and continuing for40 and continuing for as long as a woman is in good health.as long as a woman is in good health. M. D. Anderson breast cancer experts recommend that all womenM. D. Anderson breast cancer experts recommend that all women practice “breast selfawareness”practice “breast selfawareness” (BSA) as part of the triad of breast cancer screening guidelines,(BSA) as part of the triad of breast cancer screening guidelines, which includeswhich includes breast exams by physicians (clinical breast exams) andbreast exams by physicians (clinical breast exams) and mammograms.mammograms. TipsTips ••
- 12. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 1212 TipsTips •• Schedule a clinical breast exam at the time of or just before yourSchedule a clinical breast exam at the time of or just before your regularly scheduledregularly scheduled mammogram.mammogram. •• If you are age 35 or older, ask your doctor to calculate your breastIf you are age 35 or older, ask your doctor to calculate your breast cancer risk.cancer risk. •• Consider additional screening if you are at risk.Women atConsider additional screening if you are at risk.Women at increased risk of breastincreased risk of breast cancer (e.g., family history, genetic predisposition, past breastcancer (e.g., family history, genetic predisposition, past breast cancer) should talk to theircancer) should talk to their doctor about the benefits and limitations of starting mammogramsdoctor about the benefits and limitations of starting mammograms earlier, having additionalearlier, having additional test (e.g., breast ultrasound or MRI) or having more frequent exams.test (e.g., breast ultrasound or MRI) or having more frequent exams. These recommendations are provided as a guide. If exam resultsThese recommendations are provided as a guide. If exam results suggest cancer, more extensivesuggest cancer, more extensive diagnostic tests, such as an ultrasound or biopsy of the breastdiagnostic tests, such as an ultrasound or biopsy of the breast tissue, should be conductedtissue, should be conducted
- 13. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 1313 Reducing Your RiskReducing Your Risk You can take action to reduce your risk of developing breastYou can take action to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer. M. D. Anderson suggests:cancer. M. D. Anderson suggests: •• talking to your doctor about your use of oraltalking to your doctor about your use of oral contraceptives and hormonal therapycontraceptives and hormonal therapy •• maintaining your ideal weightmaintaining your ideal weight •• eating at least five servings of fruits and vegetableseating at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per dayper day •• following recommended screening guidelinesfollowing recommended screening guidelines •• exercising regularlyexercising regularly •• eliminating tobacco use and using alcohol in moderationeliminating tobacco use and using alcohol in moderation •• getting your breast cancer risk assessedgetting your breast cancer risk assessed •• if you’re at increased risk, talk to your doctor aboutif you’re at increased risk, talk to your doctor about medications that can reduce your risk of developingmedications that can reduce your risk of developing breast cancer.breast cancer. Take time to discuss your own risks with your health careTake time to discuss your own risks with your health care
- 14. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 1414 Biopsy:Biopsy: a small sample of the suspicious area of thea small sample of the suspicious area of the breast is removed for examination under a microscope.breast is removed for examination under a microscope. Biopsies can be done in the following ways:Biopsies can be done in the following ways: Surgical biopsy:Surgical biopsy: an incision is made in the breast.an incision is made in the breast. Surgeons locate the tumor by palpation or with the aid ofSurgeons locate the tumor by palpation or with the aid of images from a CT scan, ultrasound or mammogram. Inimages from a CT scan, ultrasound or mammogram. In anan excisional biopsyexcisional biopsy , the entire mass is removed. In, the entire mass is removed. In anan incisional biopsyincisional biopsy , only a portion of the tumor is, only a portion of the tumor is removed.removed. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA):Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): a thin, hollow needlea thin, hollow needle is inserted into the breast to the tumor, and fluid andis inserted into the breast to the tumor, and fluid and cells are removed from the tumor. While this test cancells are removed from the tumor. While this test can help to determine if there is cancer present, it cannothelp to determine if there is cancer present, it cannot determine if the cancer is invasive and additionaldetermine if the cancer is invasive and additional biopsies may be needed if cancer is actually present.biopsies may be needed if cancer is actually present. Core biopsy:Core biopsy: a thicker needle is used to remove one ora thicker needle is used to remove one or more small cylinder-shaped tissue samples from themore small cylinder-shaped tissue samples from the tumor.tumor.
