Uncollectable account expense
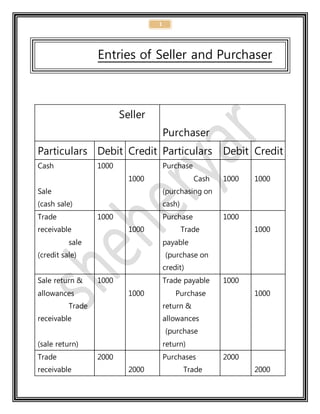
- 1. 1 Entries of Seller and Purchaser Seller Purchaser Particulars Debit Credit Particulars Debit Credit Cash Sale (cash sale) 1000 1000 Purchase Cash (purchasing on cash) 1000 1000 Trade receivable sale (credit sale) 1000 1000 Purchase Trade payable (purchase on credit) 1000 1000 Sale return & allowances Trade receivable (sale return) 1000 1000 Trade payable Purchase return & allowances (purchase return) 1000 1000 Trade receivable 2000 2000 Purchases Trade 2000 2000
- 2. 2 Sale (credit sale to KLM) payable (purchase from KLM) Cash Sale return & allowances Trade Receivable (on-settlement of defective goods & Note: Sale return and allowance account is revenue account. 1400 600 2000 Trade payable Purchase return & allow Cash (settlement of defective goods ) Note: Purchase return and allowance expense A/C is expense contra account. 2000 600 1400 Trade receivable Allowance & sale discount Sale 4000 1000 5000 Purchase Allowance & sale discount Trade receivable 5000 1000 4000
- 3. 3 Cash Sale discount & Allowance Trade receivable Credit term 2/10 , N/30 Sale made on 01-03-2001 Payment received 11-03- 2001 980 20 1000 Trade payable Purchase discount & allow Cash Credit term 2/10 , N/30 Sale made on 01-03-2001 Payment received 11-03- 2001 1000 20 980 Note: 2/10-N/30 credit-term, 2% interest on every 20 days 18% 2x18=36=36% Example:
- 4. 4 Present entries in general journal form for the following related transactions of Ramzan Decorators, recording merchandise purchases returns and allowances in the purchases account. a) Purchases PRs 800 of fabrics from Pak Mills on credit, terms 2/10- N/30. b) Paid the amount owed on the invoice within the discount period. c) Discovered that many of the fabrics were not colour fast and returned items with an invoice price of PRs 450, receiving credit d) Purchased PRs 350 of fabrics from Pak Mills on credit, terms 2/10- N/30. e) Received a cheque for the balance owed from the return in (c), after deducting for the purchase in (d). Solution: Particulars Debit Credit Purchase 800
- 5. 5 Trade payable (Purchase fabrics on credit-terms 2/10-N/30) 800 Trade payable Purchase return & discount Cash (Paid payment in discount period) 800 16 784 Trade payable Purchase discount & allowances 441 09 450 Purchases Trade payable Purchase discount & allowance ( Purchase fabrics on credit term 2/10-N/30) 350 343 07 Cash Trade payable 98 98 Trade Payable Account
- 6. 6 800 441 98 800 343 1143 1143 Uncollectible account expense Definition: When a business or company does not receive payment for goods or services, the transaction must be recorded as an expense for unpaid balance. Accounts receivable that cannot be collected are called Uncollectible Accounts. The amount of accounts receivable not collected is recorded as an expense in the Uncollectible Accounts Expense
- 7. 7 Uncollectible Account Expense, also known as a bad-debt expense At the end of the fiscal year, a business does not know which customer accounts will become uncollectible, so a business can calculate an estimate amount of uncollectible accounts expense. Before an account is classified as uncollectible, it usually becomes a "doubtful" account. Companies and banks keep a cash reserve for these accounts, which is a contra account to the loan or receivable account. Once an account is deemed uncollectible, it must be written off. Estimating uncollectible accounts expense does two things: Reports a balance sheet amount for Accounts Receivable that reflects the amount the business expects to collect in the future. Recognizes the expense of uncollectible accounts in the same period in which the related revenue is recorded. We record uncollectible accounts with two methods Direct method & Direct write off method Provision method Direct Method: When a business is unable to collect payment on goods and services that were sold on credit to its customers, it "writes off," or recognizes this loss on its books. The direct write-off of Uncollectible expense or
- 8. 8 bad debt is a method commonly used by small businesses and companies that are not required to use generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, to maintain their books. Direct write-off method is one of the two most common accounting techniques of debts treatment. In the direct write-off method, uncollectible accounts receivable are directly written off against income at the time when they are actually determined as bad debts or Uncollectible expense. When debt is determined as uncollectible, a journal entry is passed in which bad debts expense account or Uncollectible account expense account is debited and accounts receivable account is credited as shown below. Direct write-off method does not use Any allowance or reserve account. Although the direct write-off method is simple, it has a major drawback. Often it violates the matching principle of accounting because it recognizes bad debt expense which is partly related to previous accounting period. For example if sales are made at the end of accounting year 20X1, bad debts will be realized in the beginning months of accounting year 20X2. Thus the use of direct write-off method would cause deduction of expenses of previous period against Uncollectible account expense —— Accounts Receivable ——
