Oculomotor nerve
- 2. 1 2 3 3rd Nerve PRESENTATION CONTENT •Origin & Insertion •Relation with eye •Important supply
- 3. Embryology • By the fourth week of development , nuclei of all cranial nerves are present. • Parasympathetic (visceral efferent) ganglia and somatic efferent nuclei are derived from neural crest cells.
- 5. Introduction • Third cranial nerve. • It is the largest of the ocular motor nerves. • It contains some 15,000 axons, including motor fibers and parasympathetic motor fibers. • Entirely motor in function. • Supplies LPS and all extra ocular muscles except lateral rectus and superior oblique. • Also supplies the intraocular muscles namely sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscle.
- 8. 1 2 3 5 FASCICULUS NUCLEAR COMPLEX BASILAR INTRACAVERNOUS PATHWAY OF OCULAR MOTOR NERVE 4 ORBITAL
- 9. Main parts of the Brain
- 11. 1. Nucleus and cisternal portion ORIGIN : The oculomotor nerve originates from the upper part of the midbrain/Mesencephalon. The oculomotor nucleus lies in the deep periaqueductal grey matter at the level of the superior colliculus anterior to the cerebral aqueduct. It is a longitudinal column of about 10mm length. Two Nucleus : Oculomotor Nucleus » somatic motor fibers (general somatic efferents) Edinger-Westphal nuclei » visceral motor fibers (general visceral efferent)
- 13. OCULOMOTOR NERVE NUCLEI: Include two motor nuclei: Main Motor Nucleus: Site : ventral part of central grey matter "surrounding the cerebral aqueduct", of midbrain, at the level of superior colliculus, close to median plane. Supply : all extrinsic muscles of the eye except superior oblique & lateral rectus. The levator palpebrae superioris muscles of both sides are supplied by single central group of cells "central caudal nucleus". The superior rectus muscle is supplied by contralateral oculomotor nucleus. The remaining muscles are innervated by ipsilateral oculomotor nucleus.
- 14. • Classically, this complex has been described with four paired subnuclei supplying innervation to the inferior, medial, and superior rectus muscles and to the inferior oblique muscle. • There is a single caudal, dorsal midline nucleus providing innervation to the levator muscle. • Innervation of the extraocular muscle from the paired nuclei is ipsilateral for the inferior and medial rectus muscles and the inferior oblique muscle. • However, innervation of the superior rectus is contralateral. • The motor fibers to the superior rectus decussate within the third nerve nucleus and join the fascicle of the contralateral oculomotor nerve.
- 16. • It is composed of subnuclei supplying individual extraocular muscles as follows : 1. Dorsolateral Nucleus : Ipsilateral Inferior Rectus 2. Intermedial Nucleus : Ipsilateral Inferior Oblique 3. Ventromedial Nucleus : Ipsilateral Medial Rectus 4. Paramedial (Scattered) Nucleus : Contralateral Superior Rectus 5. Caudal Central Nucleus : Bilateral Levator Palpebrae Superioris
- 17. From To Uncrossed fibers ipsilateral oculomotor nucleus Medial rectus. Inferior rectus. Inferior oblique. Crossed fibers Contralateral oculomotor nucleus Superior rectus. uncrossed fibers oculomotor nuclei Levator palpebrae superioris muscle. Uncrossed para- sympathetic fibers Ipsilateral Edinger Westphal nucleus Constrictor pupliae muscle. Ciliary muscle.
- 19. Accessory parasympathetic (EDINGERWESTPHAL) nucleus: Site : it lies dorsal to the main motor nucleus. Supply : the axons, which are preganglionic accompany other oculomotor fibres to relay within ciliary ganglion in orbit and supply sphincter pupillae & ciliary muscles via short ciliary nerves. It consists of a median and two lateral components. Perhaps, the cranial half of the nucleus is concerned with light reflexes and the caudal half with accommodation.
