Organizational structure and comm incl assignm comm kc
- 1. Organizational Structure & Communication CommunicationKnowledgeCenter@Outlook.com
- 2. Organizational Structure & Communication • Organization uses communication to balance with its environment: stakeholders, target audiences. • Structure of organization influences how it reacts on changes in its environment. • This behavior makes it more/ less attractive for its employees, customers, investors etc.
- 3. Assignment • Analyze the structure of your organization and conclude which Structural Configuration according to Mintzberg is valid here. • Explain why you conclude this.
- 4. 7 structural configurations of organizations (Mintzberg p110) 1. Entrepreneurial organization 2. Machine organization 3. Professional organization 4. Diversified organization 5. Innovative organization 6. Missionary organization ? ation s iz ur organ nization 7. Political organization ration fits yo of Orga re igu tu al Co n f the Struc tr uctur erstand Wh ich S uld und ho we s First
- 5. Structure of Organization: Organogram of simple organization
- 6. Structure of Organization: Organogram of simple organization Strategic apex Strategic apex: oversees whole system. Middle line Operating core
- 7. Structure of Organization: Organogram of simple organization Strategic apex Support Techno- Middle line Staff structure Operating core
- 8. Structure of Organization: Organogram of simple organization Ideology (culture) Strategic apex Support Techno- Middle line Staff structure Operating core
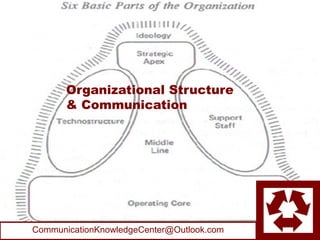
- 9. Six Basic Parts of the Organization (Mintzberg p99)
- 10. Six Basic Parts of the Organization (Mintzberg p98) • Operating core: those people who perform the basic work of producing the products and rendering the services. • Middle Line: a hierarchy of authority between the operating core and the strategic apex. • Strategic Apex: oversees whole system. • Technostructure: analysts outside the hierarchy who perform administrative duties: plan & control. • Support Staff: provides internal services: cafeteria, mailroom, legal counsel, PR, etc. • Ideology: culture; traditions and beliefs of an organization that distinguishes it from other organizations; it infuses a certain life into the skeleton of its structure.
- 11. Assignment • Analyze the structure of your organization and conclude which Structural Configuration according to Mintzberg is valid here. • Explain why you conclude this. • Check Prime Coordinating Mechanism; • Check Key Part of Organization; • Check Type of decentralization • Decide which Structural Configuration seems most appropriate.
- 12. 7 structural configurations of organizations (Mintzberg p110 - 237) Entrepreneurial Start-up Any organization can be a political organization organization at a stage in its existence. Machine McDonald’s; Swiss Railroad organization Diversified Result of merges: ABN Amro; organization ING Adhocracy: no strong hierarchy. Reacts ad hoc Professional University to impulses: no rigid strategy that can’t be organization changed. Opposite of Machine Organization. Innovative = “adhocracy”; Google organization Missionary Norms & beliefs in place of organization standards & procedures; Toyota Political Finding order & integration by
- 13. 7 structural Key Part of configurations Organization (Mintzberg p110) Entrepreneurial Strategic apex organization Machine organization Technostructure Professional Operating core organization Diversified Middle line organization Innovative Support staff organization Missionary Ideology organization Political organization None
- 14. Coor dinating the Six Basic Par ts 1. Mutual Adjustment: coordination by informal communication between two employees. 2. Direct supervision: one person issues orders/ instructions to several others. 3. Standardization of work processes: coordination by specifying work processes of people carrying out interrelated tasks. 4. Standardization of outputs: coordination by specifying results of different work. 5. Standardization of skills (& knowledge): different work is coordinated by offering several employees the same trainings. 6. Standardization of norms: everyone functions according to the same set of beliefs.
- 15. 7 structural Prime Coordination configurations Mechanism (Mintzberg p110) Entrepreneurial Direct supervision organization Machine organization Standardization of work processes Professional Standardization of organization skills Diversified organization Standardization of outputs Innovative organization Mutual adjustment Missionary Standardization of organization norms Political organization None
- 16. Decentralization: diffusion of decision-making power. (Mintzberg p105) • Centralized: all power rests at a single point in an organization. • Decentralized: extent to which power is dispersed among many individuals. In case of rapid change, which form would work best, centralized or decentralized? Why? What could be advantages of a decentralized structure?
- 17. Decentralization: vertical & horizontal (Mintzberg p105) • Vertical decentralization: delegation of formal power down the hierarchy to line managers. • Horizontal decentralization: the extent to which formal or informal power is dispersed out of the line hierarchy to nonmanagers (operators, analysts and support staffers).
