Absorption Pharmacokinetics.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•1,883 views
Absorption, Different mechanism of absorption, Factors affecting absorption (General Pharma; Pharmacokinetics)
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Clinical Pharmacokinetics-I [half life, order of kinetics, steady state]![Clinical Pharmacokinetics-I [half life, order of kinetics, steady state]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Clinical Pharmacokinetics-I [half life, order of kinetics, steady state]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Clinical Pharmacokinetics-I [half life, order of kinetics, steady state]
Similar to Absorption Pharmacokinetics.pptx
A power point presentation on general aspects of Pharmacokinetics suitable for undergraduate medical students beginning to study Pharmacology. Also suitable for Post Graduate students of Pharmacology and Pharmaceutical Sciences.Pharmacokinetics - drug absorption, drug distribution, drug metabolism, drug ...

Pharmacokinetics - drug absorption, drug distribution, drug metabolism, drug ...http://neigrihms.gov.in/
Similar to Absorption Pharmacokinetics.pptx (20)
Pharmacokinetics - drug absorption, drug distribution, drug metabolism, drug ...

Pharmacokinetics - drug absorption, drug distribution, drug metabolism, drug ...
Pharmacokinetics of Drug_Pharmacology Course_Muhammad Kamal Hossain.pptx

Pharmacokinetics of Drug_Pharmacology Course_Muhammad Kamal Hossain.pptx
More from FarazaJaved
More from FarazaJaved (20)
Androgens and Anabolic Steroids and Anti-androgens.pptx

Androgens and Anabolic Steroids and Anti-androgens.pptx
Recently uploaded
Models Call Girls In Hyderabad 9630942363 Hyderabad Call Girl & Hyderabad Escort ServiceModels Call Girls In Hyderabad 9630942363 Hyderabad Call Girl & Hyderabad Esc...

Models Call Girls In Hyderabad 9630942363 Hyderabad Call Girl & Hyderabad Esc...GENUINE ESCORT AGENCY
🌹Attapur⬅️ Vip Call Girls Hyderabad 📱9352852248 Book Well Trand Call Girls In Hyderabad Escorts Service
Escorts Service Available
Whatsapp Chaya ☎️ : [+91-9352852248 ]
Escorts Service Hyderabad are always ready to make their clients happy. Their exotic looks and sexy personalities are sure to turn heads. You can enjoy with them, including massages and erotic encounters.#P12Our area Escorts are young and sexy, so you can expect to have an exotic time with them. They are trained to satiate your naughty nerves and they can handle anything that you want. They are also intelligent, so they know how to make you feel comfortable and relaxed
SERVICE ✅ ❣️
⭐➡️HOT & SEXY MODELS // COLLEGE GIRLS HOUSE WIFE RUSSIAN , AIR HOSTES ,VIP MODELS .
AVAILABLE FOR COMPLETE ENJOYMENT WITH HIGH PROFILE INDIAN MODEL AVAILABLE HOTEL & HOME
★ SAFE AND SECURE HIGH CLASS SERVICE AFFORDABLE RATE
★
SATISFACTION,UNLIMITED ENJOYMENT.
★ All Meetings are confidential and no information is provided to any one at any cost.
★ EXCLUSIVE PROFILes Are Safe and Consensual with Most Limits Respected
★ Service Available In: - HOME & HOTEL Star Hotel Service .In Call & Out call
SeRvIcEs :
★ A-Level (star escort)
★ Strip-tease
★ BBBJ (Bareback Blowjob)Receive advanced sexual techniques in different mode make their life more pleasurable.
★ Spending time in hotel rooms
★ BJ (Blowjob Without a Condom)
★ Completion (Oral to completion)
★ Covered (Covered blowjob Without condom
★ANAL SERVICES.
🌹Attapur⬅️ Vip Call Girls Hyderabad 📱9352852248 Book Well Trand Call Girls In...

