Equilibrium 3
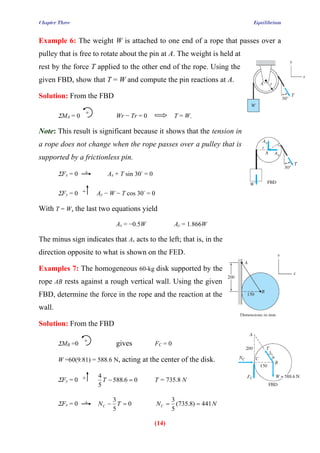
- 1. Chapter Three Equilibrium (14) Example 6: The weight W is attached to one end of a rope that passes over a pulley that is free to rotate about the pin at A. The weight is held at rest by the force T applied to the other end of the rope. Using the given FBD, show that T = W and compute the pin reactions at A. Solution: From the FBD MA = 0 Wr − Tr = 0 T = W. Note: This result is significant because it shows that the tension in a rope does not change when the rope passes over a pulley that is supported by a frictionless pin. Fx = 0 Ax + T sin 30◦ = 0 Fy = 0 Ay − W − T cos 30◦ = 0 With T = W, the last two equations yield Ax = −0.5W Ay = 1.866W The minus sign indicates that Ax acts to the left; that is, in the direction opposite to what is shown on the FED. Examples 7: The homogeneous 60-kg disk supported by the rope AB rests against a rough vertical wall. Using the given FBD, determine the force in the rope and the reaction at the wall. Solution: From the FBD MB =0 gives FC = 0 W =60(9.81) = 588.6 N, acting at the center of the disk. Fy = 0 0 6 . 588 5 4 = − T T = 735.8 N Fx = 0 0 5 3 = − T NC N NC 441 ) 8 . 735 ( 5 3 = = + + + + + +
- 2. Chapter Three Equilibrium (15) Another Method of Analysis MA = 0 200NC − 150(588.6) = 0 NC = 441 N Example 8: The homogeneous, 120-kg wooden beam is suspended from ropes at A and B. A power wrench applies the 500-N · m clockwise couple to tighten a bolt at C. Use the given FBD to determine the tensions in the ropes. Solution: W =mg =120(9.81) =1177.2 N acting at the center of the beam, From the FBD of the beam MA = 0 4TB − 1177.2(3) − 500 = 0 TB =1007.9 N Fy = 0 TA + TB − 1177.2 = 0 Substituting TB =1007.9 N and solving for TA, we get TA =169.3 N Other Methods of Analysis Another, equally convenient option is to compute TA using MB = 0 as MB = 0 − 4TA + 1177.2(1.0) − 500 = 0 TA =169.3 N Example 9: The Frame shown supports part of the roof of small building. Knowing the tension in the cable is 150 kN, determine the reaction at the fixed end E. + + + +
- 3. Chapter Three Equilibrium (16) Solution: Noting that 5 . 7 ) 6 ( ) 5 . 4 ( 2 2 = + = DF m, Fx = 0 ; Ex + 5 . 7 5 . 4 (150) = 0 Ex = -90.0 kN = 90.0 kN Fy = 0 ; Ey – 4(20) - 5 . 7 6 (150) = 0 Ey = 200 kN ME = 0 ; (20)(1.8) + (20)(3.6) + (20)(5.4) + (20)(7.2) - 5 . 7 6 (150)(4.5) + ME = 0 ME = 180.0 kN.m Example 10: The box wrench in Figure (a) is used to tighten the bolt at A. If the wrench does not turn when the load is applied to the handle, determine the torque or moment applied to the bolt and the force of the wrench on the bolt. Solution: MA = 0 MA – [52 13 12 ](0.3) - 30 sin60o (0.7)= 0 MA = 32.6 N.m Fx = 0 Ax - 52 13 5 + 30 cos60o = 0 Ax = 5.00 N + + + + +
- 4. Chapter Three Equilibrium (17) Fy = 0 Ay - 52 13 12 - 30 sin60o = 0 Ay = 74.0 N Note that MA must be included in this moment summation. This couple moment is a free vector and represents the twisting resistance of the bolt on the wrench. By Newton's third law, the wrench exerts an equal but opposite moment or torque on the bolt. Furthermore, the resultant force on the wrench is 1 . 74 ) 0 . 74 ( ) 00 . 5 ( 2 2 = + = A F N Note: Although only three independent equilibrium equations can be written for a rigid body, it is a good practice to check the calculation using a fourth equilibrium equation. For example, the above computations may be verified in part by summing moments about point C; MC = 0 ; 13 12 52 (0.4) + 32.6 -74(0.7) = 0 19.2 + 32.6 -51.8 = 0 Example 11: The 420-lb homogeneous log is supported by a rope at A and loose- fitting rollers at B and C as it are being fed into a sawmill. Calculate the tension in the rope and the reactions at the rollers, using the given FBD. Which rollers are in contact with the log? + +
