GHH Supportive Tissue
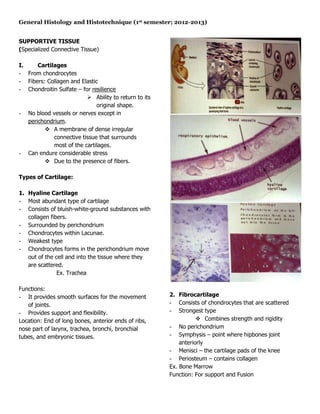
- 1. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) SUPPORTIVE TISSUE (Specialized Connective Tissue) I. Cartilages - From chondrocytes - Fibers: Collagen and Elastic - Chondroitin Sulfate – for resilience Ability to return to its original shape. - No blood vessels or nerves except in perichondrium. A membrane of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds most of the cartilages. - Can endure considerable stress Due to the presence of fibers. Types of Cartilage: 1. Hyaline Cartilage - Most abundant type of cartilage - Consists of bluish-white-ground substances with collagen fibers. - Surrounded by perichondrium - Chondrocytes within Lacunae. - Weakest type - Chondrocytes forms in the perichondrium move out of the cell and into the tissue where they are scattered. Ex. Trachea Functions: - It provides smooth surfaces for the movement 2. Fibrocartilage of joints. - Consists of chondrocytes that are scattered - Provides support and flexibility. - Strongest type Location: End of long bones, anterior ends of ribs, Combines strength and rigidity nose part of larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchial - No perichondrium tubes, and embryonic tissues. - Symphysis – point where hipbones joint anteriorly - Menisci – the cartilage pads of the knee - Periosteum – contains collagen Ex. Bone Marrow Function: For support and Fusion
- 2. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) Location: Pubic symphysis, Intervertebral discs, Menisci of knee, and portions of Tendons that insert into cartilage. Growth and repair of cartilage: - Grow slowly - Relatively inactive tissue - When injured or inflamed, repair proceeds slowly since it is avascular. Two basic patterns of cartilage growth: 1. Interstitial growth - Increases rapidly Due to the existing division of chondrocytes - Expansion from within Due to the existing chondrocytes that is continuously dividing. - Occurs while the cartilage is young and pliable. 3. Elastic Cartilage From Childhood to adolescence. - Consists of chondrocytes located in the thread- like collagen fibers. 2. Appositional growth - With perichondrium - Activity of cells in the inner chondrogenic layer Functions: of the perichondrium leads to growth. - Gives support and maintain shape - Starts later that interstitial growth and - Provide strength and elasticity continues through adolescence. Location: External ear, auditory tubes, and lid on - Fibroblast divide, some differentiate into top of Larynx. chondroblasts - Chondroblasts surround themselves with matrix and become chondrocytes. Steps: 1. Ridges in Periosteum create groove for periosteal blood vessel.
- 3. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) Crystallization and tissue hardening by mineral deposits. 2. Periosteal ridges fuse, forming an endosteum- lined tunnel. II. Bone or Osseus Tissues - 65% of bone weight in calcium hydroxyapatite (Calcium phosphate), calcium hydroxide, calcium carbonate. (65% - Calcium phosphate only) - Contains Tropocollagen Subunits giving the bone elasticity and fracture resistance. - Highly vascular and well innervated 3. Osteoblasts in endosteum build new concentric - Contains lymph channels lamellae inward toward center of tunner, - Functions in mineral storage and blood cell forming a new osteon. production. Bone - Connective tissue components: 1. Periosteum - Covering the bone - Tough sheet of dense irregular connective tissue surrounding the bone surface 2. Endosteum - Inner part; Membrane that lines the space within the bone that stores the yellow bone 4. Bone grows outward as osteoblasts in marrow. Periosteum build new circumferential lamellae. Osteon formation repeats as new periosteal 3. Red bone marrow ridges fold over blood vessels. - Produces RBC, WBC’s, Platelets - Osteoblast initiates calcification or - Process: Hematopoietic/hemopoiesis mineralization.
- 4. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) 4. Yellow bone marrow - Consists primarily of adipocytes - Infused scattered blood cells. Functions of bones: 1. Support - Framework for soft tissue - Provide attachment pint of the bones 2. Protection 2. Osteoblasts - Protect many internal organs of the body - Bone building cell Ex. Skull – brain; ribcages – lungs, heart - Secrete collagen fibers and other substances needed to build matrix of bone. 3. Assistance in movement - Initiates calcification - During muscle contraction, it will pull the bone in order to assists movement. 3. Osteocytes - Maintains bone tissue, mature cell 4. Mineral homeostasis - Principal cells of bone tissues - Bone stores minerals (Ca2PO4, Ca2C03) Function: Maintain the daily cellular activities of the bone 5. Blood cell production tissue. - From red bone marrow Exchange of nutrients and waste 6. Triglyceride storage in the blood. - Yellow bone marrow to adipocytes Four types of cells in bone tissue: 1. Osteogenic cells - Develops into osteoblasts; desired mesenchyma. - Unspecified stem cells derived from mesenchyme - Only bone cell to undergo cell division Location: Inner portion of the Periosteum in endosteum, and in canals without bone that contain blood vessels. 4. Osteoclasts - Contains a powerful lysosomal enzymes that digest protein and mineral components of underlying bones - Functions in resorption, the breakdown of bone matrix. Ruffled border – deeply folded plasma membrane.
