polarization of light
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
2 likes•399 views
types of polarization and methods to achieve polarization
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT - BIREFRINGENCE AND HUYGEN'S THEORY OF DOUBLE REFRACTION

POLARIZATION OF LIGHT - BIREFRINGENCE AND HUYGEN'S THEORY OF DOUBLE REFRACTION
Polarization of Light and its Application (healthkura.com)

Polarization of Light and its Application (healthkura.com)
Similar to polarization of light
Similar to polarization of light (20)
POLARIZATION - BIREFRINGENCE AND HUYGEN'S THEORY OF DOUBLE REFRACTION 

POLARIZATION - BIREFRINGENCE AND HUYGEN'S THEORY OF DOUBLE REFRACTION
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)

Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)
Raman spectroscopy.pptx M Pharm, M Sc, Advanced Spectral Analysis

Raman spectroscopy.pptx M Pharm, M Sc, Advanced Spectral Analysis
fundamental of entomology all in one topics of entomology

fundamental of entomology all in one topics of entomology
TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...

TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...
Biopesticide (2).pptx .This slides helps to know the different types of biop...

Biopesticide (2).pptx .This slides helps to know the different types of biop...
9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000

9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000
Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics

Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics
Botany krishna series 2nd semester Only Mcq type questions

Botany krishna series 2nd semester Only Mcq type questions
Disentangling the origin of chemical differences using GHOST

Disentangling the origin of chemical differences using GHOST
❤Jammu Kashmir Call Girls 8617697112 Personal Whatsapp Number 💦✅.

❤Jammu Kashmir Call Girls 8617697112 Personal Whatsapp Number 💦✅.
VIRUSES structure and classification ppt by Dr.Prince C P

VIRUSES structure and classification ppt by Dr.Prince C P
Recombination DNA Technology (Nucleic Acid Hybridization )

Recombination DNA Technology (Nucleic Acid Hybridization )
Lucknow 💋 Russian Call Girls Lucknow Finest Escorts Service 8923113531 Availa...

Lucknow 💋 Russian Call Girls Lucknow Finest Escorts Service 8923113531 Availa...
polarization of light
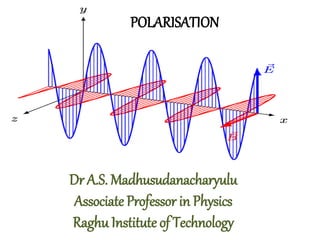
- 1. POLARISATION Dr A.S. Madhusudanacharyulu Associate Professor in Physics Raghu Institute of Technology
- 5. If the sunglasses are polarized, you will notice the glare disappears. When you look through one of the lenses, it should be very dark and you should see little to no glare, but it will still look like the light is shining on the surface.
- 14. The reason we tend to concentrate on the electric field is that it interacts strongly with charges, e.g. electrons, and there are a lot of electrons around. The magnetic field would interact strongly with magnetic charges, i.e. magnetic monopoles, but as far as we know magnetic monopoles don't exist. So generally speaking it's the electric field that dominates the interaction of light with matter B=E/c here c is very large ie, approx= 3*10^8 so magnetic field magnitude is one by 3*10^8 times the electric field intensity... so compared to electric field magnitude, magnetic field magnitude is very low, hence negligible
- 16. A light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. Light emitted by the sun, by a lamp in the classroom, or by a candle flame is unpolarized light.
- 18. material in thin plastic sheets that produces a high degree of plane polarization in light passing through it.
- 22. Polarization by Reflection. If light strikes an interface so that there is a 90o angle between the reflected and refracted rays, the reflected light will be linearly polarized
- 28. Polarization by Selective Absorption A polarized light can be obtained by using a material which transmits waves whose electric fields vibrate in a plane parallel to a certain direction of orientation and absorbs waves whose electric fields vibrate in all other directions.
- 30. Polarization by double refraction - definition When the unpolarized light ray falls on certain crystals like calcite, quartz etc. then it is found that 2 refracted rays are produced. This phenomena is called double refraction. Light passing through a calcite crystal is split into two rays. This process, first reported by Erasmus Bartholinus in 1669, is called double refraction. The two rays of light are each plane polarized by the calcite such that the planes of polarization are mutually perpendicular.
- 36. A Nicol prism is a type of polarizer, an optical device made from calcite crystal used to produce and analyse plane polarized light. It is made in such a way that it eliminates one of the rays by total internal reflection, i.e. the ordinary ray is eliminated and only the extraordinary ray is transmitted through the prism. It was the first type of polarizing prism, invented in 1828 by William Nicol (1770–1851) of Edinburgh. It consists of a rhombohedral crystal of Iceland spar (a variety of calcite) that has been cut at an angle of 68° with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally, and then rejoined as shown, using a layer of transparent Canada balsam as a glue.
- 46. Two common types of waveplates are the half-wave plate, which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the quarter-wave plate, which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well. Definition of half-wave plate. : a crystal plate that reduces by ¹/₂ cycle the phase difference between the two components of polarized light traversing it Definition of quarter-wave plate : a crystal plate that changes the phase difference between the two components of polarized light traversing it by one-fourth cycle
- 48. A quarter-wave plate consists of a carefully adjusted thickness of a birefringent material such that the light associated with the larger index of refraction is retarded by 90° in phase (a quarter wavelength) with respect to that associated with the smaller index. The material is cut so that the optic axis is parallel to the front and back plates of the plate. Any linearly polarized light which strikes the plate will be divided into two components with different indices of refraction. One of the useful applications of this device is to convert linearly polarized light to circularly polarized light and vice versa. This is done by adjusting the plane of the incident light so that it makes 45° angle with the optic axis. This gives equal amplitude o- and e-waves. When the o-wave is slower, as in calcite, the o-wave will fall behind by 90° in phase, producing circularly polarized light.
- 52. A wave passing through a half-wave plate
- 53. A wave passing through a half-wave plate
- 56. Optical activity describes the phenomenon by which chiral molecules are observed to rotate polarized light in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. This rotation is a result of the properties inherent in the interaction between light and the individual molecules through which it passes. Definition of optical rotation. : the angle through which the plane of vibration of polarized light that traverses an optically active substance is rotated