🌹Attapur⬅️ Vip Call Girls Hyderabad 📱9352852248 Book Well Trand Call Girls In...Call Girls In Delhi Whatsup 9873940964 Enjoy Unlimited Pleasure
9630942363 THE GENUINE ESCORT AGENCY VIP LUXURY CALL GIRLS
HIGH CLASS MODELS CALL GIRLS GENUINE ESCORT BOOK
BOOK APPOINTMENT - 9630942363 THE GENUINE ESCORT AGENCY
BEST VIP CALL GIRLS & ESCORTS SERVICE 9630942363 VIP CALL GIRLS ALL TYPE WOMEN AVAILABLE
INCALL & OUTCALL BOTH AVAILABLE BOOK NOW
9630942363 VIP GENUINE INDEPENDENT ESCORT AGENCY
VIP PRIVATE AUNTIES
BEAUTIFUL LOOKING HOT AND SEXT GIRLS AND PARTY TYPE GIRLS YOU WANT SERVICE THEN CALL THIS NUMBER 9630942363
ROOM ALSO PROVIDE HOME & HOTELS SERVICE
FULL SAFE AND SECURE WORK
WITHOUT CONDOMS, ORAL, SUCKING, LIP TO LIP, ANAL, BACK SHOTS, SEX 69, WITHOUT BLOWJOB AND MUCH MORE
FOR BOOKING
9630942363Call Girls Ahmedabad Just Call 9630942363 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Ahmedabad Just Call 9630942363 Top Class Call Girl Service AvailableGENUINE ESCORT AGENCY
Recently uploaded (20)
Call Girls Service Jaipur {8445551418} ❤️VVIP BHAWNA Call Girl in Jaipur Raja...

Call Girls Service Jaipur {8445551418} ❤️VVIP BHAWNA Call Girl in Jaipur Raja...
Call Girls Madurai Just Call 9630942363 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Madurai Just Call 9630942363 Top Class Call Girl Service Available
Call Girls Coimbatore Just Call 8250077686 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Coimbatore Just Call 8250077686 Top Class Call Girl Service Available
Low Rate Call Girls Bangalore {7304373326} ❤️VVIP NISHA Call Girls in Bangalo...

Low Rate Call Girls Bangalore {7304373326} ❤️VVIP NISHA Call Girls in Bangalo...
Call Girls Rishikesh Just Call 9667172968 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Rishikesh Just Call 9667172968 Top Class Call Girl Service Available
Call Girls Rishikesh Just Call 8250077686 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Rishikesh Just Call 8250077686 Top Class Call Girl Service Available
Models Call Girls In Hyderabad 9630942363 Hyderabad Call Girl & Hyderabad Esc...

Models Call Girls In Hyderabad 9630942363 Hyderabad Call Girl & Hyderabad Esc...
🌹Attapur⬅️ Vip Call Girls Hyderabad 📱9352852248 Book Well Trand Call Girls In...

🌹Attapur⬅️ Vip Call Girls Hyderabad 📱9352852248 Book Well Trand Call Girls In...
Jogeshwari ! Call Girls Service Mumbai - 450+ Call Girl Cash Payment 90042684...

Jogeshwari ! Call Girls Service Mumbai - 450+ Call Girl Cash Payment 90042684...
Call Girls Varanasi Just Call 8250077686 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Varanasi Just Call 8250077686 Top Class Call Girl Service Available
Call Girls Ahmedabad Just Call 9630942363 Top Class Call Girl Service Available

Call Girls Ahmedabad Just Call 9630942363 Top Class Call Girl Service Available
Independent Call Girls Service Mohali Sector 116 | 6367187148 | Call Girl Ser...

Independent Call Girls Service Mohali Sector 116 | 6367187148 | Call Girl Ser...
Top Quality Call Girl Service Kalyanpur 6378878445 Available Call Girls Any Time

Top Quality Call Girl Service Kalyanpur 6378878445 Available Call Girls Any Time
Call Girls Kolkata Kalikapur 💯Call Us 🔝 8005736733 🔝 💃 Top Class Call Girl Se...

Call Girls Kolkata Kalikapur 💯Call Us 🔝 8005736733 🔝 💃 Top Class Call Girl Se...
VIP Hyderabad Call Girls Bahadurpally 7877925207 ₹5000 To 25K With AC Room 💚😋

VIP Hyderabad Call Girls Bahadurpally 7877925207 ₹5000 To 25K With AC Room 💚😋
Russian Call Girls Lucknow Just Call 👉👉7877925207 Top Class Call Girl Service...

