MODEL OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
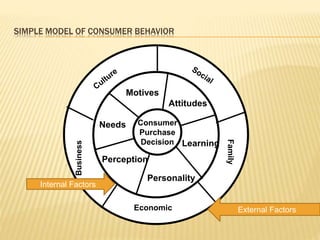
- 1. Consumer Purchase Decision Motives Personality Needs Perception Learning Attitudes Business Economic Family External Factors Internal Factors SIMPLE MODEL OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- 2. External Influences in Consumer Behavior
- 3. INTRODUCTION Consumer purchasing decisions are often affected by factors that are outside of their control but have direct or indirect impact on how we live and what we consume. Consumers are faced with many external influences, including an individual’s culture, subculture, household structure, and groups that he/she associates with. Marketers and business owners call these external influences because the source of the influence comes from outside the person rather than from inside. Today consumers are faced with an array of product selection, and competition is fierce among companies. This is why your understanding of consumer behaviour is vital to the success of your business. Both internal and external factors are inter connected and work together to assist the consumer decision making process.
- 4. INFLUENCING FACTORS IN CONSUMER DECISION MAKING
- 5. GROUP BEHAVIOR Man is social animal who loves to be in groups. Groups represent two or more individuals who share a set of norms, values, or beliefs and interact to accomplish individual or mutual goal. Almost all consumer behavior takes place in a group setting of some sort. A group's norms cover usually all the important behavioural aspects for the functioning of that group and breaking those rules can bring up penalties. When do Group Exert Influence?- The group influence on an individual’s buying behavior depends on three factors- Attitude towards the group: This includes Pride, Status, etc. Nature of the group: This includes, Cohesive, Frequently interacting, Exclusive membership. Nature of the Product: This includes visibility of the product, Uniqueness of the product. Examples: Hardly Davidson Bike group, Friends connection, Aluminas of an institute, etc.
- 7. REFERENCE GROUP A reference group is any person or group that serves as a point of comparison for an individual in forming either general or specific values, attitudes, or a specific guide for behavior. In marketing prospective, reference group are groups that serve as a frames of reference for individuals in their purchase or consumption decisions. Often a distinction is made between group and reference group. Group is defined as two or more individuals who share a set of norms, values, or beliefs and have certain implicit and explicit relationship. Where as reference group is one whose presumed perspective or values are being used by an individual to take decisions. Examples: Shopping with friends, family, educational decisions.
- 8. NATURE OF REFERENCE GROUP Norms Norms’ are generally rules and standards of behavior. Values Values are shared beliefs among group Roles Roles are functions that an individual hold in a group. Status Status is the achieved or ascribed position that the individual holds. Socialization refers to the process by which new members learn the groups system. Power A groups influence on its member behavior is closely related to it power.
- 9. Positive membership Aspiration group Disclaimant group Dissociative group Membership Non-membership Types of Membership Positive membership Aspiration group Disclaimant group Dissociative group Primary Secondary Informal Formal Anticipatory Symbolic Types of aspiration group TYPES OF REFERENCE GROUP
- 10. TYPES OF REFERENCE GROUP An individual can be a member of a reference group such as the family and would be said to be part of a membership group The same individual may aspire to belong to a cricket club and would be said to be part of an aspiration group. A disclaimant group is one to which an individual may belong to or join then reject the group’s values. Also an individual may also regard the membership in a specific group as something undesirable and to avoidable. Such a group is a dissociative group. Primary Informal group: It includes family, peer group, friends etc. Primary formal group: Business group, working colleagues etc. Secondary Informal group: Women kitty party, sports group, etc. Secondary formal: Only frequently meet are not so cohesive in nature.
- 11. CULTURE Culture influences consumers through the norms and values established by the society in which they live. It is the broadest environmental factor that influences consumers behavior. Culture is inculcated- It is passed down from one generation to another through institutions such as family members and religion. As culture evolves, it may be possible to associate benefits of a product or brand with new values or it may be necessary to change the product if that value is no longer gratifying the society. Example: Movies, TV serials, etc. Definition: “Culture as the complex whole that includes knowledge, beliefs, art, law, morals, customs and any other capabilities and habits acquired by humans as a member of a society.”
- 12. CHARACTERISTIC OF CULTURE Culture is invented: It cannot be viewed as something that just exists and is waiting to be discovered. People are responsible for inventing their culture. Culture is learnt: It is not biological feature or instinctive. The process of learning cultural values begin early in life largely through social interactions among families, friends etc. Culture is Shared: Culture by at large is shared by huge group of human beings, generally religion, language, etc. Culture satisfies needs: Culture offers order, direction and guides societies in all phases of life by providing tried and trusted ways of meeting physiological, personal and social needs. Cultures are similar but different : There are certain similarities among all cultures and many elements are present in all societies such as cooking, dressing, etc. Culture is not static: Culture do change gradually and continuously. These change however may be very slow or very fast.
