Eykaryotes
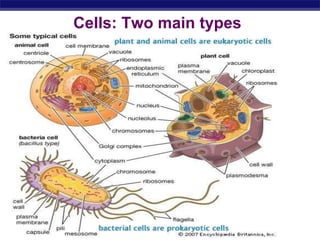
- 1. Regents Biology Cells: Two main types
- 3. Regents Biology Prokaryotes 1. NO nucleus 1. unicellular 1. NO membrane-bound organelles (just ribosomes) 2. Forerunner to eukaryotic cells (smaller, simpler) 3. DNA – single strand and circular -Bacteria, archaea
- 4. Regents Biology Eukaryotes 1.Has a nucleus with a nuclear envelope 2.Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes 3.Have membrane bound organelles 4.DNA – double-stranded and forms chromosomes (highly organized) 5. Uni- OR multicellular organisms animals, plants, fungi…
- 5. Regents Biology Similarities 1. Contain all four biomolecules (lipids, carbs, proteins, and nucleic acids) 1. Have ribosomes (eukaryotes 80S, prokaryotes 70S) 2. Have DNA 3. Similar Metabolism 4. Can be unicellular 5. Have cell/plasma membranes or cell wall
- 6. Regents Biology Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
- 7. Regents Biology Organelles Organelles do the work of cells each structure has a job keeps the cell alive; keeps you alive Model Animal Cell
- 8. Regents Biology cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals Cytoplasm lattice-like material holding organelles in place
- 9. Regents Biology Cell membrane Function Barrier Control O2,CO2, food, H2O, nutrients, waste Communication between cells Structure phospholipid bilayer receptor molecules proteins lipid “tail” phosphate “head”
- 10. Regents Biology Vesicles Function Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Structure membrane sac large food particle vesicle Proteins etc Endocytosis! Exocytosis!
- 11. Regents Biology Vacuoles: Storage plant cells contractile vacuole animal cells central vacuole food vacuoles
- 12. Regents Biology cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals cytoplasm lattice material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles storage transport
- 13. Regents Biology Lysosomes Function little “stomach” of the cell digests macromolecules “clean up crew” of the cell cleans up broken down organelles Structure vesicles of digestive enzymes only in animal cells synthesized by rER, transferred to Golgi Where old organelles go to die! lyso– = break apart –some = body
- 14. Regents Biology Lysosomes white blood cells attack & destroy invaders = digest them in lysosomes 1974 Nobel prize: Christian de Duve Lysosomes discovery in 1960s 1960 | 1974
- 15. Regents Biology When things go bad… Diseases of lysosomes are often fatal digestive enzyme not working in lysosome picks up biomolecules, but can’t digest one lysosomes fill up with undigested material grow larger & larger until disrupts cell & organ function lysosomal storage diseases more than 40 known diseases example: Tay-Sachs disease build up undigested fat in brain cells
- 16. Regents Biology But sometimes cells need to die… Lysosomes can be used to kill cells when they are supposed to be destroyed some cells have to die for proper development in an organism apoptosis “auto-destruct” process lysosomes break open & kill cell ex: tadpole tail gets re-absorbed when it turns into a frog ex: loss of webbing between your fingers during fetal development
- 17. Regents Biology Fetal development 15 weeks 6 weeks syndactyly
- 18. Regents Biology Apoptosis programmed destruction of cells in multi- cellular organisms programmed development control of cell growth example: if cell grows uncontrollably this self-destruct mechanism is triggered to remove damaged cell cancer must over-ride this to enable tumor growth
- 19. Regents Biology
- 20. Regents Biology lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals cytoplasm lattice-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport storage
- 21. Regents Biology Making Energy Cells must convert incoming energy to forms that they can use for work mitochondria: from glucose to ATP chloroplasts: from sunlight to ATP & carbohydrates ATP = active energy carbohydrates = stored energy + ATP ATP
- 22. Regents Biology Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Important to see the similarities transform energy generate ATP double membranes = 2 membranes semi-autonomous organelles move, change shape, divide internal ribosomes, DNA & enzymes
- 23. Regents Biology Mitochondria Function make ATP energy from cellular respiration sugar + O2 ATP fuels the work of life Structure double membrane in both animal & plant cells ATP
- 24. Regents Biology lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals cytoplasm lattice-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2
- 25. Regents Biology Plants make energy two ways! Mitochondria make energy + O2 from sugar cellular respiration sugar + O2 ATP Chloroplasts make energy + sugar from sunlight photosynthesis sunlight + CO2 ATP & sugar ATP = active energy sugar = stored energy build leaves & roots & fruit out of the sugars ATP sugar ATP
- 27. Regents Biology Dividing Mitochondria Who else divides like that? What does this tell us about the evolution of eukaryotes?
