Cell membranes and transport
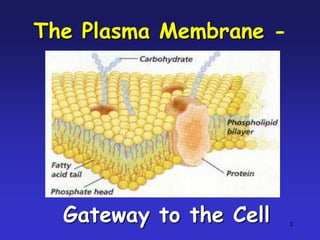
- 1. The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1
- 2. Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2
- 3. Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3
- 4. Homeostasis • Balanced internal condition of cells • Also called equilibrium • Maintained by plasma (or cell) membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell 4
- 5. Functions of Plasma Membrane Protective fence Controls transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable) Allow cells recognize “friend or Foe” Provide anchoring sites the cytoskeleton support framework 5
- 6. Functions of Plasma Membrane Provide a tie on site for enzymes Place for cells to bind together Contains the cytoplasm (fluid in cell) 6
- 7. Structure of the Cell Membrane Peripheral protein Lipid Bilayer Integral Protein 7
- 8. Phospholipids-3 models Make up the cell membrane Contains 2 fatty acid chains that are nonpolar Head is polar & contains a –PO4 group 8
- 9. FLUID MOSAIC MODEL Fluid mosaic model FLUID- because individual phospholipids and proteins can move around freely within the layer, like it’s a liquid. MOSAIC-little pieces put together in a pattern 9
- 10. • Mosaic 10
- 11. Cell Membrane Polar heads are hydrophilic “water loving” Nonpolar tails are hydrophobic “water fearing” Makes membrane “Selective” in what crosses11
- 12. Cell Membrane The cell membrane is made of 2 layers of Hydrophobic molecules phospholipids called the pass easily; hydrophillic lipid bilayer DO NOT 12
- 13. Solubility • Materials that are soluble in lipids can pass through the cell membrane easily 13
- 14. Selectively Permeable Membrane Small molecules like water move across easily, most larger molecules need help- and need energy to be added so they can cross. 14
- 15. IMPORTANT! Kinds of Transport Across Cell Membranes 15
- 16. 1. Passive Transport Movement of substances across the cell membrane without any input of energy on the part of the cell. 16
- 17. 2. Simple Diffusion • Requires NO energy • Molecules move from area of HIGH to LOW concentration or down the concentration gradient. 17
- 18. Simple Diffusion continued • Concentration Gradient is the difference ( change) in the concentration of a substance from one location to another. 18
- 19. DIFFUSION Diffusion is a PASSIVE process which means no energy is used to make the molecules move, they have a natural KINETIC ENERGY 19
- 20. Diffusion of Liquids 20
- 21. Diffusion through a Membrane Cell membrane Solute moves DOWN concentration gradient (HIGH to LOW) until equilibrium is reached 21
- 22. Osmosis Diffusion across a membrane • Diffusion of water across a membrane • Moves from HIGH Semipermeable water potential membrane (low solute) to LOW water potential (high solute) 22
- 23. A Hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of dissolved particles than the cell. A Hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of dissolved particles than the cell. An Isotonic solution has the same concentration of dissolved particles as the cell. 23
- 24. Diffusion of H2O Across A Membrane High H2O potential Low H2O potential Low solute concentration High solute concentration 24
- 25. Cell in Isotonic Solution 10% NaCL ENVIRONMENT 90% H2O CELL NO NET 10% NaCL MOVEMENT 90% H2O What is the direction of water movement? equilibrium The cell is at _______________. 25
- 26. Cell in Hypotonic Solution 10% NaCL 90% H2O CELL 20% NaCL 80% H2O What is the direction of water movement? 26
- 27. Cell in Hypertonic Solution 15% NaCL ENVIRONMENT 85% H2O CELL 5% NaCL 95% H2O What is the direction of water movement? 27
- 28. Cells in Solutions 28
- 29. Isotonic Solution Hypotonic Hypertonic Solution Solution NO NET MOVEMENT OF H2O (equal amounts CYTOLYSIS PLASMOLYSIS entering & leaving) (cell rupture) (cell shrinkage) 29
- 30. Osmosis in Red Blood Cells Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic 30
- 31. Osmosis in plant cells In plant cells, plasmolysis results in wilting and osmotic pressure results in turgor pressure. 31
- 32. hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic isotonic hypotonic 32
- 33. Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane 33
- 34. Passive Transport Simple Diffusion Doesn’t require energy Moves high to low concentration Example: Oxygen or water diffusing into a cell and carbon dioxide diffusing out. 34
- 35. Facilitated diffusion Doesn’t require energy Uses transport proteins to move high to low concentration Examples: Glucose or amino acids moving from blood into a cell. 35
- 36. Proteins Are Critical to Membrane Function 36
- 37. Types of Transport Proteins • Channel proteins are embedded in the cell membrane & have a pore for materials to cross • Carrier proteins can change shape to move material from one side of the membrane to the other 37
- 38. Facilitated Diffusion Molecules will randomly move through the pores in Channel Proteins. 38
- 39. Facilitated Diffusion • Some Carrier proteins do not extend through the membrane. • They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. 39
- 40. Carrier Proteins • Other carrier proteins change shape to move materials across the cell membrane 40
- 41. Remember this? It’s Facilitated Passive Transport. 41
- 42. Passive Transport Review Movement of particles across the cell membrane without energy input on the part of the cell. 42
- 43. Passive Transport Review Three major types: 1) Diffusion 2) Osmosis 3) Facilitated Diffusion 43
- 44. Active Transport 44
- 45. Active Transport Requires energy or ATP Moves materials from LOW to HIGH concentration AGAINST concentration gradient 45
- 46. Major Types • Endocytosis (including pinocytosis and phagocytosis) • Exocytosis • Pumps (including proton pump and sodium-potassium pump) 46
- 47. Endocytosis 47
- 48. Endocytosis • Endocytosis is the process of taking liquids or larger molecules into a cell by engulfing them in a membrane. • This is done when the cell membrane makes a pocket around the substance that breaks off inside the cell. • This pocket is called a vesicle. 48
- 49. Moving the “Big Stuff” Large molecules move materials into the cell by one of three forms of endocytosis. 49
- 50. Pinocytosis • Endocytosis that involves movement of liquids. • Called “Cell Drinking” 50
- 51. Pinocytosis Most common form of endocytosis. Takes in dissolved molecules as a vesicle. 51
- 52. Example of Pinocytosis pinocytic vesicles forming mature transport vesicle 52 Transport across a capillary cell (blue).
- 53. Endocytosis – Phagocytosis •Endocytosis that involves taking in large particles such as food, bacteria, etc. into vesicles •Called “Cell Eating” 53
- 54. Phagocytosis About to Occur 54
- 55. Phagocytosis - Capture of a Yeast Cell (yellow) by Membrane Extensions of an Immune System Cell (blue) 55
- 56. Exocytosis • moving things out • essentially the opposite of endocytosis • Molecules are moved out of the cell by vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. • This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another 56
- 57. Exocytosis 57
- 58. Exocytosis Exocytic vesicle immediately after fusion with plasma membrane. 58
- 59. Exocytosis The opposite of endocytosis is exocytosis. Large molecules that are manufactured in the cell are released through the cell membrane. Inside Cell Cell environment 59
- 60. Pumps • Pumps are similar to facilitated diffusion in that they use transport proteins. • Pumps use proteins to move materials against the concentration gradient. 60
- 61. Three Types of Pumps • Sodium-Potassium Pump (3 Na out, 2 K in) • Proton Pump • Contractile Vacuole (pumps excess water out of single-cell organisms) 61
- 62. Sodium-Potassium Pump 3 Na+ pumped out for every 2 K+ pumped in; creates a membrane potential 62