- 13. SUB CULTURE A sub culture is a segment within a culture that share a set if meanings, values or activities that differ in certain respects from those of the overall culture. Sub culture analysis enables the marketing manager to focus on beliefs, values, and customs shared by member of a specific sub group make them desirable candidates for special marketing attention. Sub culture therefore can be defined as a distinct culture group that exists within a layer, complex society as an identifiable segments in terms of its beliefs customs and values. Therefore sub culture are relevant units of analysis for marketing research. Sub culture tend to transfer their beliefs and values from generation to generation. Example: Youths
- 14. Category Sub- Culture Geography North Indian, South Indian, East Indian Regional Gujarati, Marathi, Punjabi, Tamilians, Malayalees, etc. Age Children, Teenagers, Youth, Working professional, etc. Elderly People 50 Plus. Women Children, Teenagers, Youth, Married women, etc. Caste Muslims, Christians, Hindu, etc. EXAMPLES FOR SUB CULTURE
- 15. FAMILY Family is defined as a group of two or more people related by birth, marriage or adoption and residing together. House hold is a family and any unrelated person residing in the same house and consuming food from a common kitchen at least once a day. Eg: Hostel All families are households but all households are not families. An individual’s immediate family members play an essential role in influencing his/her buying behaviour. Family consists of Parent, Siblings, Spouse, Grandparents, Relatives, etc. What an individual imbibes from his parents becomes his/her culture. What he sees from his childhood becomes his habit or in other words lifestyle. Family by far is the most important reference group. It is also the most basic consumption unit for most consumer goods.
- 16. FUNCTIONS OF FAMILY Emotional Support Suitable Life Style Social Relationships Morals and Ethical Values Religious Values Interpersona l Skills Economic Well Being Provides
- 17. FAMILY LIFE CYCLE STAGE Bachelor stage Young, single person <35 Income Expense Newly married Young couples no children Income Expense Full Nest I Young couples with <6 yrs children Income Expense Full Nest II Young couples with 6-12 yrs children Income Expense Full Nest III Old married couples with dependent teenage Income Expense Empty Nest I Old married couples with no children living Income Expense Solitary Survivor Older single person Income Expense
- 18. Communication targeted at Children Communication targeted at Parents Influencer (Children) Initiator (Parents, Children) Decision Maker (Parents, Children) Purchaser (Parents) User (Parents, Children)Information Gathering FAMILY/HOUSEHOLD DECISION MAKING PROCESS
- 19. Some form of class structure or social stratification has existed in all societies throughout human history. A consumer's social class refers to his or her standing in society. It is determined by a number of factors, including education, occupation and income. While income is an important indicator of social class, the relationship is far from perfect since social class is also determined by such factors as place of residence, cultural interests and world-view. Social Class is “defined as the division of members of a society into a hierarchy of distinct status classes, so that members of each class have relatively the same status and members of all other classes have either more or less status. Social Class is often measured on the bases of: relative wealth, Power, prestige. SOCIAL CLASS
- 20. SOCIAL CLASS CATEGORY Life-style Orientations & Purchasing Tendencies of the Different Social Classes. Social Class Life-style Orientation Purchasing Tendencies Upper Class Good taste Graceful living Good Things in life Individual expression Interest in arts and culture Quality merchandise Expensive hobby and recreation equipment Travel Art Middle Class Respectability Conformity social esteem Items in fashion Items related to self presentation Nice clothing, and home items. Working Class Fun oriented Focus on Possessions Work related life Newest appliances Sporting events Food items Lower Class Close family relationships Not interested in world affairs Neighborhood oriented Readily available products Status symbols
- 21. “UPWARD PULL STRATEGY “- TARGETED AT MIDDLE CLASS Middle Class Aspiration s To belong to upper- middle class Prefer Products consumed by upper- middle class Positionin g Upper class symbolism for middle class products
- 22. OPINION LEADERS HIP Opinion leaders are those people who, in a given situation, are able to exert personal influence. They are the ones most likely to influence others through word-of-mouth communication because others seek advice and information from them. Opinion leaders can influence the behavior of consumers positive and negative towards to the product. “Opinion leadership is the process by which one person (the opinion leader) informally influences the actions or attitudes or others, who may be opinion seekers or merely opinion recipients. In marketing context opinion leaders are those people who have used the product by them self. Young consumers often take the assistance of opinion leaders in there purchase. Opinion leadership is category specific – an opinion leader in one product category is often an opinion seeker in others.
- 23. OPINION LEADERSHIP FLOW OF INFORMATION
- 24. SITUATION IN WHERE OPINION LEADERS ARE CONSIDERED