- 18. Decentralization: selective & parallel (Mintzberg p105) • Selective decentralization: the dispersal of power over different decisions to different places in the organization. For example: decisions about communication & media are made by the communication department. • Parallel decentralization: the power over various kinds of decisions is delegated to the same place. For example: the communication department is consulted for almost any decision.
- 19. 6 types of decentralization (Mintzberg p105) 1. Vertical & horizontal centralization: all power rests at strategic apex. 2. Limited horizontal decentralization (selective): strategic apex shares some power with technostructure that standardized everybody else’s work. 3. Limited vertical decentralization (parallel): managers of market- based units are delegated the power to control most of the decisions concerning their line units.
- 20. 6 types of decentralization (Mintzberg p105) 4. Vertical & horizontal decentralization: most of the power rests at the operating core. 5. Selective vertical and horizontal decentralization: the power over different decisions is dispersed to various places in the organization, among managers, staff experts, and operators who work in teams at various levels in the hierarchy. 6. Pure decentralization: power is shared more or less equally by all members of the organization.
- 21. 6 types of Che is m ck wh ost ic app h typ decentralization rop e riate of De for ce you ntraliz (Mintzberg p105) r or a gan tion izat ion. 1. Vertical & horizontal centralization 2. Limited horizontal decentralization (selective) 3. Limited vertical decentralization (parallel) 4. Vertical & horizontal decentralization 5. Selective vertical and horizontal decentralization 6. Pure decentralization
- 22. 7 structural Type of configurations Decentralization (Mintzberg p110) Entrepreneurial Vertical and horizontal organization centralization Machine organization Limited horizontal decentralization Professional Horizontal organization decentralization Diversified Limited vertical organization decentralization Innovative Selected organization decentralization Missionary Decentralization organization Political organization Varies
- 23. 7 structural configurations of organizations (Mintzberg p110) Configuration Prime Key Part of Type of Coordination Organization Decentralization Mechanism Entrepreneurial Direct supervision Strategic apex Vertical and organization horizontal centralization Machine Standardization of Technostructure Limited horizontal organization work processes decentralization Professional Standardization of Operating core Horizontal organization skills decentralization Diversified Standardization of Middle line Limited vertical organization outputs decentralization Innovative Mutual adjustment Support staff Selected organization decentralization Missionary Standardization of Ideology Decentralization organization norms Political organization None None Varies
- 24. 7 structural configurations of organizations (Mintzberg p110 - 237) Entrepreneurial Start-up organization Machine McDonald’s; Swiss Railroad organization Diversified Result of merges: ABN Amro; organization ING Professional University organization Innovative = “adhocracy”; Google organization Missionary Norms & beliefs in place of organization standards & procedures; Toyota Political Finding order & integration by organization power, not structure
- 25. Entrepreneurial organization (Mintzberg p117) Structure Strategy • Simple, informal, flexible, with Often visionary process, broadly little staff or middle-line hierarchy deliberate but emergent and • Activities revolving around the flexible in details chief executive, who controls Leader positions malleable personally, through direct organization in protected niches. supervision. Issues Context Responsive, sense of mission • Simple and dynamic But environment. Vulnerable, restrictive • Strong leadership, sometimes charismatic, autocratic. Danger of imbalance toward strategy or operations • Startup, crisis, and turnaround • Small organizations, “local producers”
- 26. Strategy Machine organization Ostensibly planning process, but (Mintzberg p132) that is really strategic programming Structure Resistance to strategic change, Centralized bureaucracy necessary to overlay innovative Formal procedures, specialized work, sharp configuration for turnaround divisions of labor, usually functional groupings, Hence quantum pattern of extensive hierarchy change: long periods of stability Key is technostructure, charged with standardizing interrupted by occasional bursts the work, but clearly separated from middle line of strategic revolution. Also extensive support staff to reduce uncertaintyIssues Context Efficient, reliable, precise, Simple and stable environment. consistent But Usually larger, more mature organization. Rationalized work, rationalizing (but not Obsession with control leads to automated) technical system Human problems in operating External control -> instrument form core, leads to Otherwise can be closed system form. Coordinating problems in administrative center, leads to Common in mass production, mass service, government, organizations in business of control Adaptation problems at strategic and safety. apex.
- 27. Strategy Diversified • Headquarter manages “corporate” organization strategy as portfolio of businesses, (Mintzberg p155) divisions manage individual business strategies. Structure Issues • Market based “divisions” loosely • Resolves some problems of integrated coupled together under central functional structures (spreading risk, headquarters. moving capital, adding and deleting • Divisions run business autonomously , businesses, etc.) subjected to performance control but system that standardizes their outputs. • Conglomerate diversification sometimes • Tendency to drive structures of divisions costly and discouraging of innovation; toward machine configuration, as improvements in functioning of capital instruments of headquarter. markets and boards may make Context independent business more effective than divisions. • Market diversity, especially of products and services. • Performance control system risks driving organization toward socially • Typically found in largest and most unresponsive or irresponsible behavior. mature organizations, especially business corporations but also, • Despite tendency to use in public sphere, increasingly government and other dangers there even greater due to non- public spheres. measurable nature of many goals.
