Ppt atelectasis
- 1. Atelectasis
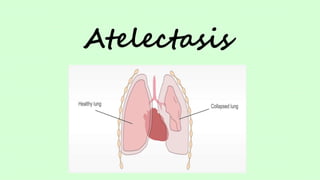
- 2. • Atelectasis is derived from the Greek words “ateles” and “ektasis”, meaning incomplete expansion. • Refers to closure or collapse of alveoli.
- 3. DEFINITION Atelectasis is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid.
- 5. Related Anatomy and Physiology
- 6. Related Anatomy and Physiology
- 7. NEONATAL ATELECTASIS ADULT/ ACQUIRED ATELECTASIS
- 8. RISK FACTOR • Age — being younger than 3 or older than 60 years of age. • Lung disease, such as asthma in children, COPD, bronchiectasis or cystic fibrosis. • Premature birth. • Recent abdominal or chest surgery. • Recent general anaesthesia. • Respiratory muscle weakness, due to muscular dystrophy, spinal cord injury or another neuromuscular condition. • Confinement to bed with infrequent changes of position.
- 9. ETIOLOGY • Atelectasis may be the result of a blocked airway (obstructive) or of pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive).
- 10. OBSTRUCTIVE ATELECTASIS CAUSES • Mucus plug • Foreign body • Tumour in a major airway • Blood clot
- 11. NON-OBSTRUCTIVE ATELECTSIS CAUSES • Injury • Pleural effusion • Pneumonia • Pneumothorax • Scarring of lung tissue • Tumour
- 12. CLASSIFICATION OF ATELECTASIS: • Resorption Atelectasis • Compression Atelectasis • Contraction/Cicatrization Atelectasis
- 13. RESORPTION ATELECTASIS: • Refers to the condition where airway obstruction cause the loss of pre-existing air in the alveoli, leading to alveolar collapse.
- 14. Causes MUCUS PLUG FOREIGN BODY TUMOR
- 15. COMPRESSION ATELECTSIS: •Compressive atelectasis refers to collapse of the small airway or alveoli deep to the pleura that occurs when air or fluid in the pleural cavity is under increased pressure.
- 17. CONTRACTION/CICATRIZATION ATELECTASIS: • It is a condition which occurs due to diffuse contraction or inflammation of the lung parenchyma.
- 18. ROUNDED ATELECTASIS: • Combination of contraction and compression atelectasis. • Occurs due to asbestos exposure or possibly a pleural effusion.
- 19. Due to etiological factors (Obstructive or non-obstructive) Obstruction of passage of air from & to alveoli Trapped alveolar air absorbed into bloodstream and outside air cannot replaced the absorbed air Affected portion of alveoli becomes airless ATELECTASIS Lung becomes airless Lung contracts and air inside lung is expelled out Deposition of lot of collagen fibres Compression of the lung due to increased pressure given by fluid or tumor in the thoracic cavity Causes air to expel from the lung and prevents the lung/affected part to expand Affected portion of lung becomes airless
- 20. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS DYSPNEA COUGH WITH SPUTUM PRODUCTION CHEST PAIN
- 21. CENTRAL CYANOSIS ABSENT BREATH SOUNDS LOW O2 SATURATION
- 22. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION • History collection • Physical examination • Chest X-ray • CT scan • MRI • Bronchoscopy (Diagnostic and therapeutic) • Arterial Blood Gas analysis • Positron-emission tomography
- 23. MANAGEMENT • Goal: Re-expand the collapsed portion of the lung MEDICAL MANAGEMENT • Treatment of the underlying cause
- 25. • BRONCHODILATORS • INCENTIVE SPIROMETER • CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY • POSITIONING • POSITIVE END EXPIRATORY PRESSURE • INTUBATION AND VENTILATION
- 28. NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Ineffective breathing pattern related to excessive mucus production and bronchoconstriction as evidenced by dyspnea, tachypnea, nasal flaring and altered chest excursion. • DESIRED OUTCOME: Improvement in breathing pattern. • NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Monitor respiratory and oxygenation status to determine any changes in status. Auscultate breath sounds, noting areas of decreased or absent ventilation and presence of adventitious sounds. Position to minimize respiratory efforts (e.g., elevate the head of the bed and provide overbed table for patient to lean on) to reduce oxygen needs. Encourage slow deep breathing, turning and coughing to promote effective breathing pattern. Monitor for respiratory muscle fatigue to provide additional support if needed. Initiate and maintain supplemental oxygen to improve respiratory status. Administer medications (e.g., bronchodilators and inhalers) that promote airway patency and gas exchange. Provide suctioning as needed for patients who are intubated or unable to clear their own secretions. Offer reassurance and emotional support because the patient’s limited breathing capacity may frighten him.