Russian Call Girls Lucknow Just Call 👉👉7877925207 Top Class Call Girl Service...
Top Rated Pune Call Girls (DIPAL) ⟟ 8250077686 ⟟ Call Me For Genuine Sex Serv...

Top Rated Pune Call Girls (DIPAL) ⟟ 8250077686 ⟟ Call Me For Genuine Sex Serv...
Russian Call Girls Service Jaipur {8445551418} ❤️PALLAVI VIP Jaipur Call Gir...

Russian Call Girls Service Jaipur {8445551418} ❤️PALLAVI VIP Jaipur Call Gir...
Independent Call Girls In Jaipur { 8445551418 } ✔ ANIKA MEHTA ✔ Get High Prof...

Independent Call Girls In Jaipur { 8445551418 } ✔ ANIKA MEHTA ✔ Get High Prof...
Absorption Pharmacokinetics.pptx
- 1. (The General Pharmacology) By Dr. Faraza Javaid
- 2. General Pharmacology The interactions between a drug and the body are conveniently divided into two classes. Pharmacokinetic processes Pharmacodynamic processes
- 3. Pharmacokinetics Pharmaco- Greek word (pharmackon) for “drug,”, and kinetics from the Greek word (kinetikos) for “moving,”. Pharmacokinetics (PK) is the study of drug movement into, around, and out of the body How the human body act on the drugs?
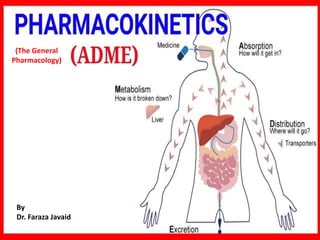
- 4. Pharmacokinetics of drugs (ADME) Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion of drugs
- 7. Absorption Absorption is the transfer of a drug from the site of administration to the bloodstream Or Is the passage of drug through cell membranes to reach its site of action.
- 8. Mechanisms of drug absorption 1. Simple/ Passive diffusion. 2. Facilitated diffusion. 3. Active transport. 4. Phagocytosis (Endocytosis & Exocytosis). Passive Transport
- 10. Passive Diffusion Passive diffusion is the process by which molecules diffuse from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Passive diffusion does not involve a carrier, is not saturable, and shows low structural specificity. Vast majority of drugs are absorbed by this mechanism.
- 11. Water soluble drug (ionized or polar) is readily absorbed via diffusion through aqueous channels or pores in cell membrane. Lipid soluble drug (nonionized or non polar) is readily absorbed via diffusion through lipid cell membrane itself.
- 13. Facilitated Diffusion Other agents can enter the cell through specialized transmembrane carrier proteins that facilitate the passage of large molecules. These carrier proteins allow the passage of drugs or endogenous molecules into the interior of cells. This process is known as facilitated diffusion.
- 14. Active Transport This mode of drug entry also involves specific carrier proteins that span the membrane. Energy dependent Move drugs against a concentration gradient, (from a region of low drug concentration to one of higher concentration)
- 16. Carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion Active transport Along concentration gradient (From high to low) Against concentration gradient (From low to high) Needs carriers Needs carriers Selective, saturable Selective, saturable No energy is required Energy is required
- 18. Mechanisms of drug absorption 1. Simple/ Passive diffusion. 2. Facilitated diffusion. 3. Active transport. 4. Phagocytosis (Endocytosis & Exocytosis). Passive Transport
- 19. Endocytosis: Uptake of membrane-bound particles. Exocytosis: Expulsion of membrane-bound particles. High molecular weight drugs or Highly lipid insoluble drugs
- 21. Factors Influencing Rate of Absorption Route of Administration Drug Concentration Ph Molecular Size Surface Area Blood Flow Contact time at the absorption surface Expression of P-Glycoprotein
- 22. Route of Administration IV administration- Immediate and complete absorption. Extravascular administered- Carried through various barriers to reach the circulation and their site of action.
- 23. pH Most drugs are weak organic acids or bases, so they undergo ionization Ionization of drugs reduces its ability to permeate membranes (REDUCES LIPOPHILICITY…) A drug is present in solution as both the Lipid-soluble, diffusible, non-ionized form and The ionized form - lipid insoluble and poorly diffusible across a membrane. The degree of ionization of a drug is determined by the surrounding pH and pKa of the drug.
