Distribution Management.pptx
- 2. INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT • Distribution management refers to the process of overseeing the movement of goods from supplier or manufacturer to point of sale. It is an overarching term that refers to numerous activities and processes such as packaging, inventory, warehousing, supply chain, and logistics.
- 3. WHAT IS A DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL? • A distribution channel is a chain of businesses or intermediaries through which a good or service passes until it reaches the final buyer or the end consumer. • Distribution channels can be short or long, and depend on the number of intermediaries required to deliver a product or service. • The target for any business is to bring their product or service to the market and make it available for consumers by creating a distribution path or channel. The link between producers and the end consumer is normally intermediaries, such as wholesalers, retailers, or brokers. • A distribution channel must be efficient and effective. It means that transportation and other logistical requirements need to be used at maximum capacity and at the lowest rates possible.
- 4. ROLE OF DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS Distribution channels help in the following ways: (i) Enhance Efficiency: The components of distribution channels enhance the efficiency of the system. A system of manufacturers directly dealing with consumers will be less efficient than the decentralized system involving distribution agents. (ii) Smooth Flow of Goods and Services: The distribution channels smoothen the flow of goods and services by creating possession, time and place utilities. (iii) Reducing Cost of Transactions: The cost of transactions is minimized if they are undertaken regularly. The distribution through intermediates will be possible if products are standardized. The terms and conditions of purchase, sale, payments will be standardized resulting into increased number of transactions. Instead of casual transactions, routine dealings will reduce the cost of marketing.
- 5. (iv) Facilitate Search: The buyers and sellers search for each other in the market to transact for products and services. This function is facilitated by distribution agents. These intermediaries remain in touch with sellers and buyers, thus facilitate exchange. (v) Less Stocks of Goods: In the absence of distribution agents manufacturers are required to keep large stocks of goods. When middlemen enter the chain of distribution then stocks are maintained by large number of intermediaries and it reduces the burden of producers. (vi) Proximity to Consumers: The intermediaries are more near to the consumers as compared to the producers. They are in direct touch with the users of goods and services and understand their reactions to the supplies. The intermediaries help producers in knowing the reactions of consumers to the goods and services brought out by them. This information is of immense value to producers in planning for their products.
- 6. DISCREPANCIES AND DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS Distribution channel members take care of the four discrepancies that exist in the market place:
- 7. • SPATIAL DISCREPANCY- This discrepancy occurs due to the space or distance between the production point of a product or service and its consumption point. • TEMPORAL DISCREPANCY- This refers to the time difference between the production point and the time at which the product may get bought or consumed. • NEED FOR BREAKING THE BULK- To minimize the production costs, products have to be made in large quantities or in bulk. However, consumption of these products is in smaller quantities. There is, therefore, a need to break the bulk into consumable quantities • NEED FOR ASSORTMENT- One company make one set of products in one plant and another set of products in another plant located far away. At the consumer level, when they visit any retail store, they expect all the products of the company at one location.
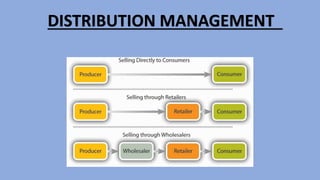
- 8. TYPES OF DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS • There are two major types of distribution channels. One is direct channel and the other one is indirect channel.
- 9. • Direct channel: In the direct channel method, the manufacturer directly sell the goods to the customers. There is no involvement of intermediaries in this distribution. This is also called as zero level distribution. The manufacturer distribute their products mainly by setting up retail outlets and internet selling. This distribution gives a company control over relationships with the customers. The companies using direct distribution channel has higher profits than the companies using indirect distribution channels. But this may suits only for the smaller companies. • Indirect channel: Indirect distribution channel has divided into 3 types according to the usage of intermediaries or channel methods. They are one level, two level and three level channel. In one level channel, manufacturer sells the goods directly to a retailer. Mostly this channel is used by expensive watches and FMCG products. In the two level channel, the manufacturer sells the goods to a wholesaler, the wholesaler to a retailer and then to the customer. The wholesales purchases large volumes from the manufacturer and then distribute them to retailers in small volumes. This channel is mainly used to sell soaps, sugar, cigarette etc. In the three level channel, one more level is added to two level channel in the form of agents. This agents reduce the distance between the manufacturers and wholesaler. This is suitable for very big companies like Toyota, Pepsi etc.
