Anticoagulation in hd dr. nadia mohsen
- 3. ANTICOAGULATION REQUIRED DURING IHD/CRRT TO PREVENT CLOTTING IN THE EXTRACORPOREAL SERVICE.
- 4. CLOTTINGOF THE EXTRACORPOREAL CIRCUIT leads to ➢ blood loss ➢ reduced solute clearance and ultrafiteration due to reduction in dialyser surface area. Hence it is important to prevent clotting and assess the adequacy of anticoagulation.
- 5. What does induce clotting?? The hemodialysis circuit represents a large extracorporeal surface area and the simple passage of blood through the circuit could potentially lead to the deposition and activation of plasma coagulation proteins thus initiating clotting.
- 6. to minimizeclottingin the extracorporealcircuit Dialyser priming Heparin administration Vascular access a. Ensuring adequate blood flow. b. Correct needle position c. preventing repeated machine alarm situation
- 8. EUROPEAN BEST PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR ANTICOAGULATION IN HEMODIALYSIS significant risk of bleeding We recommend that systemic anticoagulation should be avoided or kept to a minimum. This may be achieved by using a high blood flow rate and regular flushing of the extracorporealcircuit with saline every 15-30 minutes or regional citrate infusion. Low-dose unfractionated heparin may be used with caution in patients with intermediate risk of bleeding. (1C) Anticoagulation without added risk of bleeding: We recommend that patients without increased bleeding risk should be given unfractionated heparin or LMWH during HD to reduce the risk of clotting of the extracorporealsystem. (1A) NephrolDial Transplant 2002; 17: Supplement7 S1-S111
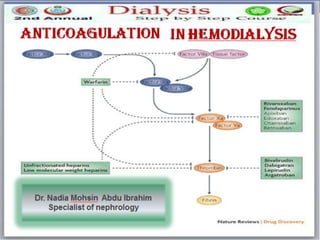
- 10. • Heparin enhance the anticoagulant activity of antithrombin III which inactivates thrombin and factor Xa and to lesser extent IXa , XIa and XIIa. • raises the blood clotting time, monitoring with APTT • Highly negatively charged and binds non-specifically to endothelium, platelets, circulating proteins, macrophages and plastic surfaces. • The effect of heparin is immediate and has a short half-life (30 minutes to 2 hours after discontinuation). • Protaminesulfate as antidote. Guidelines for Anticoagulation of Extracorporeal
- 11. HEPARIN ADMINISTRATION TECHNIQUES (UFH) 1. STANDARD HEPARINISATION (routine anticoagulation) (full dose heparinisation) 2. Tight heparinization (reduced, minimum) 3. Heparin free dialysis
- 12. STANDARDHEPARINISATION (routineanticoagulation) • Those patients who do not have increased risk of hemorrhage or co morbidities like CNS bleed, GI haemorrhage, uremic pericarditis and are not currently taking oral anticoagulants Delivery techniques Intermittent boluses: • Initial bolus followed by repeated intermittent maintenance boluses • Initial bolus followed by bolus on demand • Single dose continuous infusions Initial bolus followed by continuous infusions
- 14. • Termination of heparin infusion a. AV fistula-One hour before end of dialysis b. Venous catheters- at the end of dialysis • Reversal of over heparinisation: Injection protamine 1 mg for every 100 units heparin • Target clotting times during dialysis • Routine heparinisation: the clotting time at 1½ -2 times the baseline clotting time. • Tight heparinisation: the clotting time at 1¼ times the baseline clotting time.
- 15. POTENTIALCOMPLICATIONSOF USE OF HEPARIN Heparin use may be associated with complications like • heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) • drug drug interaction • bleeding events The long-term use of heparin has been associated with serious side effects such as: hair loss (alopecia) Hyperkalemia due to Heparin induced suppression of aldosterone synthesis osteoporosis Hyperlipidaemia (↑TG & Cholesterol,↓ HDL). pruritis and rashes( anaphylactoid reaction ( first use yndrome) The risk of bleedng is Related to the level of APTT not to the heparin dose
- 17. LOW MOLECULAR WEIGHT HEPARIN (LMWH)
- 19. Anticoagulation in patients with HIT type 2 We suggest that patients with HIT type 2 or HITTS should not be prescribed unfractionated heparin or low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) (2B).