- 28. Professional organization (Mintzberg p174) Structure Strategy Bureaucratic yet decentralized, Many strategies, largely fragmented, dependent on training to standardize the but forces for cohesion too. skills of its many operating Most made by professional judgment professionals. and collective choice, some by Key to functioning is creation of systems administrative fiat. of pigeonholes within which individual Overall strategy very stable but in professionals work autonomously, detail continually changing subject to controls of the profession. Issues Minimal technostructure and middle-line Advantages of democracy and hierarchy, meaning wide spans of autonomy control over professional work, and large support staff, more machinelike, to But support the professionals. Problems of coordination between the Context pigeonholes, of misuse of professional discretion, of reluctance Complex yet stable. to innovate. Simple technical system. Public responses to these problems Often, but not necessarily, service often dysfunctional.
- 29. Innovative organization (Mintzberg p198) Structure • Fluid, organic, selectively decentralized, Strategy “adhocracy” • Primarily learning, or “grassroots” • Functional experts deployed in process. multidisciplinary teams of staff, operators, • Largely emergent, evolving through a and managers to carry out innovative variety of bottom-up processes, projects. shaped rather than directed by • Coordination by mutual adjustment, management. encouraged by liaison personnel, • Characteristic cycles of convergence integrating managers, and matrix structure. and divergence in strategic focus. Context Issues • Complex and dynamic environment, • Combines more democracy with less including high technology, frequent product bureaucracy. change, temporary and mammoth projects. • Effective at innovation • Typically young due to bureaucratic But pressure with aging. • Effectiveness achieved at the price of • Common in young industries. inefficiency. • 2 basic types: 1.operating adhocracy for • Also human problems of ambiguity contract project work; 2. administrative and dangers of inappropriate adhocracy for own project work. transition to another configuration.
- 30. Ideology & Missionary organization (Mintzberg p223) Ideology Missionary organization Rich system of values & beliefs • Clear, focused, inspiring, that distinguishes an distinctive mission. organization • Coordination through Rooted in sense of mission standardization of notms associated with charismatic (“pulling together”), reinforced by leadership, developed through selection, socialization, and traditions and sagas and then indoctrination of members. reinforced through identifications. • Small units (“enclaves”), loosely organized and highly Can be overlaid on conventional decentralized but with powerful configuration, most commonly normative controls. entrepreneurial, followed by innovative, professional and then • Reformer, converter, and cloister machine. forms. Sometimes so strong that it • Threats of isolation on one side, evokes its own configuration: assimilation on the other. The Missionary Organization.
- 31. Politics & Political organization (Mintzberg p236) • “I am no fan of politics in organizations. (…) politics can be seen as an organizational illness, working both against and for the system. On one hand, politics can undermine healthy processes, infiltrating them to destroy them. But on the other, it can also work to strengthen a system, acting like fever to alert a system to a graver danger (…)” • “Political activity can be found in every organization (…).
- 32. Politics & Political organization (Mintzberg p237) Politics Political organization Means of power technically • Conventional notions of concentrated illegitimate, often in self-interest, coordination and influence absent, replaced resulting in conflict that pulls by the play of informal power. individuals or units apart. • Dimensions of conflict – moderate/ intense, Expresses itself in political confined/ pervasive, as well as enduring/ games, some coexistent with, brief – combine into 4 forms: confrontation, some antagonistic to, some that shaky alliance, politicized organization, substitute for legitimate systems complete political arena. of power. • Can trace development of forms through life Usually overload on cycle of impetus, development, resolution of conventional organization, but the conflict. sometimes strong enough to • Politics and political organizations serve a create own configuration: series of functional roles in organizations, Political Organization. especially to help bring about necessary change blocked by legitimate systems of influence. Do you think that informal communication is more or less relevant in Political Organizations than in other organizations? What does that mean for the communication professional?
- 33. Attraction of organization is also dependent on context Context factors (Mintzberg p106- 109) • Age & Size • Technical system • Environment • Power Relevant for Communication & Media professionals who want to promote the organization to employees, customers, investors, etc.
- 34. Hypothesis about Context: Age and Size Find Age & Size of your organization, and conclude if these hypotheses are correct. • The older an organization, the more formalized its behavior. • The larger an organization, the more formalized its behavior. • The larger an organization, the more elaborate its structure. • Structure reflects the age of the industry from its founding. Would you like to work at an old, large organization? Why?