- 15. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 1515 shaped tissue samples from the tumor.shaped tissue samples from the tumor. Diagnostic mammogram:Diagnostic mammogram: this procedure is similar tothis procedure is similar to the mammogram used for screening, but provides morethe mammogram used for screening, but provides more detailed images of the breast tissue. detailed images of the breast tissue. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): images ofimages of the breast are created with powerful magnets thatthe breast are created with powerful magnets that interact with a computer.interact with a computer. Ultrasound:Ultrasound: a special wand placed against the skina special wand placed against the skin transmits sound waves, which bounce off breast tissuetransmits sound waves, which bounce off breast tissue and are used create an image on a monitor. and are used create an image on a monitor. Sentinel lymph node biopsy:Sentinel lymph node biopsy: lymph nodes are olive-lymph nodes are olive- sized glands which are part of a system that circulatessized glands which are part of a system that circulates lymph fluid throughout the body. The lymphatic systemlymph fluid throughout the body. The lymphatic system can also carry cancer cells from the tumor site to othercan also carry cancer cells from the tumor site to other areas of the body. In breast cancer patients, the firstareas of the body. In breast cancer patients, the first nodes to be affected are under the armnodes to be affected are under the arm
- 16. 6 JUN 10 FF 16 Staging TNM SYSTEM • Primary tumor (T) • Tx: Primary tumor cannot be assessed • T0: No evidence of primary tumor • Tis: (DCIS) Carcinoma in situ • Tis: (LCIS) Carcinoma in situ • Tis: Paget disease of the nipple with no tumor (Paget disease associated with a tumor is classified according to the size of the tumor.) • T1: Tumor 2 cm or smaller in greatest diameter – T1mic: Microinvasion 0.1 cm or less in greatest dimension – T1a: Tumor >0.1 but not >0.5 cm in greatest diameter – T1b: Tumor >0.5 but not >1 cm in greatest diameter – T1c: Tumor >1 cm but not >2 cm in greatest diameter • T2: Tumor >2 cm but not >5 cm in greatest diameter • T3: Tumor >5 cm in greatest diameter • T4: Tumor of any size, with direct extension to (a) the chest wall or (b) skin only, as described below – T4a: Extension to the chest wall, not including the pectoralis muscle – T4b: Edema (including peau d’orange) or ulceration of the skin of the breast or satellite skin nodules confined to the same breast – T4c: Both T4a and T4b – T4d: Inflammatory disease
- 17. 6 JUN 10 FF 17 • Regional lymph nodes (N) • Nx: Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed (eg, previously removed) • N0: No regional lymph node metastasis • N1: Metastasis in movable ipsilateral axillary lymph node(s) • N2: Metastasis in ipsilateral axillary lymph node(s) fixed or matted, or in clinically apparent ipsilateral internal mammary nodes in the absence of clinically evident axillary lymph node metastasis – N2a: Metastasis in ipsilateral axillary lymph nodes fixed to one another or to other structures – N2b: Metastasis only in clinically apparent ipsilateral internal mammary nodes and in the absence of clinically evident axillary lymph nodes • N3: Metastasis in ipsilateral infraclavicular or supraclavicular lymph node(s) with or without axillary lymph node involvement, or clinically apparent ipsilateral internal mammary lymph node(s) and in the presence of axillary lymph node – N3a: Metastasis in ipsilateral infraclavicular lymph node(s) – N3b: Metastasis in ipsilateral internal mammary lymph node(s) and axillary lymph node(s) – N3c: Metastasis in ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node(s)
- 18. 6 JUN 10 FF 18 • Distant metastasis • Mx: Distant metastasis cannot be assessed • M0: No distant metastasis • M1: Distant metastasis
