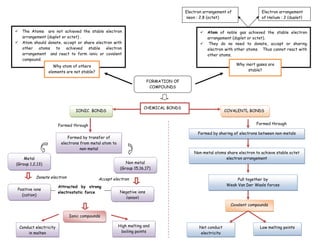
Chemical bonds
- 1. Electron arrangement of Electron arrangement neon : 2.8 (octet) of Helium : 2 (duplet) The Atoms are not achieved the stable electron Atom of noble gas achieved the stable electron arrangement (duplet or octet) . arrangement (duplet or octet). Atom should donate, accept or share electron with They do no need to donate, accept or sharing other atoms to achieved stable electron electron with other atoms. Thus cannot react with arrangement and react to form ionic or covalent other atoms. compound. Why atom of others Why inert gases are elements are not stable? stable? FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS CHEMICAL BONDS IONIC BONDS COVALENTL BONDS Formed through Formed through Formed by sharing of electrons between non-metals Formed by transfer of electrons from metal atom to non-metal Non-metal atoms share electron to achieve stable octet Metal electron arrangement (Group 1,2,13) Non metal (Group 15,16,17) Donate electron Accept electron Pull together by Attracted by strong Weak Van Der Waals forces Positive ions electrostatic force Negative ions (cation) (anion) Covalent compounds Ionic compounds Conduct electricity High melting and Not conduct Low melting points in molten boiling points electricity
- 2. Positive ion (cation) Atom Negative ions (anion) Donate electron accept electron (Neutral) Sodium ions , Na+ Sodium atom, Na Chlorine atom, Cl Chlorine atom, Cl- - + accept electron Donate electron 2.8 2.8.1 2.8.7 2.8.8 Charge of 11 protons = +11 Charge of 11 protons = +11 Charge of 17 protons = +17 Charge of 17 protons = +17 Charge of 10 electrons = -10 Charge of 11 electrons = -11 Charge of 17 electrons = -17 Charge of 18 electrons = -18 Total charge = +1 Total charge =0 Total charge =0 Total charge = -1 Formation of Sodium Chloride Formation of Magnesium Chloride Na NaCl Cl Atom Magnesium has 2 valence electron and atom Cl has 7 valence electron 2.8.1 Electron arrangement 2.8.7 Electron arrangement of magnesium atom is 2.8.2 Magnesium atom donate two electron to two atom chlorine Donate one electron Accept one electron form magnesium ion, Mg2+ and achieve a stable octet electron to achieve the stable arrangement. 2.8 octet electron 2.8 Mg Mg2+ + 2e arrangement Electron arrangement of Chlorine atom is 2.8.7 Draw the diagram of the formation of sodium chloride, NaCl Each chlorine atom accept one electron from magnesium atom + to form chloride ion, Cl- and achieve the stable octet electron - arrangement. Cl + e Cl- The magnesium ion, Mg2+ and chloride ion, Cl- are attracted to each other with strong attraction force to form ionic compound, Magnesium chloride MgCl2 - 2+ - Sodium ion, Na+ and chloride ion, Cl- are attracted to each other with strong attraction force to form sodium chloride compound, NaCl
