Body coordination
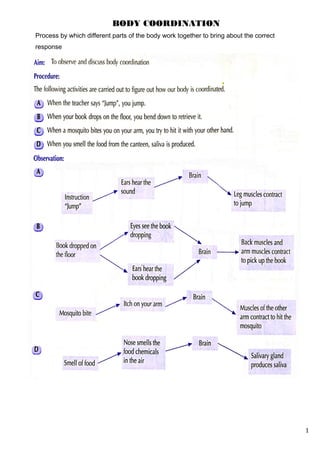
- 1. 1 BODY COORDINATION Process by which different parts of the body work together to bring about the correct response
- 2. EXAMPLE : 2 Detect the stimulus Carry out the response Changes detected are called STIMULI Eg : light , heat , sound , pressure , touch , chemicals
- 3. Body coordination is important because: (a) It enables our body to respond to changes in our surroundings. (b) It regulates appropriate responses to these changes. (c) It protects our body from injuries. ACTIVITY Q1 : Figure 2.3 shows a boy accidentally hammering his hand (a) What is the stimulus in this reaction? (b) What is the response? (c) Which part of the body coordinates this action? Q2 : Figure 2.4 shows a boy being chased by a dog. 3
- 4. (a) What is the stimulus in the diagram given above ? (b) What is the response? (c) Which part of the body coordinates this action? Q3 : Walking is an activity that all of us carry out everyday. (a) Name the systems that control and regulate this activity. (b) Explain how the systems you named in 3(a) help to control and regulate this activity. 4 HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM
- 5. 5
- 6. MIND MAP : HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM MIND MAP : NEURONE 6
- 7. COMPARISON BETWEEN THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF NEURONES ACTIVITY Q1 . (a) Name the components of the central nervous system. (b) Name the components of the peripheral nervous system. (c) To which system do the spinal nerves and the cranial nerves belong to? Q2. (a) What is the smallest functional unit in the nervous system? (b) Draw a labelled diagram of that functional unit. Q3. (a) Name the three types of neurones present in our nervous system. (b) What is the function of each type of neurone named in 3(a)? Aspect Sensory neurone Relay neurone Motor neurone Axon Short Short Long Dendron Long Short Short Cell body In the middle of the neurone, in the dorsal ganglion In the middle of the neurone At one end of the neurone, in the grey matter of the spinal cord Function To transmit impulses from the receptors to the central nervous system To transmit impulses from the sensory neurones to motor neurones To transmit impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors 7
- 8. REFLEX ACTION • An automatic and rapid response to a stimulus that does not involve the brain • Controlled by the spinal cord • Function : To avoid or protect us from serious injuries Example of reflex action 8
- 9. Activity Q1. Which of the following is the correct pathway of body coordination? A Skin Stimulus Brain Response Muscle B Skin Stimulus Response Brain -> Muscle C Stimulus Skin Brain Muscle Response D Stimulus Brain Skin Muscle Response Q2. 9
- 10. Q3 (a) What is a receptor? (b) Give two examples of receptors. Q4 (a) What is an effector? (b) Give two examples of effectors. Q5 Draw a diagram to show the path taken by an impulse in a reflex arc. Q6 (a) What is a reflex action? (b) Give two examples of reflex actions. PROPRIOCEPTORS - sensors that provide information about joint angle, muscle length, and muscle tension • Receptors that are connected to sensory neurons • Respond to stimuli that related to position and movement of the body • Found in : muscles , tendons , ligaments and joints • Function : Help to coordinate muscular activites and maintain body balance and posture • Examples : buttoning shirt , climbing a ladder , tying shoe lace, locking the door ( without looking ) 10
- 11. 11
- 12. ACTIVITY Q1 (a) What are proprioceptors? (b) Name two places in the body where they can be found. Q2 Explain how impulses from the proprioceptors are transmitted. Q3 (a) What is the importance of proprioceptors? (b) Name two occasions when it is very important for a person to keep his balance The human brain 12
- 13. Differences between voluntary and involuntary actions Aspect Voluntary Involuntary Awareness We are aware of the actions We are not aware of the actions Control Action can be controlled Action cannot be controlled Controlled by Controlled by the somatic nervous system Controlled by the autonomic nervous system Stimuli Receives stimuli from the external environment through the sensory organs Receives stimuli from the internal organs Examples • Writing • Dancing • Constriction of the pupil • Beating of the heart ACTIVITY Q1 The diagram shows a human brain. 13