- 35. Hypothesis about Context: Technical System Find out what kind of machines etc. are used in your organization, and conclude if these hypotheses are correct. • The more machines control the work of employees, the more formalized the work & the more bureaucratic the structure. • The more complex the machines, the more elaborate & professional the support staff. • Automation of the operating core transforms a bureaucratic administrative structure into an organic one. Would you like to work at an organization dominated by machines? Why?
- 36. Hypothesis about Context: Environment Find out your organization’s markets, political climate, economic conditions etc., and conclude if these hypotheses are correct. • The more dynamic an organization’s environment, the more organic its structure. • The more complex an organization’s environment, the more decentralized its structure. • The more diversified an organization’s markets, the greater the propensity to split into market- based units. • Extreme hostility in its environment drives any organization to centralize its structure temporarily. Would you like to work at an organization in a dynamic, complex environment? Why?
- 37. Hypothesis about Context: Power Find out powers in the environment of the organization, and conclude if these hypotheses are correct. • The greater the external control of an organization, the more centralized and formalized its structure. • A divided external coalition will tend to give rise to a politicized internal coalition. • Fashion favors the structure of the day (and of the culture) sometimes even when inappropriate. Would you like to work at an organization subject to strong external powers? Why?
- 38. Assignment • Analyze the structure of your organization and conclude which Structural Configuration according to Mintzberg is valid here. • Explain why you conclude this. • Check Prime Coordinating Mechanism; Check Key Part of Organization; Check Type of decentralization & decide which Structural Configuration seems most appropriate. • Then read the accompanying chapter & conclude to which extent this Structural Configuration fits – perhaps the organization also has elements of other Structural Configurations, mention this too.
- 39. Further reading Mintzberg, Henry (1989) Mintzberg on Management, Free Press • Ch6 Deriving Configurations (20p’s) • Ch7 The Entrepreneurial Organization (15p’s) • Ch8 The Machine Organization (21p’s) • Ch9 The Diversified Organization (19p’s) • Ch10 The Professional Organization ( 22p’s) • Ch11 The Innovative Organization (35p’s) • Ch12 Ideology and the Missionary Organization (14p’s) • Ch13 Politics and the Political Organization (16p’s)
Notes de l'éditeur
- Mintzberg Ch6 Deriving Configurations (20p ’s) Mintzberg Ch7 The Entrepreneurial Organization (15p ’s) Mintzberg Ch8 The Machine Organization (21p ’s) Mintzberg Ch9 The Diversified Organization (19p ’s) Mintzberg Ch10 The Professional Organization ( 22p ’s) Mintzberg Ch11 The Innovative Organization (35p ’s) Mintzberg Ch12 Ideology and the Missionary Organization (14p ’s) Mintzberg Ch13 Politics and the Political Organization (16p ’s)
- Conclude which Basic Part is most important for your organization. xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- Adhocracy : no strong hierarchy. Reacts ad hoc to impulses: no rigid strategy that can ’t be changed. Opposite of Machine Organization. Any organization can be a political organization at a stage in its existence. xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- ?1 = centralized: easier/ faster to make decisions. BUT: a decentralized structure facilitates observing relevant changes more rapidly. Example: Steve Jobs decided on every detail (even the shape of the staircase in Apple Stores). This helped to make Apple a Strong Brand and introduce new products more rapidly than Nokia. ?2 Example: hospitals introduce smaller units in neighborhoods: closer to people. (At the same time hospitals specialize, resulting in for example less places where people can be operated on their heart: further away from people, but of higher quality – and cheaper.) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- ? Example 1: Advantage & disadvantage? = C&M professionals are free to do what they want. C&M professionals are supposed to solve any problem by applying media. (Also when company applies child labor/ when CEO bribes governments/ etc.) ?Example 2: Advantage & disadvantage? = CorpCom department of Nestle is consulted for any new market introduction. If CorpCom dept. thinks that purple packaging for sauerkraut does not fit Corporate Identity the marketing manager has to come up with a new packaging (really happened). Advantage is that Nestle is consistent & strong brand. Disadvantage is that marketing manager may not be allowed to perfectly tune in to what market desires. xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- Technostructure standardized everybody elses work: IT is becoming more important dept. Organization & Development (O&O) dictates that modules should be 5 ec etc. xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- Adhocracy : no strong hierarchy. Reacts ad hoc to impulses: no rigid strategy that can ’t be changed. Opposite of Machine Organization. Any organization can be a political organization at a stage in its existence. xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- SO: C professional has to take informal communication circuit into account: grapevine, rumors etc. Employees might take internal media not very serious. If C manager wants to get budget he/ she might have to use informal circuit: play golf together, visit football matches etc. xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- Propensity = neiging xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 12/25/12 xxxxxxxxxxxxx
