Gout
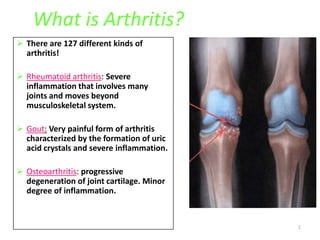
- 1. What is Arthritis? There are 127 different kinds of arthritis! Rheumatoid arthritis: Severe inflammation that involves many joints and moves beyond musculoskeletal system. Gout: Very painful form of arthritis characterized by the formation of uric acid crystals and severe inflammation. Osteoarthritis: progressive degeneration of joint cartilage. Minor degree of inflammation. 1
- 2. GOUT
- 3. • Gout is a metabolic disorder of purine metabolism, characterized by intermittent attacks of acute pain, swelling and inflammation. • It always preceded by hyperuricaemia (6.0mg/dl) Hyperuricaemia due to excessive amount of uric acid production or decreased excretion
- 4. • Hyperuricaemia - primary or secondary. • Primary hyperuricaemia classified as “Overproducers” or “under execrators”
- 5. • Primary Hyperuricemia and Gout with No Associated Condition Secondary Hyperuricemia and Gout with Identifiable Associated Condition • Uric acid undersecretion(80%– 90%) • develop during course of other diseases (Leukaemias, lymphomas, chemotherapy) • Idiopathic • Some drug therapy (Thiazide diuretics, furosamide, ethacrynic acid) • Urate overproduction (10%– 20%) • HGPRT deficiency • • PRPP synthetase overactivity (Phasphoribosyl pyrophosphate) • Some disorders Diabeticketoacidosis, lead poison, Lymphoproliferative diseases, Hemolytic anemias, psoriasis • Dual mechanism Obesity, Hypoxemia and hypoperfusion
- 6. Uric acid production and excretion RNA,DNA PURINES PRPP HYPOXANTHINES Xanthine oxidase XANTHINES Xanthine oxidase URIC ACID (low water soluble) Hyperuricemia Gout Deposits of urate crystal Nephrolithiasis Uric acid freely filtrated through by glomerulus and reabsorbed by tubular fluid Probencid
- 7. Pathophysiology of gout Uricacid Blood React with sodium Sodium crystals (tophi) Deposited in soft tissues and joints Inflammation(ry) Indomethacin Colchicine Infiltration of granulocytes that phagocytise the urate crystals Generate free radicals Free radical damage the tissue Colchicine Release of proteolytic enzyme glycoprotein Release of lactic acid Release of lysosomal enzymes More ppt of urate crystals Destruction of joints Colchicine
- 8. Acute gout • Painful arthritic attack of sudden onset. • Usually occurring at night or in early morning • Arthritic pain worsen progressively • Generally involves one or few joints • Most common site of initial attack metatarsophalangeal joint. • Other sites ankle, heel, knee, wrist, elbow and fingers.
- 9. Chronic gout • Frequency of attacks increases, continuous deposit leads to damage joints and chronic pain • Patients may develop large subacutenous tophi (Stones) in pinna of external ear, eyelids, nose and around joints • The ureate crystals in kidney leads renal disease. • Articular cartilage may be destroyed result in joint deformities
- 10. GOUT - TREATMENT GOALS: 1. terminate acute attack 2. provide rapid, safe pain/anti-inflammatory relief 3. prevent complications • destructive arthropathy • tophi • renal stones
- 11. Classification of drugs used in gout ACUTE GOUT : 1. NSAIDS 2. Corticosteroids 3. Colchicine CHRONIC GOUT: • • Inhibit uric acid synthesis:- Allopurinol, febuxostate (Urostatic) Increase uric acid excretion:- Probencid, Sulphinpyrazole (Urosuric)
- 12. Colchicine • Alkaloid from colchium autumnale. (1973) • Neither analgesic nor anti inflammatory, but specific for gouty inflammation. • It is only effective in prophylaxis of acute gout • It has no effect on synthesis or promote excretion • MOA • Colchicine binds to intracellular protein ‘Tubulin’ and causes depolymerisation and disappearance of microtubules in granulocytes & Inhibit granulocyte migration so dec phagocytic activity
- 13. • Colchicine inhibit glycoprotein release – Other actions- arrest of mitosis in metaphas “spindle poison” - increases gut motility. - Antipyretic , respiratory depressant - Inhibit histamine , Insulin release - hypertensive at high dose , Increase vasomotor tone - direct vasoconstrictor
- 14. Uses Colchicine preferred in pts without confirmed diagnosis of gout. Acute gout-1mg orally followed by 0.25 mg 3 hrly till control. (EHC) 3-7days With safer alternatives NSAIDs use of Colchicine have declined ADR:- diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain. Acute toxicity - bloody diarrhoea, throat pain, respiratory depression, haematuria. Chornic toxicity- agranulocytosis, peripheral neuritis and myopathy, renal tubular necrosis.
