Agriculture part 2
- 2. The First Agricultural Revolution- Animal Domestication • Animals such as goats, pigs and sheep were domesticated about 8,000 yrs. ago. • Domesticated animals in captivity are very different from their wild counterparts. • Southeast Asia-pigs, water buffalo, chickens, ducks and geese were domesticated.
- 4. • South Asia-cattle, elephants-but never bred in captivity, • Southwest Asia-goats, sheep and camel • Central Asia-yak, horse, goats, sheep and reindeer • Meso America and South America-llama, alpaca, pig and turkey • Africa-guinea fowl-only became herders after cattle were brought in from SW Asia • Total-only about 40 species were
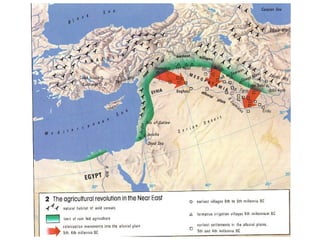
- 6. World Areas of Agricultural Innovations Carl Sauer identified 11 areas where agricultural innovations occurred.
- 7. Chief Source Regions of Important Crop Plant Domestications
- 8. • World-wide most farmers are subsistence-growing Subsistence Farming just enough to feed their families. • They find building material and fuel in the natural environment-no cash economy • Small fields-intensive farming on land they often don’t own. • Methods and tools used are generally very low tech. • Found in South & Central America, Africa, South Asia, and South
- 9. On the Greek island of Crete, a peasant plows a field with a donkey
- 12. Shifting Agriculture-Slash & Burn, Patch or Milpa • Tropical areas-red soil is heavily leached. • Plot of land is cleared by burning-ash replenishes soil. • A type of crop rotation- tubers in warm tropics, grains in humid subtropics, fruit in cooler regions. • Not nomadic-central village with parcels of land worked in succession • Conserves forests & soil,
- 13. • Intertillage spreads food production over the farming season • It reduces the loss from disease or pests or drought. • It helps control soil erosion and soil depletion. • Hill planted crops have deeper root systems and tall stalks while flat earth crops are spreaders. • No expensive fertilizer, pesticides, herbicides
- 14. • Agricultural Societies are classified as: – Subsistence or Primitive – Intermediate or Traditional – Developed or Modern • Colonial Powers-Bad Points – Tried to compel subsistence farmers to modernize by charging them taxes – Made them devote valuable land to cash crops like cotton • Colonial Powers-Good Points – Conducted soil surveys – Built irrigation systems – Established lending agencies to loan money to farmers
Notes de l'éditeur
- With sedentary communities wild animals kept as pets or ceremonial sacrifices-some wild animals hung around as scavengers of food and gradually were kept as protection against other predators or to aid in the hunt. Even today-in African Wildlife Preserves-wild animals hang around camps at night and scatter by day.
- Top-Zebu Cattle in India Horse drawing a hay rake
- About 8,000 BC man began to select, breed and domesticate and cultivate various species of plants and animals It was a slow, gradual process that occurred at different times in various places-due to climate or soil limitations it did not spread all over the world. World Population increased X16 between 8,000 BC and 4,000 BC due to increased and reliable food supply.
- Iranian farmer harrowing a field with mules
- Crete-a peasant plows a field with a donkey
- Various kinds of maize Oxen pull a plow in Portugal
- Definitions of subsistence vary-Indian and China are not shaded because farmers sell some produce in markets. In equatorial Africa and South America, subsistence allows little of this
- Shifting Cultivation is usually practiced in tropical areas with poor soils-soil fertility is maintained by rotating fields-note burned stumps with corn and beans interplanted. (land cleared is called Swidden) Requires less intense farming or work-but supports a lower population density than traditional farming. To outsiders Slash and Burn appears to be destructive, wasteful and disorganized- there are no neat rows of monocrops-no carefully plowed soil- Instead there are a variety of crops grown next to each other in what appears to be a jumble.
- Not only are crops interplanted, but they are planted at different times, assuring harvest over a long period of time. The variety of crops ensures that there won’t be a catastrophic loss to disease, pest or drought.
- In some areas the forced changes caused famines