- 20. • In addition to the extraocular muscle motor fibers, the Edinger-Westphal nuclei supply the parasympathetic preganglionic neurons that project to the ciliary ganglion. • All evidence suggests that these fibers project ipsilaterally.
- 21. Oculomotor Nerve Somato motor Four extraocular muscle Superior Rectus Inferior Rectus Medial Rectus Inferior Oblique Levator palpebral superiosis Edinger-Westphal (visceral motor) constrictor pupillae Ciliary muscles IMPORTANT SUPPLY TO THE EYE
- 23. 2. FASCICULUS: The fibers run through the tegmentum, red nucleus and medial aspect of the substantia nigra to emerge from the medial aspect of the cerebral peduncle. Emerge from the midbrain and pass into interpeduncular space
- 24. Mid Brain/ Mesencephalon Periequedoctor grey matter
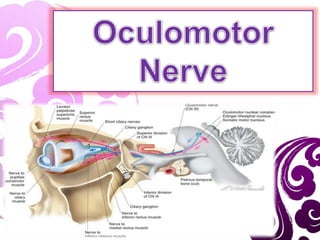
- 26. 2. The Basilar part : • Starts as a series of 15-20 rootlets in the interpeduncular fossa. • These rapidly coalase to form a large medial and a small lateral root, which unite to form a flattened nerve, which gets twisted bringing the inferior fibres superiorly and superior fibers inferiorly; and thus the nerve becomes a rounded cord. • The nerve then passes below the posterior cerebral artery, and above the superior cerebellar artery and running lateral to & parallel with the posterior communicating artery to reach the cavernous sinus.
- 29. * Starts Upper part of the mid brain
- 30. 3. Cavernous sinus part: • It moves anteriorly, passing the nerve pierces the dura mater. and enters the lateral aspect of the cavernous sinus superiorly. • Within the cavernous sinus, it receives sympathetic branches from the internal carotid plexus. • These fibres do not combine with the oculomotor nerve – they merely travel within its sheath. • In the anterior part of cavernous sinus, the nerve divides into superior and inferior branches which enters the orbit through SOF within the annulus of zinn.
- 35. 4. Orbital part: • The nerve enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure in the common tendinous ring which were already divided into two branches; one superior and one inferior.
- 36. a. Superior branch: Motor innervation to the superior rectus and levator palpabrae superioris. Sympathetic fibres run with the superior branch to innervate the superior tarsal muscle. b.Inferior branch: Motor innervation to the inferior rectus, medial rectus and inferior oblique. Parasympathetic fibres to the ciliary ganglion, which ultimately innervates the sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles. The larger, inferior division divides into three branches : 1. Nerve To The Medial Rectus passes inferior to the optic nerve. 2. Nerve To Inferior Rectus passes downward and enters the muscle on its upper aspect, and 3. Nerve To Inferior Oblique (longest of the three branches) passes in b/w the IR & LR and supplies the IO from its posterior border. It gives off the motor root to the ciliary ganglion.
- 40. Parasympathetic (Motor) Root: • Carries preganglionic parasympathetic fibres which arise from cells of Edinger- Westphal nucleus and run through oculomotor nerve & its branch to inferior oblique to reach the ganglion. • These fibres are relayed in the ganglion and postganglionic fibres travel in the short ciliary nerves.
- 42. • They carry: Parasympathetic fibres: supply sphincter pupillae & ciliary muscles (more than 95% of these fibres are distributed to ciliary muscle which is much larger in volume).
- 43. BLOOD SUPPLY
- 44. • All nerves are supplied with blood from adjacent vessels, which are usually small and variable. • The blood supply to the medial aspect of the brainstem is from vessels directly off the Basilar artery. • Small perforators off circumflex arteries (posterior cerebral, superior cerebellar artery) may also supply the fascicular portion of the third nerve as it courses through the ventral midbrain. • The vascular supply of 3rd nerve in subarachnoid space is via vascular twigs from the post. Cerebral A., the sup. Cerebellar A., and the tentorial and dorsal meningeal branches of the meningohypophyseal trunk of the Internal Carotid Artery. • In the cavernous sinus, the tentorial, dorsal meningeal, and inferior hypophyseal branches of the meningohypophyseal trunk supply the nerve along with branches from the ophthalmic artery.