- 14. Name the parts labelled X, Y and Z and list their functions. Q2 (a) What is an involuntary action? (b) Give one example of an involuntary action. (c) State three differences between involuntary and voluntary actions. Q3 Name five possible effects due to injury to the brain. Endocrine system • Consists of endocrine gland • gland without ducts which secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream 14
- 16. 16
- 17. COMPARISON BETWEEN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Hormones Functions of hormones Effects of excessive hormones Effects of deficiency of hormones Growth hormone (from the Pituitary gland • Controls the qrowth of muscles and bones • Stimulates the activities of other endocrine qlands • Controls the reabsorption of water • Gigantism in childhood • Acromegaly in adults • Dwarfism Thyroxin (from the thyroid gland) • Controls the metabolism of the body • Ensure normal physical and mental development • Goitre – swelling the thyroid gland • cretinism: Stunted physical and mental development Insulin (from the pancreas) • Controls the level of qlucose in the blood • hypoglycaemia -Low blood glucose level • Diabetes mellitus -High blood glucose level Adrenaline (from the adrenal glands) • Prepares the body for action in an emerqency • Extreme tiredness - Oestrogen (from the ovaries) • Stimulates the development of female secondary sexual characteristics • Excessive female characteristics and early puberty • Deters the development of female secondary sexual characteristics Progesterone (from the ovaries) • Controls the menstrual cycle • Failure in delivery at the correct time Menstrual problems Abortion of embryo Testosterone (from the testis glands) • Controls the development of male sex orqans • Produces sperms • Stimulates the development of male secondary sexual characteristics • Excessive male characteristics and early puberty • Deters the development of male secondary sexual characteristics • Reduced sperm production 17 NERVOUS SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM SIMILARITIES • Control and coordinate activites in body • Perform appropriate reactions when being stimulated DIFFERENCES COMPONENTCOMPONENT
- 18. ACTIVITY Q1 Identify the following hormones: (a) The hormone that prepares the body for emergency (b) The hormone that reduces the amount of glucose in the blood (c) The hormone that controls the metabolic rate of the body (d) The hormone that controls the formation of male secondary sexual characteristics (e) The hormone that controls the menstrual cycle Q2 State the function of a hormone produced by: (a) The thyroid gland (b) The ovary (c) The pancreas Q3 Name the diseases caused by: (a) Insufficient insulin (b) Excessive thyroxine (c) Insufficient growth hormones COORDINATION BETWEEN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS 18 FORM OF IMPULSEFORM OF IMPULSE TARGET AREATARGET AREA SPEED OF IMPULSESPEED OF IMPULSE EFFECTIVE PERIODEFFECTIVE PERIOD
- 19. EFFECT PF DRUG ABUSE ON BODY COORDINATION Drug abuse : Taking of drugs in high or excessive dosage for non-medical purposes Groups of drugs Examples The effects on body coordination and the nervous system Stimulants • Caffeine • Cocaine • Nicotine • Amphetamines • Increase the rate of metabolism • Activate the nervous system • Make an individual more active • Cause the same effect as adrenaline Depressants • Heroin • Cannabis Barbiturates • Alcohol • Reduce stress • Calm the mind • Slow down the flow of nerve impulses 19
- 20. • Slow down responses to stimuli • Make an individual feel sleepy and less anxious Anti- depressants • Morphine • Opium • Relieve pain • Ease mental stress • Induce sleep Hallucinogens • Cannabis • Ecstasy • Diethylamide lysergic acid (LSD) • Cause imaginations • Change the pathways of impulses in the brain • Cause unpredictable behaviour Inhalants • Petroleum • Organic solvents • chloroform • Cause hallucinations • blackouts • Unconsciousness 20
- 21. 21
