Chemistry formulas
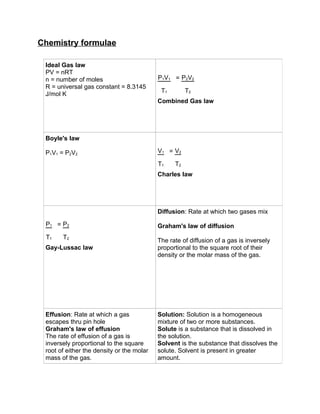
- 1. Chemistry formulae Ideal Gas law PV = nRT n = number of moles P1V1 = P2V2 R = universal gas constant = 8.3145 T1 T2 J/mol K Combined Gas law Boyle's law P1V1 = P2V2 V1 = V2 T1 T2 Charles law Diffusion: Rate at which two gases mix P1 = P2 Graham's law of diffusion T1 T2 The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely Gay-Lussac law proportional to the square root of their density or the molar mass of the gas. Effusion: Rate at which a gas Solution: Solution is a homogeneous escapes thru pin hole mixture of two or more substances. Graham's law of effusion Solute is a substance that is dissolved in The rate of effusion of a gas is the solution. inversely proportional to the square Solvent is the substance that dissolves the root of either the density or the molar solute. Solvent is present in greater mass of the gas. amount.
- 2. Concentration is the ratio of solute Unit of Morality (M) : mol/L : moles per liter and solvent. Unit of Morality (M) : mol/kg : moles per Concentration can be measured using kg morality, morality and mole fraction. Morality (M) = moles of solute liters of solution Morality (m) = moles of solute kg of solution Mole fraction: Mole fraction of a Dilution: Diluting a solution means adding component in solution is the number of more solvent in solution without the addition moles of that component divided by of more solute. the total number of moles of all components in the solution. MiVi = MfVf Mi: Morality of solution before diluting. Vi: Volume of solution before diluting. Mf: Morality of solution after diluting.
- 3. molesa Vf: Volume of solution after diluting. Mole-fraction (Xa)= molesa + molesb .... Mole: Mole is the amount of One mole of gas has volume of 22.4 liter substance that contains same number at STP. of particles as there are atoms in Carbon-12. One mole of substance is Avogadro's number (i.e. 6.023 x 1023). Relation between moles and grams Ionization Enthalpy: It is the energy 1 mole = molecular weight of needed to remove an electron from an atom substance in grams. or molecule (i.e from low state to n=∞). It is always endothermic (i.e. positive).OR Ionization energy: energy needed to remove an electron from an atom [A-] pH = pKa + log10 [HA] Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: where [A-]: Concentration of conjugate base [HA]: concentration of the acid OR [Conjugate Base] pH = pKa + log10 [Acid]
- 4. Ideal Gas Law The ideal gas law is given by: PV = nRT Where: P: the absolute pressure of the gas V: volume of the gas n: number of moles, which is the ratio of mass and molar mass R: universal gas constant, which is R = 8.3145 J · mol-1 · K-1 T: the absolute temperature Henry's Law Henry's law is given by: p = K · x Where:p-partial pressure of the solute , H – Henry’s Constant Hess' Law Hess' Law can be expressed in 3 ways and they are: For enthalpy we have: For entropy we have: For Gibbs' free energy we have: Raoult's Law
- 5. Raoult's law is given by: Pi = xi - Pi * Where: Pi pressure of component , xi – mole fraction in the solution , Pi * - vapour pressure of the pure substance. i. In a solution with two liquids A and B, if no gas are present, the total vapor pressure is given by: Ptot = PA + PB Where: PA – vapor pressure of liquid A , PB – vapor pressure of liquid B For an ideal solution of liquids A and B, which obeys Raoult's law over the full range of composition. The total pressure is given by: ptot = xA pA* + xB pB* , where xA + xB = 1 Molar Enthalpy Hm = H / n Where: H: enthalpy; n: number of moles Molar Mass The molar mass equation is given by; M=Mr.g. mol-1 Where: M: molar mass, which is the mass of one mole of a substance Mr. Relative molar mass, also called molecular weight This equation is obtained from the following equation: Where:
- 6. NA: Avogadro Constant which is NA = 6.0221·1023mol-1 mu: molar mass constant, which is mu = 1 g · mol-1 Dilution To calculate dilution, we can use the following formula: M1 * V1 = M2 * V2 Where: M: Morality which is given by: M = n/NA which is given by: M = n/NA V: Volume Morality (M): Moles of Solute/Liters of solution Unit of Morality (M): mol/L ; moles per liters Moles of Solute/Liters of solution Enthalpy The enthalpy is given by the formula: H = U + pV Where: H: Enthalpy U: Internal energy p: pressure V: volume Gibbs ‘Free Energy Gibbs’ free energy is given by: ΔG = ΔH- TΔS Where:
- 7. H: Enthalpy T: Temperature S: entropy Temperature Conversion To convert between Kelvin and Celsius you can use the following formulas: • From Kelvin to Celsius : °C= K - 273 • From Celsius to Kelvin: K = °C + 273