Imperial India
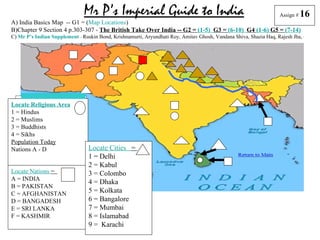
- 1. Mr P’s Imperial Guide to India Assign # 16 A) India Basics Map -- G1 = (Map Locations) B)Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 - The British Take Over India -- G2 = (1-5) G3 = (6-10) G4 (1-6) G5 = (7-14) C) Mr P’s Indian Supplement – Ruskin Bond, Krishnamurti, Aryundhati Roy, Amitav Ghosh, Vandana Shiva, Shazia Haq, Rajesh Jha, etc. Locate Religious Area 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 2. Mr P’s Guide to Imperial India Assign # 12 Locate Religious Area 1 = Hindus A 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 3. Assign # 12 B Locate Religious Area 1 = Hindus A 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 4. Assign # 12 C B Locate Religious Area 1 = Hindus A 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 5. Assign # 12 C B Locate Religious Area A 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 6. Assign # 12 C B Locate Religious Area 1 = Hindus A 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 7. Assign # 12 C F B Locate Religious Area 1 = Hindus A 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 8. Assign # 12 C F B 1 Locate Religious Area A 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 9. Assign # 12 C 2 F B 1 Locate Religious Area A 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims D 3 = Buddhists 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 1 = Delhi E 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 10. C 2 F B 1 Locate Religious Area A 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 11. Assign # 12 C 2 F B 1 Locate Religious Area 4 1 = Hindus A 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 12. Assign # 12 C 2 F B 1 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 13. Assign # 12 C 2 F B 1 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 14. Assign # 12 C 2 F B 1 Locate Religious Area 4 A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 15. Assign # 12 C 2 8 F B 1 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 16. Assign # 12 C 2 8 F B 9 1 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 17. Assign # 12 C 2 8 F B 9 1 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 1 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 18. Assign # 12 C 2 8 F 2 B 2 9 1 2 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 1 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 2 = Kabul E Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 19. Assign # 12 C 2 8 F 2 B 2 9 1 2 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 1 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 3 E 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi
- 20. Assign # 12 C 2 8 F 2 B 2 4 9 1 2 4 Locate Religious Area A 5 1 = Hindus 7 2 = Muslims 1 3 = Buddhists D 4 = Sikhs Population Today 6 Nations A - D Locate Cities = 3 1 = Delhi 3 E 2 = Kabul Locate Nations = 3 = Colombo A = INDIA 4 = Dhaka B = PAKISTAN C = AFGHANISTAN 5 = Kolkata D = BANGADESH 6 = Bangalore E = SRI LANKA 7 = Mumbai F = KASHMIR 8 = Islamabad 9 = Karachi Back to Main
- 21. A) The British Take Over India G2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A B 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 22. A) The British Take Over India G2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A B 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 23. G2 A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer… B 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 24. G2 A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions… B 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 25. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 26. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 27. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 28. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 29. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 30. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 31. G2 A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) Reduced banditry 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) A B) B C) C
- 32. G2 A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) Reduced banditry 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) Western education and legal procedures A B) B C) C
- 33. G2 A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) Reduced banditry 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) Western education and legal procedures A B) Missionaries brought Christianity B C) C
- 34. A) The British Take Over India G2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) Reduced banditry 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) Western education and legal procedures A B) Missionaries brought Christianity B C) Tried to end slavery, caste system… C
- 35. G2 A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) Reduced banditry 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) Western education and legal procedures A B) Missionaries brought Christianity B C) Tried to end slavery, caste system, improve Women’s C position, banned Sati...