- 5. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) Huge cell – derived from fusion of 50 monocytes - It is where articulation with another bone contain in the endosteum. forms. - Reduces friction and absorbs shocks at freely removable joints. 5. Periosteum - Outer covering - Tough covering of dense tissues - Contains the bone forming cells, osteocytes, that in enables the bone to grow in diameter but not in length Functions: - Protects the bone - Assists in fracture repair - Helps nourish bone tissue - Serves as attachment point for ligaments and tendons. 6. Medullary cavity/ Marrow cavity - A space within diaphysis that contains the fatty- yellow bone marrow Structure of bone macroscopic anatomy 7. Endosteum - Membrane containing bone forming cells and 1. Diaphysis line the medullary cavity. - The bone’s body or shaft which is a long- cylindrical main portion of the body. 2. Epiphysis - Proximal and Distal epiphysis – ends of bones. 3. Metaphysis - Epiphyseal plate - Part of the bone where diaphysis joins the epiphysis and diaphysis. - Includes epiphyseal line - A point where cartilage is replaced by bone - Hyaline cartilage that allows the diaphysis to grow in length but not in width. Types of bone tissues: I. Compact bone tissue 4. Articular - Osteon or haversian system: - Thin-layer hyaline cartilage covering the epiphysis. 1. Concentric Lamellae
- 6. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) - Concentric ring of matrix that consists of minerals with CaPO4, CaOH, CaCO3; more on Calcium and Phosphate. - Contains fiber-collagen – for strength - Haversian – 20-40 2. Lacunae (Lacuna) - Small spaces between lamellae that contains the osteocytes. 3. Canaliculi - Small canals that project from lacuna. Provide route or blood for the nutrients and oxygen 4. Haversian canal - Volmann’s/Perforating canal - Contain 1 or 2 blood vessels/nerves - Connected with one another and communicate with the free surfaces and bone marrow via the perforating canal. For movement of nutrients system. 5. Interstitial System - Contains in the interstitial system/Lamellae Angular fragments of lamellar bone Made up of the interstitial lamellae. - Fragment of older osteons that have been partially destroyed during bone rebuilding. 6. Cement lines II. Spongy bone tissues - Does not contain true osteon. - Consist of trabeculae Lamellae that are arranged in an irregular columns of bones. Function: Reduces weight Ossification – process of bone formation - Spaces between lamellae are filled with red bone marrow
- 7. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) - It is light which reduces the overall weight of bone. Bone formation: Ossification Two kinds: 1. Intramembranous ossification - Formation of bone directly on within fibrous connective tissue membranes - Formed by condensed mesenchymal cells - Form directly from mesenchyma without first 4. Development of Periosteum going through a cartilage stage. Fibrous collagen - layer – Osteogenic layer Steps: Layer under 1. Development of ossification center Periosteum. 2. Calcification Osteocytes need to deposit mineral salts so that it will harden matrix. 2. Endochondral ossification - The formation of bone within hyaline cartilage - Mesenchymal cells are transformed into chondroblasts, which initially produce a hyaline cartilage model of the bone - Subsequently, osteoblasts gradually replace the cartilage with bone. Steps: 3. Formation of trabeculae 1. Development of cartilage model. Fused with one - Consists of hyaline cartilage and perichondrium another that create the spongy bone. 2. Growth of cartilage model - Blood vessels – grow into spaces of spongy Two growths: - Development period: Spongy and compact a. Interstitial growth bone tissue. - Continuous cell division/growth from within. b. Apositional growth
- 8. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013) - Addition of more matrix by new chondroblasts (grow in diameter). 5. Development of secondary ossification center - Secondary ossification 3. Development of primary ossification center - As blood move upward into ossification plate. - Nutrient artery stimulates Osteogenic cells to differentiate onto osteoblasts - Include the formation of primary ossification center. A region where bone tissue replaced most of the cartilages. 6. Formation of articular cartilage and epiphyseal plate. - Hyaline cartilage that covers the epiphyseal/epiphysis become the articular cartilage but haversian canal is present in between the epiphysis and diaphysis forming 4. Development of medullary (marrow) cavity. the epiphysis. - it is done by osteoclast that breaks the newly Responsible for formed spongy bone trabeculae lengthwise growth. - Cavity filled with Blood vessels
- 9. General Histology and Histotechnique (1st semester; 2012-2013)
