Modern bio ii bact,fung,prot
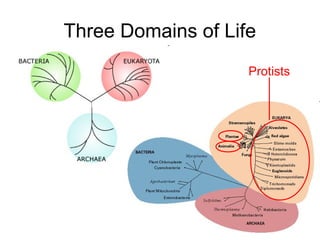
- 1. Three Domains of Life Protists
- 2. Three Domains of Life
- 3. Changes in Classification • The ‘old school’ method of classification included 5 Kingdoms (what I learned in school) – Monera – Protista – Fungi – Plantae – Animalia • Today, advances in molecular technology expanded our understanding (and interpretation) of systematics
- 4. Modern Systematics • Three Domain classification of life • Numerous, virtually countless Kingdoms • Bacteria and Archaea are now 2 distinct Domains (once included together in Kingdom Monera) • Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia remain classified as distinct Kingdoms, although classification of the kingdom Protista has been met with complications
- 5. Prokaryotes • Includes the kingdoms Archaea & Bacteria • Oldest, structurally-simplest, and most abundant forms of life • Photosynthesis Bacterial and Eukaryotic Diversity • Important decomposers and symbionts
- 6. Prokaryotes • Unicellular • Typically 1μm or less (1000 μm = 1mm; 1000mm = 1 meter) • No membrane-bound nucleus; instead a single circular chromosome made of DNA • Asexual reproduction by binary fission • Photosynthetic bacteria utilize oxygen or chemical compounds, such as sulfur
- 7. Prokaryotic Cell Structure • Three basic forms: – Bacillus – rod-shaped – Coccus - sphercal or ovoid-shaped – Spirillum – spiral or helical
- 8. Prokaryotic Cell Structure • Prokaryotes have a tough cell wall and other external structures • Cell wall consists of peptidoglycan; a rigid network of polysaccharide strands cross-linked by peptide side chains; unique to Bacteria • Maintains the shape of the cell and protects it from swelling and rupturing
- 9. • Prokaryotes can have 1 or more flagella (much less complex than in Eukaryotes) • Some Prokaryotes possess pilli, which helps fasten cell to host membrane
- 10. Domain Archaea • Once considered a subdivision of the Kingdom Monera, now its own domain • Like all prokaryotes, Archaea are singlecelled microorganisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles • Best known for the “extremophiles” – Archaea which thrive in extremely harsh environments
- 11. Archea - Extremophiles • Thermophiles – thrive at 60-80°C (>176°F!) • Acidophiles – thrive at pH at or below pH 3 • Xerophiles – grow in extremely dry conditions • Halophiles – require extremely high concentrations of salt http://www.dpchallenge.com/image.php?IMAGE_ID=448561
- 12. Archaea - Extremophiles • Evidence for evolution of life on Earth? • Many of the harsh conditions which extremophiles require to survive were characteristic of our early Earth • Likely that extremophiles evolved to dwell in such conditions billions of years ago and retained ability to survive today in specific environments
- 13. • Archaea differ from Bacteria in numerous ways – Plasma membranes are made of different kinds of lipids – RNA and ribosomal proteins more like those of Eukaryotes – Mostly anaerobic Photosynthetic
- 14. Domain Bacteria • Two types: – Gram-positive – Gram negative • Refers to the Gram Stain (purple dye) • Gram-positive bacteria – possess a thicker peptidoglycan cell wall; retain stain • Gram-negative bacteria – contain less peptidoglycan; do not retain stain
- 16. Bacterial Conjugation • Transfer of genetic material • Horizontal gene transfer • NOT sexually (no gametes)
- 17. Eukaryotic origin • The nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum arose from infolding of the prokaryotic cell membrane
- 18. Eukaryotic origin • Eukaryotic organelles arose from a consortium of symbiotic prokaryotes – Mitochondria were aerobic heterotrophic prokaryotes – Chloroplasts (for photosynthesis) were photosynthetic prokaryotes
- 19. Endosymbiotic theory • Evidence? – Mitochondria have their own independent DNA, and a double membrane – Chloroplasts resemble cyanobacteria; also have their own independent DNA and a double membrane
- 21. Kingdom Protista (the trouble-maker) • Kingdom Protista is NOT monophyletic Paraphyletic – includes common ancestor but not all descendents
- 22. Kingdom Protista • Eukaryotic (must be! Domain Eukarya) • Largely unicellular with some multi-cellular ‘exceptions’ (e.g., kelps, seaweed) • May be autotrophic or heterotrophic • Debate over classification – – Are some protists members of other kingdoms? – Would protists best be considered as several different kingdoms?