- 28. Regents Biology Mitochondria Almost all eukaryotic cells have mitochondria there may be 1 very large mitochondrion or 100s to 1000s of individual mitochondria number of mitochondria is correlated with aerobic metabolic activity more activity = more energy needed = more mitochondria What cells would have a lot of mitochondria? active cells: • muscle cells • nerve cells
- 29. Regents Biology Mitochondria are in both cells!! animal cells plant cells mitochondria chloroplast
- 30. Regents Biology Chloroplasts Function photosynthesis generate ATP & synthesize sugars transform solar energy into chemical energy produce sugars from CO2 & H2O Semi-autonomous moving, changing shape & dividing can reproduce by pinching in two Who else divides like that? bacteria!
- 31. Regents Biology
- 32. Regents Biology Endosymbiosis theory Mitochondria & chloroplasts were once free living bacteria engulfed by ancestral eukaryote Endosymbiont cell that lives within another cell (host) as a partnership evolutionary advantage for both one supplies energy the other supplies raw materials & protection Lynn Margulis U of M, Amherst 1981 | ??
- 33. Regents Biology Endosymbiosis theory Evolution of eukaryotes
- 34. Regents Biology Endosymbiosis Evidence • Mitochondrial has its own DNA • Mitochondrial DNA more similar to bacterial DNA than nuclear DNA of cell • Mitochondria divide by binary fission, not mitosis
- 35. Regents Biology central vacuole storage: food, water or waste mitochondria make ATP in cellular respiration chloroplast make ATP & sugars in photosynthesis cell wall support cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals lysosome digestion & clean up cytoplasm
- 36. Regents Biology Cells need workers (proteins)! Making proteins to run daily life & growth, the cell must… read genes (DNA) build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors organelles that do this work… nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus
- 37. Regents Biology Proteins do all the work! cellsDNA proteins one of the major job of cells is to make proteins, because… proteins do all the work! signals structure enzymes receptors
- 38. Regents Biology Nucleus Function control center of cell protects DNA instructions for building proteins Structure nuclear membrane nucleolus ribosome factory chromosomes DNA
- 39. Regents Biology Ribosomes on ER Ribosomes Function protein factories Eukaryotes have 80S, prokaryotes 70S read instructions to build proteins from DNA Structure 2 subunits some free in cytoplasm some attached to ER large subunit small subunit
- 40. Regents Biology Endoplasmic Reticulum Function part of protein factory helps complete the proteins makes membranes Structure rough ER ribosomes attached works on proteins smooth ER makes membranes
- 41. Regents Biology lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 nucleus protects DNA controls cell ribosomes builds proteins ER helps finish proteins makes membranes
- 42. Regents Biology transport vesicles vesicles carrying proteins Golgi Apparatus Function finishes, sorts, labels & ships proteins like UPS headquarters shipping & receiving department ships proteins in vesicles “UPS trucks” Structure membrane sacs
- 43. Regents Biology cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals cytoplasm lattice material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 nucleus protects DNA controls cell ribosomes builds proteins ER helps finish proteins makes membranes Golgi apparatus finishes, packages & ships proteins lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling
- 44. Regents Biology central vacuole storage: food, water or waste mitochondria make ATP in cellular respiration chloroplast make ATP & sugars in photosynthesis cell wall support cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals Golgi apparatus finish & ship proteins nucleus control cell protects DNA endoplasmic reticulum processes proteins makes membranes lysosome digestion & clean up cytoplasm ribosomes make proteins