- 5. Chapter Three Equilibrium (18) Solution: From the FBD Fx = 0 −NB cos 30◦ − NC cos 30◦ = 0 (a) MA = 0 -420 (7.5 sin 30◦ ) - 10NB - 15NC = 0 (b) The solution of Eqs. (a) and (b) is NB = 315.0 lb and NC = −315.0 lb The signs indicate that the sense of NB is as shown on the FBD, whereas the sense of NC is opposite to that shown. Therefore, the upper roller at B and the lower roller at C are in contact with the log. Fy = 0 T − 420 − NB sin 30◦ − NC sin 30◦ = 0 Because NB = −NC, this equation yields: T = 420 lb Example 12: The structure in Fig. (a) is loaded by the 240-lb·in. counterclockwise couple applied to member AB. Neglecting the weights of the members, determine all forces acting on member BCD. Solution: Referring to the FBD of the entire structure in Fig. (b), MA = 0 TC cos 30◦ (8) − ND(12) + 240 = 0 ND = 0.5774 TC + 20 (a) From the FBD of member BCD in Figure (c), MB = 0 TC cos 30◦ (4) + TC sin 30◦ (3) − ND (8) = 0 ND = 0.6205 TC (b) Solving Eqs. (a) and (b) simultaneously yields TC = 464 lb and ND = 288 lb + + + + +
- 6. Chapter Three Equilibrium (19) Also from the FBD of member BCD in Figure (c), Fx = 0 ND − TC cos 30◦ + Bx = 0 Bx =464 cos 30◦ − 288=114 lb Fy = 0 By − TC sin 30◦ = 0 By = 464 sin 30◦ = 232 lb Because the solution yields positive numbers for the unknowns, each force is directed as shown on the FBDs. The FBD of member AB, although not required in the foregoing analysis, is shown in Figure (d). Example 13: Calculate the tension T in the cable which supports 1000-lb load with the pulley arrangement shown. Each pulley is free to rotate about its bearing, and the weights of all parts are small compared with the load. Find the magnitude of the total force on the bearing of pulley C. Solution: Pulley A: MO = 0 ; -T1r + T2r = 0 T1= T2 Fy = 0 ; T1+ T2 - 1000= 0 2T1= 1000 T1= T2 = 500 lb + + + +
- 7. Chapter Three Equilibrium (20) From the example of pulley A we may write the equilibrium of forces on pulley B by inspection as T3= T4 = T2/2 = 250 lb For Pulley C the angle = 30o in no way affects the moment of T about the center of the pulley, so that moment equilibrium requires T= T3 or T = 250 lb Equilibrium of the pulley in the x and y directions requires Fx = 0 ; 250 cos30o - Fx = 0 Fx = 217 lb Fy = 0 ; Fy + 250sin30o – 250 = 0 Fy = 125 lb 250 ) 125 ( ) 217 ( 2 2 2 2 = + = + = y x F F F lb Example 14: An 80-N box is placed on a folding table as shown in Figure (a). Neglecting friction and the weights of the members, determine all forces acting on member EFG and the tension in the cable connecting points B and D. + +
- 8. Chapter Three Equilibrium (21) Solution: From the FBD of the entire table, Figure (b), MH = 0 80(600) − NG (800) = 0 NG = 60 N From the FBD of the tabletop, Figure (c), MA = 0 − 80(400) + Ey(1200) = 0 Ey = 26.67 N From the FBD of member EFG, Figure (d), MF = 0 Ex (360) − Ey(600) − NG(400) = 0 Ex (360) = 26.67(600) + 60(400) Ex = 111.12 N Fx = 0 Fx − Ex =0 Fx = Ex = 111.12 N Fy = 0 NG − Fy − Ey =0 Fy = 60 − 26.67=33.33 N From the FBD of the right half of the tabletop, Figure (e), MC = 0 Ey(600) − Ex (180) + TBD(180)=0 TBD(180)=111.12(180) − 26.67(600) TBD =22.22 N + + + + + +
- 9. Chapter Three Equilibrium (22) Problems 3.1 Each of the bodies shown is in equilibrium, homogeneous and has a mass of 30 kg Assume frictionless at all contact surfaces. Draw the fully dimensioned FBD for each body and compute the horizontal and vertical components of all forces acting on each of the members. 3.2 The homogeneous beam AB weighs 400 lb. For each support condition shown in (a) through (c), draw the FBD of the beam and determine the reactions.
- 10. Chapter Three Equilibrium (23) 3.3 Draw the FBD of the entire frame, assuming that friction and the weights and compute the horizontal and vertical components of all forces acting on each of the members. 3.4 The 480-kg bent bar ABC of uniform cross section is supported by a pin at A and a vertical cable at C. Determine the pin reactions and the force in the cable. 3.5 Neglecting the mass of the beam compute the reactions at A and B. 3.6 The crate weighing 400 lb is supported by three ropes concurrent at B. Find the forces in ropes AB and BC if P =460 lb.
- 11. Chapter Three Equilibrium (24) 3.7 Find the smallest value of P for which the crate in the Prob. 3.6 will be in equilibrium in the position shown. (Hint: A rope can only support a tensile force.) 3.8 Determine the rope tension T for which the pulley will be in equilibrium. 3.9 The homogeneous 18-kg pulley is attached to the bar ABC with a pin at B. The mass of the bar is negligible. The cable running over the pulley carries a tension of 600 N. Determine the magnitudes of the support reactions at A and C.