- 12. 1. INTENSIVE DISTRIBUTION- Intensive distribution aims to provide saturation coverage of the market by using all available outlets. For many products, total sales are directly linked to the number of outlets used (e.g., cigarettes, soft drinks etc.). Intensive distribution is usually required where customers have a range of acceptable brands to choose from. In other words, if one brand is not available, a customer will simply choose another. • This alternative involves all the possible outlets that can be used to distribute the product. This is particularly useful in products like soft drinks where distribution is a key success factor. Here, soft drink firms distribute their brands through multiple outlets to ensure their easy availability to the customer. • Hence, on the one hand these brands are available in restaurants and five-star hotels and on the other hand they are also available through countless soft drink stalls, kiosks, sweet marts, tea shops, and so on. Any possible outlet where the customer is expected to visit is also an outlet for the soft drink
- 14. II. SELECTIVE DISTRIBUTION- Selective distribution involves a producer using a limited number of outlets in a geographical area to sell products. An advantage of this approach is that the producer can choose the most appropriate or best-performing outlets and focus effort (e.g., training) on them. • This alternative is the middle path approach to distribution. Here, the firm selects some outlets to distribute its products. This alternative helps focus the selling effort of manufacturing firms on a few outlets rather than dissipating it over countless marginal ones. • It also enables the firm to establish a good working relationship with channel members. Selective distribution can help the manufacturer gain optimum market coverage and more control but at a lesser cost than intensive distribution. Both existing and new firms are known to use this alternative.
- 15. III. EXCLUSIVE DISTRIBUTION- Exclusive distribution is an extreme form of selective distribution in which only one wholesaler, retailer or distributor is used in a specific geographical area. • When the firm distributes its brand through just one or two major outlets in the market, who exclusively deal in it and not all competing brands, it is said that the firm is using an exclusive distribution strategy. This is a common form of distribution in products and brands that seek a high prestigious image. • Typical examples are of designer ware, major domestic appliances and even automobiles. By granting exclusive distribution rights, the manufacturer hopes to have control over the intermediary's price, promotion, credit inventory and service policies. The firm also hopes to get the benefit of aggressive selling by such outlets.
- 16. MARKET INTERMEDIARIES • A marketing intermediary is the link in the supply chain that links the producer or other intermediaries to the end consumer. These parties are used in the selling, promotion or the availability of the goods/services through contractual agreements with the manufacturer. They receive the products at a particular price point, add their margins to it and move it to the next link in the supply chain at the higher price point. They are also known as middlemen or distribution intermediaries. • The four types of marketing intermediaries are agents, distributors, wholesalers and retailers.
- 17. FUNCTIONS OF MARKET INTERMEDIARIES
- 19. There are four generally recognized broad groups of intermediaries: C&FA’s, Distributors, Wholesalers and retailers: 1. C&FA’s- They are basically transporters who act as a mid way point between company and its distributors. They store the goods in a central location for breaking bulk. They take the physical possession of the goods but do not pay for it. 2. Distributors, dealers, stockists, agents Agents or brokers are individuals or companies that act as an extension of the manufacturing company. Their main job is to represent the producer to the final user in selling a product. Thus, while they do not own the product directly, they take possession of the product in the distribution process. They make their profits through fees or commissions. 3. Wholesalers Unlike agents, wholesalers take title to the goods and services that they are intermediaries for. They are independently owned, and they own the products that they sell. Wholesalers do not work with small numbers of product: they buy in bulk and store the products in their own warehouses and storage places until it is time to resell them. Wholesalers rarely sell to the final user; rather, they sell the products to other intermediaries such as retailers, for a higher price than they paid. Thus, they do not operate on a commission system, as agents do. 4. Retailers Retailers come in a variety of shapes and sizes: from the corner grocery store, to large chains like Wal-Mart and Target. Whatever their size, retailers purchase products from market intermediaries and sell them directly to the end user for a profit.