- 23. Kingdom Protista • Characterized by: – Mode of locomotion (e.g., flagella, cilia) – Mode of nutrition (e.g., autotrophic, heterotrophic) – Body form (unicellular, multicellular) – Pigmentation (e.g., Red, Green, Brown alga) – Reproduction (asexual, sexual) • Multicellular protists are distinguished from other Kingdoms by their lack of specialized tissues
- 24. Kingdom Protista
- 25. Kingdom Protista • Have you ever eaten a protist?, or should I ask, have you ever eaten seaweed??? • Just to complicate matters, green algae is categorized as a plant in Kingdom Plantae…
- 26. Green Plants evolved from Green Algae • We’ll come back to this…
- 27. Kingdom Fungi
- 28. Kingdom Fungi • • • • • Unicellular and multi-cellular ~1.5 million species Important decomposers Includes many disease-causing organisms Others are important symbionts and fermenting organisms
- 29. Kingdom Fungi • Mycology – the study of fungi • All fungi are heterotrophic – Obtain their food by secreting digestive enzymes and absorbing the nutrients released by the enzymes • Unicellular fungi may have flagella; multicellular fungi are primarily filamentous in form • Cell walls composed of chitin
- 30. Kingdom Fungi • Six phyla – Cytrids (flagellated), Zygomycetes (inc. bread molds), Glomeromycetes (mycorrhizae), Ascomycetes (inc. yeast), Bascidiomycetes (mushrooms), and Deuteromycetes (not pictured)
- 31. Kingdom Fungi • Phylogeny based on the 5 major Phyla (based on mode of sexual reproduction)
- 32. Kingdom Fungi • Multicellular fungi consist of long, slender filaments called hyphae • Some hyphae are continuous; others are divided by septa • Mycelium – a mass of connected hyphae
- 33. Kingdom Fungi • Mycelium grows through and digests its substrate • Fungi live in their food!
- 36. Kingdom Fungi • Hyphae (mycelium) form complex structures • A mushroom is a spore-bearing body of a fungus; composed of hyphae • A puffball is a spore-bearing body of certain species of fungi, including the deadly Death Cap mushroom; composed of hyphae
- 38. Kingdom Fungi • Fungi can also be monokaryotic or dikaryotic – Monokaryotic – one nucleus per cell – Dikaryotic – two nucleii per cell • Fungi reproduce sexually and asexually – During sexual reproduction in some fungi, 2 haploid nuclei fuse creating a dikaryotic (dikaryon) stage, which precedes the normal diploid nucleus
- 39. Kingdom Fungi • Some fungi produce specialized mycelial structures to house spores (e.g., mushroom, puffballs, ‘shelf’ mcycelium on dead trees) • Spores can form as a result of sexual or asexual reproduction • Spores can withstand degradation and survive for long periods of time; because of their size, they can travel long distances
- 41. Kingdom Fungi • Chestnut Blight – a fungal disease which has virtually eliminated the American chestnut • Accidentally introduced into the U.S. on imported lumber from Asia • The roots of the tree are fairly resistant to the fungus, but the tree succumbs once it grows enough shoots to reproduce • Unknown spreading agent (the spores are everywhere!)
- 43. …Jack Frost nippin’ at your nose… • The American chestnut once covered large tracts of forest in the U.S. • The chestnut was a very important source of food for wildlife (and the inspiration for at least 1 Christmas song…) • At the turn of the twentieth century, one quarter of all trees in the eastern United States were chestnut!
- 44. The Chestnut Blight • Only a few mature survivors remain of the American Chestnut, which once consisted of 4 billion trees (that’s over 99.99% gone) • If you have ever eaten a chestnut, you had a European import; only our grandparents may have ever tasted an American chestnut • The American Chestnut Foundation seeks to restore the great chestnut, but how?
- 45. The Chestnut Blight • Development of blight-resistant American chestnuts is accomplished through a process known as “backcross breeding” • Hybrids between American and Chinese chestnuts are repeatedly crossed back onto purely American specimens, yielding offspring which are blight- resistant • The resulting offspring are ~94% American (6% Chinese) and diseaseresistant
- 46. Kingdom Fungi • Spores are frequently dispersed by wind, but may also be spread by insects and small animals • Chytrids are an ancestral group and retain flagella; have motile zoospores
- 47. Why did the mushroom go to the party? • Many fungi live underground, and can reach great sizes • One of the largest living organisms in the world is a fungus! • The largest known specimen covers more than 3.4 square miles and is thousands of years old • And some species of fungi are bioluminescent!