- 9. 9 revenue of current period which is contrary to the matching principle of accounting. Since this method is not according to GAAP, it not advised to use direct write-off method. Instead, the allowance method of bad debts treatment is preferred. Example: Company A has attempted to collect $6,350 from Company XYZ for several months. Company A's collection department has been informed that Company XYZ has gone out of business, and they have instructed the process owners to write off the amount owed. For income tax purposes, the journal entry to account for this write-off would be: Date Account Debit Credit 3/31/20XX Un collectible account expense $6,350 Accounts receivable: company XYZ $6,350 Write off of Company XYZ
- 10. 10 Examples: 07-02-2014 Using direct write off method: 10-07-2014 Note: Uncollectible account expense shows in income statement as a marketing expense. Provision or Allowance method: The provision method is one of the two common techniques of accounting for bad debts, the other being the direct write-off method. Provision method is a better alternative to the direct write-off method because it is according to the matching principle of accounting. In provision method, the doubtful debts are estimated and Uncollectible Trade receivable Sale (sale on credit) 1000 1000 Uncollectible account expense account Trade receivable (write off) 1000 1000
- 11. 11 account expense is recognized before the debts actually become uncollectible. Uncollectible expense is recognized early because bad debts are probable and they can be estimated to a fairly accurate extent therefore they fulfill the criteria required for recognition of contingent losses and it is necessary to recognize Uncollectible account expense. Recognition Entry The first step in the provision method is to pass an adjusting entry at the end of an accounting period to recognize estimated bad debts expense. Unlike direct write-off method, we do not credit accounts receivable at this stage because it is actually a control account of many individual debtor accounts and we do not yet not know which particular debtor will make a default. We only know the estimated amount of receivables which are likely to end up uncollected. Therefore a provision account called provision for doubtful accounts is credited in the adjusting entry. Thus: The Uncollectible expense account, just like any other expense account, is closed to income summary account of the period. The allowance for doubtful debts is contra-asset account. It is presented on balance sheet by subtracting it from accounts receivable as shown below:7 Uncollectible account expense 600 Provision for Doubtful Accounts 600
- 12. 12 Trade Receivable $15,000 Less: Provision for Doubtful Accounts − 600 Accounts Receivable, net $14,400 Write-off Entry In the next period, when a debt is actually determined as uncollectible, the following journal entry is passed to write it off. As more and more debts are written off, the balance in the provision account decreases. Recovered Bad Debts When any bad debt is recovered, two journal entries are passed. The first one reverses the write-off entry and the second one is a routine journal entry to record collection. Thus: Provision for Doubtful Debts 70 Trade Receivable 70 Trade Receivable 70 Provision for Doubtful Debts 70 Cash 70 Trade Receivable 70
- 13. 13 Examples: 1: 07-12-2014 31-12-2014 Adjusting entry In balance sheet: Trade receivable 100000 Less: Provision for doubtful account 40000 Balance show’s in balance Sheet 96000 In income statement: Balance show’s as Uncollectible account expense 40,000 2: 31-12-2001 Trade receivable 100000 Trade receivable 100000 Sale 100000 Uncollectible account expense 40000 Provision for doubtful account 40000
- 14. 14 Less: Doubtful debt 5000 95000 31-12-2001 Closing entry: 2002: 07-03-2002 Note: In provision method we can’t touch uncollectible account expense throughout the year. 10-07-2002 31-12-2002 Trade receivable 70000 Less: Provision for doubtful debt 6000 64000 Uncollectible account expense 5000 Provision for doubtful account 5000 Income summary account 5000 Uncollectible account expense 5000 Provision for doubtful account 1000 Trade receivable 1000 Provision for doubtful account 4500 Trade receivable 4500 Uncollectible account expense 6500
- 15. 15 Provision for doubtful account Uncollectible account expense Uncollectible account expense 3: 7-02-2003 Provision for doubtful debt 6500 5000 B 5000 5000 (balance of 2001) 5000 1000 4500 6000 5000 B 6500 11500 11500 6000 B 5000 5000 5000 5000 6500 6500 6500 6500 Provision for doubtful debt 500
- 16. 16 10-09-2003 07-11-2003 31-12-2003 Trade receivable 90000 Provision for doubtful debt 10000 80000 (Assume) Trade receivable 500 Provision for doubtful debt 1500 Trade receivable 1500 Provision for doubtful debt 2000 Trade receivable 2000 5000 B 5000 5000 (balance of 2001) 5000 1000 4500 6000 5000 B 6500
- 17. 17 31-12-2003 On receiving cash from customer treated as defaulter In provision method: 06-07-2003 In direct write off method: 11500 11500 6000 B 500 8000 1500 2000 10000 14000 14000 B 10000 Uncollectible account expense 8000 Provision for doubtful account 8000 Trade receivable 5000 Provision for doubtful account 5000 Cash 5000 Trade receivable 5000
- 18. 18 06-07-2003 Trade receivable 5000 Uncollectible account expense 5000 cash 5000 Trade receivable 5000