- 24. Ionization of Weak Acids and Weak Bases; Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation A weak acid - neutral molecule that can reversibly dissociate into an anion and a proton (a hydrogen ion). A weak base; neutral molecule that can reversibly dissociated into a cation and a proton HA H+ + A- Ka B + H+ BH+ Kb
- 25. A drug passes through membranes more readily if it is uncharged
- 26. A drug passes through membranes more readily if it is uncharged. Therefore, the effective concentration of the permeable form of each drug at its absorption site is determined by the relative concentrations of the charged and uncharged forms. The ratio between the two forms is, in turn, determined by the pH at the site of absorption and by the strength of the weak acid or base, which is represented by the ionization constant, pKa. The pKa is a measure of the strength of the interaction of a compound with a proton. The lower the pKa of a drug, the more acidic it is. Conversely, the higher the pKa, the more basic is the drug.
- 27. Molecular size: The smaller in size-----more absorption Concentration of drug- Increase in conc. increases rate of absorption Surface area - The more absorptive surface area, the more absorption. Brush borders of the intestine -1000-fold SA to that of the stomach, - Hence EFFICIENT ABSORPTION…. Blood Flow- The intestines receive much more blood flow than the stomach, so absorption from the intestine is favored over the stomach.
- 28. Contact time at the absorption surface: If a drug moves through the GI tract very quickly (in severe diarrhea), it is not well absorbed. Food in the stomach -dilutes the drug and slows gastric emptying.- drug taken with a meal is generally absorbed more slowly
- 29. Expression of P-Glycoprotein P-glycoprotein is a transmembrane transporter protein responsible for transporting various molecules, including drugs, across cell membranes . It is expressed in tissues throughout the body, including the liver, kidneys, placenta, intestines, and brain capillaries, and is involved in transportation of drugs from tissues to blood. That is, it “pumps” drugs out of cells. Thus, in areas of high expression, P-glycoprotein reduces drug absorption.
- 30. Bioavailability is defined as the fraction of unchanged drug reaching the systemic circulation, following administration by any route. Expressed as percentage. If a 1 gram dose of a drug is administered by mouth, and half of that reaches the systemic circulation, the drug is 50% bioavailable.
- 31. Determination of bioavailability: Bioavailability is determined by comparing plasma levels of a drug after a particular route of administration (for eg; oral administration) with levels achieved by IV administration. F = AUC (oral) AUC (iv) x 100
- 32. By plotting plasma concentrations of the drug versus time, the area under the curve (AUC) can be measured. Need for Bioavailability studies- To establish important pharmacokinetic parameters, dosage regimen, dose labelling. Also explains why the same dose may cause a therapeutic effect by one route and same dose may cause a toxic effect by another route.
- 35. Factors affecting Bioavailability First Pass Metabolism Solubility of Drug Chemical Instability Nature of Drug Formulation
- 36. The elimination of drug that occurs after administration but before it enters the systemic circulation (eg, during passage through the gut wall, portal circulation, or liver for an orally administered drug) Reduces amount of unchanged drug entering the systemic circulation.
- 37. Solubility of the drug: Very hydrophilic drugs are poorly absorbed because of their inability to cross lipid-rich cell membranes. Drugs that are extremely lipophilic are also poorly absorbed, because they are totally insoluble in aqueous body fluids and, therefore, cannot gain access to the surface of cells. Chemical instability: Penicillin G -unstable in gastric pH. Insulin- destroyed in the GI tract by degradative enzymes.
- 38. Nature of the drug formulation: Drug absorption may be altered by particle size, salt form, crystal polymorphism, enteric coatings, and the presence of excipients (such as binders and dispersing agents) can influence the ease of dissolution and, therefore, alter the rate of absorption.