- 29. NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Impaired gas exchange related to atelectasis as evidenced by low oxygen saturation, shortness of breath, cough, rapid, shallow breathing. • DESIRED OUTCOME: The patient will maintain optimal gas exchange as evidenced by respiratory rates between 12 to 20 breaths per minute, oxygen saturation within the target range and verbalize ease of breathing. • NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Assess the patient’s vital signs, especially the oxygen saturation and characteristics of respiration atleast every 4 hours. Also monitor the results of ABG analysis. Administer supplemental oxygen carefully as prescribed. Elevate the head of the bed. Assist patient to assume semi-fowlers position. Teach patient how to use incentive spirometer Provide pain medication to support deep breathing. Turn the patient atleast every 2 hourly, as tolerated, encourage to mobilize as tolerated. Encourage patient to cough/deep breath. Assess oxygen saturation Assess lung sounds
- 30. NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Ineffective Airway Clearance related to increased production of sputum. • DESIRED OUTCOME: Patient achieves patent airway. • NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Auscultate breath sounds, record the presence of abnormal breath sounds, eg wheezing, crackles, also assess for bronchial spasms. Assess the frequency and depth of breathing and chest movement. Give fluids at least 2500 ml / day, unless contraindicated, offer warm water to mobilize secretions. Observe color of skin, mucous membranes and nails for signs of cyanosis, which indicates hypoxemia. Give medication as indicated to relaxes smooth muscle and reduce local congestion. Provide respiratory treatment, eg, chest physiotherapy, postural drainage and percussion.
- 31. NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Self-care deficit related to fatigue secondary to increased work of breathing and insufficient ventilation and oxygenation. • DESIRED OUTCOME: Independence in self-care activities. • NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Encourage patient to coordinate diaphragmatic breathing with activity (e.g., walking, bending) Pace activities of daily living to alternate with rest periods to reduce fatigue and dyspnea. Educate patient about postural drainage if appropriate
- 32. NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Acute pain related to lungs inflammation. • DESIRED OUTCOME: Reduced pain level. • NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Assess pain score to identify the intensity of pain. Administer adequate Analgesics to control pain. Humidify inspired air and encourage adequate fluid intake to mobilize secretions. Use Postural drainage and chest percussion to remove secretions.
- 33. COMPLICATIONS • Secondary infections e.g. pneumonia, lung abscess • Respiratory failure
- 34. PREVENTION Change patient’s position frequently Encourage early mobilization from bed to chair followed by early ambulation. Encourage appropriate deep breathing and coughing Educate appropriate technique for incentive spirometry. Administer prescribed opioids and sedatives judiciously to prevent respiratory depression. Perform postural drainage and chest percussion Institute suctioning to remove tracheobronchial secretions • Multidisciplinary, evidence-based standardized intervention programs, such as IGOUGHSM hold promise in preventing atelectasis
- 35. ICOUGH INCENTIVE SPIROMETRY COUGHING AND DEEP BREATHING ORAL CARE TWICE A DAY UNDERSTANDING (PATIENT AND STAFF EDUCATION) GETTING OUT OF BED ATLEAST 3 TIMES DAILY HEAD-OF-BED ELEVATION I C O U G H
- 36. PROGNOSIS