- 36. A) The British Take Over India End of G2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 1) Who ruled Indian for over 200 years prior to the British rule starting? (p.303) Mughal Empire 2) What were the two methods used by the British East India Company to conquer India? (p.303) A Divide & Conquer – took advantage of Indian divisions, encouraged competition and disunity among rival princes B Use superior weapons when diplomacy did not work 3) What was the East India Company’s main goal in India? (p.303) Make Money $$$$ 4) What improvements were made under the East India Company? (p.303) What improvements have you made to P-ville? A) Improved roads B) Preserved peace C) Reduced banditry 5) Name 3 changes British officials introduced in the early 1800s. (p.304) Name at least 3 changes you introduced to P-ville? A) Western education and legal procedures A B) Missionaries brought Christianity B C) Tried to end slavery, caste system, improve Women’s C position, banned Sati...a Hindu custom that required a woman to throw herself on her husband’s funeral fire. Back to Main Back to Mr Roy
- 37. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 G3 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 38. A) The British Take Over India G3 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 39. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 G3 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 40. G3 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between British & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 41. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 42. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 43. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 44. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British 10) Explain the major changes occurred in thea) a) aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) b) b) a) c) b) c)
- 45. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British a) a) b) b) c) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 46. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British A) Sepoys rose up around India... a) b) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 48. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British A) Sepoys rose up around India... a) b) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 49. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British A) Sepoys rose up around India. a) B) Many marched to Delhi and… b) 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 50. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. a) • Many marched to Delhi and b) • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 51. A) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 G3 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between British & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. • Crushed revolts by torching villages and • Many marched to Delhi and • killing unarmed Indians. • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 52. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. • Crushed revolts by torching villages • Many marched to Delhi and • killing unarmed Indians. • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) b) c)
- 53. A) The British Take Over India G3 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. • Crushed revolts by torching villages • Many marched to Delhi and • killing unarmed Indians. • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) East India Trading Company no longer controlled British colonies. b) c)
- 54. A 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. • Crushed revolts by torching villages • Many marched to Delhi and • killing unarmed Indians. • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) East India Trading Company no longer controlled British colonies. b) c)
- 55. G3 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) The British Take Over India A) Indian Soldiers Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. • Crushed revolts by torching villages • Many marched to Delhi and • killing unarmed Indians. • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) East India Trading Company no longer controlled British colonies. b) Parliament placed power directly under the British Crown in 1858. c)
- 56. A) The British Take Over India End of G3 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 6) Who were the Sepoy? (p.304) Indian Soldiers 7) What was the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.304) Fight between Brits & Sepoy What policy or school policy makes you angry? 8) What British policy made the Sepoy angry? Sepoy soldiers were to load their guns with bullets greased with animal fat. Sepoy refused due to religious (Islam & Hindu) rules which forbid a follower to eat animals. Soldiers who refused were then arrested. Hindu = No eating meat. Cows are sacred… Holy Cow Muslim = No eating pork, ham, etc. (No pig) Soldiers would have to serve anywhere, including overseas. This angered Hindus since overseas travel was against their religion. 9) So what did both sides do to make this a “rebellion”? (p.304) Indians (Sepoy) British • Sepoys rose up around India. • Crushed revolts by torching villages • Many marched to Delhi and • killing unarmed Indians. • massacred British Colonist. 10) Explain the major changes occurred in the aftermath of the Sepoy Rebellion? (p.305) a) East India Trading Company no longer controlled British colonies. b) Parliament placed power directly under the British Crown in 1858. c) British sent more soldiers to India and taxed the Indians for these “expenses.” Back to Main
- 57. Start G4 A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a market and source of raw materials. 4) How did British policy ruin or change the Indian economy & agriculture? 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? 6b) What Indian traditions did he condemn?
- 58. A2) The British Take Over India Start G4 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the Rich in natural resources; good market trade Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn?
- 59. G4 A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the India is the most important of all British Colonies. It is both Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” A) rich in natural resources b) good market for trade 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn?
- 60. G4 A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the India is the most important of all British Colonies. It is both Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” A) rich in natural resources b) good market for trade 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn?
- 61. G4 A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the India is the most important of all British Colonies. It is both A) Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” rich in natural resources b) good market for trade 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn?
- 62. A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the India is the most important of all British Colonies. It is both Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” A) rich in natural resources b) good market for trade 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn?
- 63. A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the India is the most important of all British Colonies. It is both Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” A) rich in natural resources b) good market for trade 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn?