- 45. • The blood supply of the oculomotor, trochlear and abducent nerves is similarly arranged, the nutrient arteries being derived from any adjacent smaller arteries. • Though not often noted, it is obvious that deprivation of this blood supply by spasm, thrombosis or embolism may produce paralysis or paresis of the muscles supplied.
- 48. ANATOMICAL BASIS OF CLINICAL FEATURES OF THIRD NERVE PALSY • A complete & a total third nerve palsy is of common occurrence. • May be congenital or acquired. • Clinical features of complete third nerve palsy include :
- 49. 1. Ptosis - paralysis of LPS muscle. 2. Deviation – out, down and intorted – unopposed action of LR and SO. 4. Pupil is fixed and dilated – paralysis of sphincter pupillae muscle. 5. Accommodation is completely lost – paralysis of ciliary muscle.
- 54. 6. Crossed diplopia – paralytic divergent squint. 7. Head posture – if the pupillary area is uncovered, head takes a posture consistent with the directions of actions of the paralysed muscles, i.e., head is turned on the opposite side, tilted towards the same side and chin is slightly raised.
- 55. FEATURES AND CAUSES OF THIRD NERVE LESIONS AT VARIOUS LEVELS 1. Nuclear lesions • Lesions involving purely the third nerve nucleus are relatively uncommon. • Common causes include ; vascular diseases, demyelination, primary tumors and metastasis • Lesions involving nucleus cause an ipsilateral third nerve palsy with ipsilateral sparing and contralateral weakness of elevation. • Lesions involving paired medial rectus subnuclei (ventromedial nucleus) cause a wall-eyed bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia ( WEBINO ) characterised by defective convergence and adduction.
- 56. 2. Fascicular lesions • Causes are similar to nuclear lesions. Benedikt syndrome involves the fasciculus as it passes through the red nucleus and is characterised by ipsilateral 3rd nerve palsy and contralateral extrapyramidal signs such as hemitremor. Weber syndrome involves the fasciculus as it passes through the cerebral peduncle and is characterised by ipsilateral 3rd nerve palsy and contralateral hemiparesis. Nothnagel syndrome involves the fasciculus and the superior cerebellar peduncle and is characterised by ipsilateral 3rd nerve palsy and cerebellar ataxia. Claude syndrome is a combination of Benedikt and Nothnagel syndromes
- 58. COMMON CAUSES OF NUCLEAR AND FASICULAR THIRD CRANIAL NERVE CHILDREN Congenital - with neurological abnormalities - with aberrant rennervation - with cyclic oculomotor spasm Vascular ( AV malformations ) Primary tumour Metastatic tumour YOUNG ADULTS Demyelinating Vascular (hemorrhage or infarction) Tumor OLDER ADULTS Vascular (infarction) Tumour
- 59. 3. Lesions involving basilar part of the nerve: • isolated third nerve palsies are frequently basilar. Causes : 1. Aneurysms : At the posterior communicating artery cause isolated third nerve palsy with involvement of pupil. 2. Head trauma: Extradural hematomas which may cause tentorial pressure cone with downward herniation of the temporal lobe. This compresses the third nerve as it passes over the tentorial edge. Initially there occurs fixed, dilated pupil, which is followed by a total third nerve palsy. 3. Diabetes causes isolated 3rd nerve palsy with sparing of the pupillary reflexes.
- 63. 4. Lesions involving intracavernous part of the nerve: • Because of its close proximity to other cranial nerves, intracavernous 3rd nerve palsies are usually associated with involvement of the 4th and 6th nerves, and the 1st division of trigeminal nerve.