- 48. Armillaria fungus • Connected underground by hyphae!
- 49. Fungal Ecology • Fungi often have interactions or symbioses with other organisms • Obligate symbiosis – essential for survival; fungus cannot survive without symbiont • Facultative symbiosis – fungus can survive without symbiont • Mutualistic relationships – both partners benefit • Commensal relationships – one partner benefits, but the other is unaffected
- 50. Fungal Ecology • A lichen is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner (usually green algae or cyanobacteria)
- 51. Fungal Ecology • Mycorrhizae – association between a fungus and the root of a tree • Mycorrhizae function as an extension of the plant root system; the fungus increases surface area for absorption and aids in transfer of nutrients • The plant, in return, supplies organic carbon to the fungus
- 52. Mycorrhizae • Very important! • Mycorrhizal plants are more resistant to drought and even microbrial soil-borne pathogens • Two types – Arbuscular mycorrhizae – Ectomycorrhizae
- 53. Mycorrhizae
- 54. Fungal Ecology • Leaf-cutter ants – an animal symbiont with fungi! • The ants feed on special structures produced by a fungus that they have domesticated • The ants feed the fungus leaves and protect it from pests and molds • In return, the ants eat the fungus and feed it to their young
- 55. Just in case you didn’t believe me… http://www.flickr.com/photos/kellyslittlepieces/2243322652/
Notes de l'éditeur
- Archea have classified Kingdoms; Bacteria do not (yet) On the contrary, Eukaryota is composed of well-defined Kingdoms including Plants, Fungus and Animals; the exception is Protists which we’ll discover are not monophyletic and include groups that are similar in design, but not in evolutionary processes
- Monophyletic; one c.a.
- True bacteria; Existed on Earth for 1 billion years before the Eukaryotes appeared
- Although they can transfer genetic material via their plasmids (horizontal gene transfer), however not considered reproduction
- Hydrothermal vents?
- (photosynthetic: cyanobacteria and lithotrophs (Nitrosomonas which oxidizes ammonium)
- Involves cell to cell contact; does not involve fusion of gametes and the creation of a zygote There is not an equal exchange of genetic material, merely the transfer of genetic material from a donor cell to a recipient Often beneficial to the recipient cell – inc. antibiotic resistance or the ability to utilize a new metabolite Transformation – genetic material transfer that does not involve cell to cell contact; direct uptake from environment Tranduction – incorporation of new DNA from virus
- Mitochondria generate ATP (powerhouse of cell); DNA analysis shows similarities to bacterial genomes Chloroplasts originated as endosymbiotic cyanobacteria
- The 15 major protist phyla are now grouped into 7 monophyletic groups; There are 60 lineages that cannot be placed with any confidence
- Essentially you are a protist if you are not clearly an animal, plant or fungus!
- Who here eats seaweed?
- Chitin: what crab shells are made of; a polysaccharide (carbohydrate)
- Deuteromycetes – imperfect fungi – do not fit into the taxonomic classification; athletes foot, yeast infections, produce antibiotic Penicilin Sexual form of reproduction never observed (only asexual known), sexual structures never seen
- Explains worldwide presence of fungi, how disease spreads so easily
- 1/4th of eastern American trees were Chestnuts, incredibly important for wildlife, only a few surviving – trying to breed resistant (Asian) chestnuts with American to save and restore; cankers caused by fungus cause limb to crack
- 1/4th of eastern American trees were Chestnuts, incredibly important for wildlife, only a few surviving – trying to breed resistant (Asian) chestnuts with American to save and restore; cankers caused by fungus cause limb to crack
- Believed to be 2400 years old
- Inhabit extreme environments – arctic tundra, hot deserts, rocky coasts, rainforests;widespread and long-lived, but subject to environmental disturbance (melanism!)
- 92% of trees
- Arb – penetrates the outer cells of the plant root Ecto – the hyphae surround but do NOT penetrate the cell walls of the roots
- Fungus grows only in the underground chambers of the ants nest
- I don’t think the smurfs are bioluminescent though!