- 64. End of G4 A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 IMPACT OF BRITISH COLONIAL RULE – (p. 305) 1) What the heck is a One who governed in India in the name of British monarch viceroy? 2) Why India was called the “Jewel of the India is the most important of all British Colonies. It is both Crown” or “Brightest Jewel.” A) rich in natural resources b) good market for trade 3) Explain why Britain views India as both a British build roads & railroads in India, which let British sell market and source of raw materials. factory goods across the subcontinent. Indian resources could be transported to factories in England 4) How did British policy ruin or change the British flooded India w/ inexpensive, machine-made textiles, Indian economy & agriculture? ruining India’s hand-weaving industry. Farmers were pushed to grow cash crops. Massive deforestation occurred. 5a) What Indians benefited most from British rule? 5b) Who benefits most from the current US President’s rule? Upper Classes 6a) Who was Ram Mohun Roy? An Indian scholar and founder of the Hindu College in Calcutta, which emphasized western works. 6b) What Indian traditions did he Rigid caste system, child marriage, sati and purdah condemn? Back to Main
- 65. A2) The British Take Over India Start of G5 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of Western-educated Indians have on British rule? 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked a) b) together hoping for self-rule? 13) Which of the two began to dominate the party? Why? 14) Which one left the Congress party? What did they hope for? (p.307)
- 66. A2) The British Take Over India Start of A2 G5 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians wanted imperial rule. British rule? 9) In 1885, what group was formed in Indian National Congress India? (p.307) 10) What did this group believe and Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for greater call for? (p.307) democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 67. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist movement. of Western-educated Indians have on Indians were educated in London about democracy, individual rights and British rule? equal justice. Thus, naturally Indians started to demand the same back in India. Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 68. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians were educated in London about democracy, British rule? individual rights and equal justice. Thus, naturally Indians started to demand the same back in India. Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 69. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians were educated in London about democracy, British rule? individual rights and equal justice. Thus, naturally Indians started to demand the same back in India. Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 70. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians were educated in London about democracy, British rule? individual rights and equal justice. Thus, naturally Indians started to demand the same back in India. Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 71. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians were educated in London about democracy, British rule? individual rights and equal justice. Thus, naturally Indians started to demand the same back in India. Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 72. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians wanted imperial rule. British rule? Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 73. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians wanted imperial rule. British rule? Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim sate.
- 74. A2) The British Take Over India Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 2 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians wanted imperial rule. British rule? Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim state. Back to Main
- 75. A2) The British Take Over India Cont. G5 2 Chapter 9 Section 4 p.303-307 A 7) Most British knew little about Indian achievement and dismissed Indian culture with contempt. True or False (p.307) 8) What effect did educating a class of These Indians hurt British rule because it created a nationalist Western-educated Indians have on movement. Indians wanted imperial rule. British rule? Indian National Congress 9) In 1885, what group was formed in India? (p.307) Believed in peaceful protest to gain ends called for 10) What did this group believe and call for? (p.307) greater democracy and eventual self-rule Goal was self-rule in the long run 11) What was their goal? (p.307) 12) At first, what two groups worked together hoping for self-rule? a) Muslims b) Hindus 13) Which of the two began to Hindus, they outnumbered the Muslims. Hence would Dominate dominate the party? Why? Politics, Laws, Economy, Jobs and Wealth. 14) Which one left the Congress Muslims – formed Muslim League in 1906 and wanted separate party? What did they hope for? (p.307) Muslim state. Back to Main
- 76. Caste System Main
- 77. Purdah O O
- 78. Purdah
- 79. Purdah O O
- 80. Purdah O O 3) Practice of preventing women from being seen in public.
- 81. Purdah O O 3) Practice of preventing women from being seen in public. 4) Segregation of women from male dominated society.
- 82. Purdah O O 3) Practice of preventing women from being seen in public. 4) Segregation of women from male dominated society. 5) Traditionally practiced by various Islamic and Hindu cultures. Back
- 83. A) MUGHAL EMPIRE
- 84. A) MUGHAL EMPIRE
- 85. A) MUGHAL EMPIRE
- 86. A) MUGHAL EMPIRE
- 87. A) MUGHAL EMPIRE Main Back to A