- 19. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 1919 Table 2. TNM Staging System for Breast CancerTable 2. TNM Staging System for Breast Cancer Open table in new windowOpen table in new window [ CLOSE WINDOW ][ CLOSE WINDOW ] TableTable StageTumorNodeMetastasesStageTumorNodeMetastases Stage 0TisN0M0Stage IT1N0M0Stage IIAT0Stage 0TisN0M0Stage IT1N0M0Stage IIAT0 T1T1 T2N1T2N1 N1N1 N0M0N0M0 M0M0 M0Stage IIBT2M0Stage IIBT2 T3N1T3N1 N0M0N0M0 M0Stage IIIAT0M0Stage IIIAT0 T1T1 T2T2 T3N2T3N2 N2N2 N2N2 N1-2M0N1-2M0 M0M0 M0M0 M0Stage IIIBT4M0Stage IIIBT4 T4T4 T4N0T4N0 N1N1 N2M0N2M0 M0M0 M0Stage IIICAny TN3M0Stage IVAny TAny NM1M0Stage IIICAny TN3M0Stage IVAny TAny NM1StageTumorNodeMetastasesStageTumorNodeMetastases Stage 0TisN0M0Stage IT1N0M0Stage IIAT0Stage 0TisN0M0Stage IT1N0M0Stage IIAT0 T1T1 T2N1T2N1 N1N1 N0M0N0M0 M0M0 M0Stage IIBT2M0Stage IIBT2 T3N1T3N1 N0M0N0M0 M0Stage IIIAT0M0Stage IIIAT0 T1T1 T2T2 T3N2T3N2 N2N2 N2N2 N1-2M0N1-2M0 M0M0 M0M0 M0Stage IIIBT4M0Stage IIIBT4 T4T4 T4N0T4N0 N1N1 N2M0N2M0 M0M0 M0Stage IIICAny TN3M0Stage IVAny TAny NM1M0Stage IIICAny TN3M0Stage IVAny TAny NM1
- 20. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2020 THERAPIE :THERAPIE : 1.OPERASI.1.OPERASI. 2.CHEMOTHERAPIE.2.CHEMOTHERAPIE. 3.RADIASI.3.RADIASI. 4.HORMONAL.4.HORMONAL.
- 21. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2121 PROGNOSA :PROGNOSA : TERGANTUNG STADIUM.TERGANTUNG STADIUM.
- 22. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2222
- 23. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2323
- 24. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2424
- 25. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2525
- 26. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2626 Facing a mirrorFacing a mirror Stand before a mirror and compare both breasts for differencesStand before a mirror and compare both breasts for differences in size, nipple inversion (turning in), bulging, or dimpling. Note anyin size, nipple inversion (turning in), bulging, or dimpling. Note any skin or nipple changes, such as a hard knot orskin or nipple changes, such as a hard knot or nipple dischargenipple discharge.. Inspect your breasts in the following 4 steps:Inspect your breasts in the following 4 steps: – With yourWith your armsarms at your sidesat your sides – With your arms overheadWith your arms overhead – With your hands on hips - Press firmly to flex yourWith your hands on hips - Press firmly to flex your chestchest muscles.muscles. – Bent forward - Inspect your breasts.Bent forward - Inspect your breasts. In these positions, your pectoral muscles are contracted, and aIn these positions, your pectoral muscles are contracted, and a subtle dimpling of the skin may appear if a growing tumor hassubtle dimpling of the skin may appear if a growing tumor has affected a ligamentaffected a ligament
- 27. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2727 Lying downLying down Right breastRight breast and Left breastand Left breast – Place a pillow under your right shoulder.Place a pillow under your right shoulder. – Put your right hand under your head.Put your right hand under your head. – Check the entire breast area with the finger pads of your left hand.Check the entire breast area with the finger pads of your left hand. – Use small circles and follow an up-and-down pattern.Use small circles and follow an up-and-down pattern. – Use light, medium, and firm pressure over each area of the breast.Use light, medium, and firm pressure over each area of the breast. – Feel the breast with the surfaces of the second, third, and fourth fingers, movingFeel the breast with the surfaces of the second, third, and fourth fingers, moving systematically and using small, circular motions from the nipple to the outersystematically and using small, circular motions from the nipple to the outer margins.margins. – Gently squeeze the nipple for any discharge.Gently squeeze the nipple for any discharge.
- 28. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2828 In the showerIn the shower A BSE can easily be performed while you're in the bathA BSE can easily be performed while you're in the bath or shower. Some women discover breast masses whenor shower. Some women discover breast masses when their skin is moist.their skin is moist. – Raise your right arm.Raise your right arm. – With soapy hands and fingers flat, check your right breast.With soapy hands and fingers flat, check your right breast. – Use the same small circles and up-and-down pattern describedUse the same small circles and up-and-down pattern described earlier.earlier. – Repeat on the left breast.Repeat on the left breast.
- 29. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 2929
- 30. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 3030
- 31. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 3131
- 32. 6 JUN 10 FF6 JUN 10 FF 3232