- 64. • Important Causes : 1. Diabetes may cause vascular palsy. 2. Pituitary apoplexy – may cause a third nerve palsy (after child birth), if the gland swells laterally & extension into cavernous sinus. 3. Intracavernous lesions – aneurysms, meningiomas, carotid-cavernous fistulae and Tolosa-Hunt syndrome (granulomatous inflammation)
- 65. 5. Lesions of the intraorbital part of the nerve: • May cause isolated extraocular muscle palsies or may involve either superior division or inferior division or both. • Causes : orbital tumors, trauma and vascular diseases.
- 66. 6. Lesions of pupillomotor fibres • B/w the brainstem and the cavernous sinus, pupillomotor fibres are located superficially in the superior median quadrant of the nerve. • They derive the blood supply from the pial blood vessels whereas the main trunk of the 3rd nerve is supplied by vasa nervorum.
- 68. • Surgical lesions such as aneurysms, trauma and uncal herniation characteristically involve the pupil by compressing the pial blood vessels and the superficially located pupillary fibres. • Medical lesions such as diabetes and hypertension usually spare the pupil. This is because the microangiopathy associated with these diseases involves the vasa nervorum, causing infarction of the main trunk, but sparing the superficial pupillary fibres.
- 69. In ISOLATED THIRD NERVE PALSY diabetes and HTN, is the most common cause of pupil- sparing 3rd nerve palsy. In most cases spontaneous recovery occurs within 3 months. Diabetic 3rd nerve palsy is often assoc. with periorbital pain and may occasionally be the presenting feature of diabetes. The presence of pain is therefore not helpful in differentiating b/w aneurysmal and diabetic 3rd nerve palsy.
- 72. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the origin and course of III is/are correct except? a) It emerges as a number of rootlets from a nucleus lying level with the superior colliculus b) It leaves the brainstem after passing through the red nucleus c) It runs below and lateral to the free margin of the tentorium cerebelli d) It pierces the dura midway between the anterior and posterior clinoid processes e) Its branches cross the same part of the superior orbital fissure as VI 2. A patient suffers damage to the orbit in a road traffic incident resulting in damage to the third cranial nerve. Which of the following signs will be present? a) Pupillary constriction and a medial strabismus b) Pupillary dilatation and a medial strabismus c) Pupillary constriction and a lateral strabismus d) Pupillary dilatation and a lateral strabismus
- 73. 3. Regarding the distribution of fibres from III a) Levator palpebrae superioris only receives a motor supply from the superior division of III b) It innervates all the muscles at the junction of their middle and posterior thirds c) The parasympathetic supply to the iris is conveyed via the short ciliary nerves d) Superior rectus is innervated ipsilaterally e) Levator palpebrae superioris contralaterally represented at the level of the oculomotor nuclei 4. Which of the following statements regarding III is correct? a) The parasympathetic fibres lie centrally in the precavernous sinus portion of the nerve b) A third nerve palsy causes the eye down and out. c) Accommodation is unaffected by such a palsy d) Compression of the nerve causes a partial ptosis e) The Edinger-Westphal nucleus lies ventral to the main oculomotor nucleus
- 74. 5. All of the following are characteristics of oculomotor nerve except: a) Carries parasympathetic nerve fibers b) Supplies inferior oblique muscle c) Enters orbit through the inferior orbital fissure d) Causes constriction of pupil 6. The following structure(s) synpase(s) in the ciliary ganglion: a) Nasociliary nerve fibres b) Parasympathetic nerve fibres from oculomotor nerve c) Sympathetic nerve fibres from the carotid plexus d) Parasympathetic nerve fibres form the facial nerve abducent nerve fibres.
- 75. Thank You
Notes de l'éditeur
- Craniacaudel sequency
- Hemitremor:Tremor affecting the muscles of one side of the body. (lateral part) Hemiparesis: Weakness affecting one side of the body. cerebellar ataxia:failure of muscular coordination due to disease of the cerebellum.