- 20. There are multiple forms of LMWH e.g. Enoxaparin, Dalteparin, Nadroparin, Reviparin Tinzaparin
- 21. • shorter chain length consisting of ≤ 15 saccharide units. The results in: 1. less non-specific binding & less bleeding 2. longer half-life • Binds anti-thrombin III and inhibits factor Xa In most cases the affinity of LMWH for Xa versus thrombin is of the order of 3:1. • The anticoagulant effect of LMWH can be monitored by the anti-factor Xa activity in plasma:
- 23. ANTICOAGULATION IN PATIENTS WHO CARRY THE RISK FOR BLEEDING
- 24. • Tight heparinization (reduced, minimum) (CRRT, IHD) • Heparin free dialysis (CRRT, IHD) • Regional Anticoagulation • Protamine reversal anticoagulation • Regional citrate Anticoagulation (RCA) (CRRT) • Heparin coated membrane • Prostacyclin regional anticoagulation (antiplatelet agents) • Citrasate dialysate • Hiparinoids & anti thrombin agents (IHD, CRRT with HIT )
- 25. EUROPEAN BEST PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR ANTICOAGULATION IN HEMODIALYSIS significant risk of bleeding We recommend that systemic anticoagulation should be avoided or kept to a minimum. This may be achieved by using a high blood flow rate and regular flushing of the extracorporealcircuit with saline every 15-30 minutes or regional citrate infusion. Low-dose unfractionated heparin may be used with caution in patients with intermediate risk of bleeding. (1C) Anticoagulation without added risk of bleeding: We recommend that patients without increased bleeding risk should be given unfractionated heparin or LMWH during HD to reduce the risk of clotting of the extracorporealsystem. (1A) NephrolDial Transplant 2002; 17: Supplement7 S1-S111
- 26. Priming in some units with heparin (3000 IU/ L saline) (avoid in HIT) Multiple flushes of 250 ml of saline every 30 min, in association with a high blood flow rate Periodic saline rinse allows inspection of dialyser for evidence of clotting No Heparin Dialysis
- 27. Indication a. Patient at slight risk of bleeding b chronic & prolonged bleeding c. Heparin free dialysis unsuccessful due to frequent clotting Delivery technique constant infusion Initial bolus dose : 750 IU constant infusion rate : 600 IU/ hour, Monitor and keep ACT at baseline +40% (170-190 seconds) heparin infusion Continue till end of dialysis Tight heparinisation (Minimum dose heparin) Intermittent boluses bolus of 500 IU/60 minutes to keep the ACT within target ?? Do not try intermittent boluses as it will lead to rising and falling clotting times XXX
- 28. Regional citrate Anticoagulation (RCA) • Continuous infusion of isosmotic trisodium citrate solution (102 mmol/L) into the arterial side of the dialyzer. • Citrate bind to plasma calcium fall in plasma calcium preventing the coagulation cascade anticoagulation. • Calcium disturbance (monitoring) • Metabolic alkalosis (Metabolism of citrate to HCO3) • Hypernatremia( Hypertonic sodium citrate solution) • Contraindicated in patient can not metabolized citrate such as : liver failure
- 30. Others
- 31. • Constant infusion of heparin into the dialyzer inlet line and the simultaneous, constant infusion of protamine prior to the blood returning to the patient. • Rebound bleeding 2-4 hours after the end of dialysis as the reticuloendothelial system releases free heparin from the protamine-heparin complex back into the general circulation. Regional anticoagulation with Protamine reversal
- 34. Clinicalpresentation In patients with HIT Type II all heparin products must be avoided, including: 1.Topical preparations, coated products as well as intravenous preparations. 2.Systemic anticoagulation Dialysis patients may have: ‘no heparin’ dialysis / switched to P.D/ RCA or anticoagulation with non- heparins agents: commonly used include Danaparoid, Fonadparinux Hirudin, and Argatroban. Venous catheters must not be heparin locked, but can be locked with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator or citrate ( trisodium citrate 46.7%).
- 35. Conclusion • Anticoagulation in Hemodialysis is an area in dialysis that in continuous development and evolution. • UFH vs LMWH depend on your local practice and resources • good understanding for the Management of high risk for bleeding on dialysis is mandatory
- 36. Thankyou