- 15. NSAIDs • Strong anti inflammatory drugs • Use in patients without contraindication • Use maximum dose/potent NSAID e.g., Indomethacin 50 mg po t.i.d. Diclofenac 50 mg po t.i.d. Ketorolac 10 mg q4-6hrsr, Napoxen, Piroxicam • continue until pain/inflammation absent for 48 hours • MOA: inhibit urate crystal phagocytosis and chemotatic migration of leukocytes into inflammed joints. • NSAIDs are not recommended for long term. • (Salicylates are not used , have tendency to raise uric acid)
- 16. Corticosteroid Use when NSAIDS/Cholchicine risky or contraindicated e.g.,: elderly hypertensive peptic ulcer disease renal impairment liver impairment use when • NSAIDS ineffective Mode of administration – • intra articular - Depomedrol 40-80 mg with lidocaine. • Oral Prednisone 30-40 mg qd for 3-4 days, taper by 5 mg every 2-3 days & stop over 1-2 wks
- 17. Drugs for chronic gout • Uric acid synthesis inhibitors:- Allopurinol (Xanthine oxidase inhibitor) • Hypoxanthine Xanthine Uric acid Xanthine oxidase - Allopurinol
- 18. • Allopurinol prevents the synthesis of uric acid by inhibiting the enzyme Xanthine oxidase, result reduce plasma ureate levels. • Inc. xanthine ,hypoxanthines are excreted through urine • Allopurinol short acting competitive inhibitor • Metabolite alloxanthine is long acting t1/2 24hr.
- 19. • Start low 50-100 mg qd • Increase by 50-100mg every 2-3 weeks according to symptoms – “Average” dose 300 mg daily – lower dose if renal/hepatic insufficiency – higher dose in non-responders – prophylactic colchicine until allopurinol dose stable • • • • Indications: Chronic gout In patients 24 hrs urinary acid excretion exceeds 1.1g For recurrent renal ureate stones.
- 20. Allopurinol side effects • GI upset, alopecia, cataract. • Allopurinol Hypersensitivity: Pruritic papular skin rash, fever, hepatitis, eosinophilia, renal impairment • CI:– – – – – Chidrens Elderly patients Pregnancy Lacation Liver and kidney diseases.
- 21. Allopurinol drug interactions • Allopurinol prolong ½ life of Vidarabine, Cyclosporin drugs and increase toxicity • Dec. metabolism of 6-mercaptopurine, Azothiaprine inc. its effects. • Interferes with the mobilization of hepatic iron stores heamtonic should be avoided during allopurinol therapy.
- 22. Uricosuric drugs: (probencid) •Highly lipid soluble benzoic acid. •It blocks reabsorption of urate in proximal tubule by blocking transport (Bidirectional transport) •PK: Dose dependent t1/2 life •Dose -250- 500mg b.d. with plenty of fluids, alkalinization of urine. Uses : chronic gout along with NSAIDs / colchicine for initial 1-2 months.
- 23. Sulfinpyrazone • It is a Pyrazolone derivaties related to Phenylbutazone. • Inhibits tubular reabsorption of uric acid at therapeutic doses. • Its action is additive with probenecid. • Use -chronic gout • Dose :100-200mg BD gradually increase according to the response.
- 24. Benzbromarone • It is newer and more potent uricosuric drug • Used in patients allergic to probenecid or sulfinpyrazone • It is reversible inhibitor of tubler reabsorption • Effective dose 60-80mg/day • With allopurinol more effective
- 25. • A 56yrs old male awake in the night with sudden severe pain in his first metatarsophalangeal joint which lasted for a week. Over the next few months, he had similar acute episode of pain in his ankles and knees, as well as his big toe. The GP suspected gout and referred him to specialist • What treatment should be GP institute for the acute attacks prior to the specialist diagnosis?
- 26. • what test could the rheumatologist do to confirm the suspected diagnosis? • What is the cause of gout? • Which drugs act for acute attacks? • What would you prescribe for prophylaxis to reduce recurrent attacks ?
Notes de l'éditeur
- Uric acid derived 1/3 from dietary source and 2/3 from purine metabolism
- Excess uric acid deposited in interstititum of kiedney
- GIT effects due toenterohepatic circulation so long duration drug present in GIT.
