Third Quarter Week 1.docx
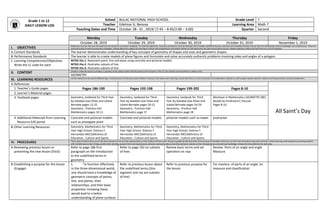
- 1. Grade 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School BULAC NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Grade Level 7 Teacher Edelmar G. Benosa Learning Area Math 7 Teaching Dates and Time October 28– 31 , 2019/ (7:45 – 8:45/2:00 – 3:00) Quarter Second Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday October 28, 2019 October 29, 2019 October 30, 2019 October 31, 2019 November 1, 2019 I. OBJECTIVES Objectives must be met over the week and connected to curriculum standards. To meet the objectives, necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed during Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. A.Content Standards The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of geometry of shapes and sizes and geometric shapes. B.Performance Standards The learner is able to create models of plane figures and formulate and solve accurately authentic problems involving sides and angles of a polygon. C.Learning Competencies/Objectives Write the LC code for each M7GE-IIIa-1. Represent point, line and plane using concrete and pictorial models. M7GE-IIIa-2. Illustrates subsets of line. M7GE-IIIa-3. Illustrates subsets of line. II. CONTENT Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach. In the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. GEOMETRY III. LEARNING RESOURCES List the materials to be used in different days. Varied sources of materials sustain children’s interest in the lesson and in learning. Ensure that there is a mix of concrete and manipulative materials as well as paper-based materials. Hands-on learning promotes concept development. A.References All Saint’s Day 1.Teacher’s Guide pages Pages 186-190 Pages 192-198 Pages 199-202 Pages 8-10 2.Learner’s Material pages 3.Textbook pages Geometry, textbook for Third Year by Soledad Jose-Dilao and Julieta Bernabe pages 12-25 Geometry , Prentice Hall Mathematics pages 10-11 Geometry, textbook for Third Year by Soledad Jose-Dilao and Julieta Bernabe pages 20-22 Geometry , Prentice Hall Mathematics page 17 Geometry, textbook for Third Year by Soledad Jose-Dilao and Julieta Bernabe pages 54-59 Geometry , Prentice Hall Mathematics page 28 Worktext in Mathematics GEOMETRY (BEC based) by Ferdinand C.Pascual Pages 8-10 4.Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) portal Concrete and pictorial models such as pineapple plant Concrete and pictorial models pictorial models such as tower protractor B.Other Learning Resources Geometry, Mathematics for Third Year High School, Dolores F. Hernandez MECS(Ministry of Education , Culture and Sports Geometry, Mathematics for Third Year High School, Dolores F. Hernandez MECS(Ministry of Education , Culture and Sports Geometry, Mathematics for Third Year High School, Dolores F. Hernandez MECS(Ministry of Education , Culture and Sports IV. PROCEDURES These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn things, practice their learning, question their learning processes and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. A.Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson (Elicit) Refer to page 186 first paragraph on the introduction to the undefined terms in geometry Refer to page 192 on subsets of lines Review basic terms and set operation on rays Review Parts of an angle and angle Measure B.Establishing a purpose for the lesson (Engage) 1. To function effectively in the three-dimensional world, one should have a knowledge of geometric concepts of points, line, and planes, their relationships, and their basic properties. Knowing these would lead to a better understanding of plane surfaces Refer to previous lesson about the undefined terms.(line segment and ray are subsets of line) Refer to previous purpose for the lesson For mastery of parts of an angle ,its measure and classification
- 2. and their areas, solids, and their volumes. Our environment is rich with patterns of different shapes and sizes. These motivate and facilitate the learning of geometry because of their appeal to our perception of beauty and order. Recognition and analysis of their properties and measures not only develop one’s knowledge in geometry, but also open the path for logical thinking 2. MENTAL CONCEPTS OR IDEAS. However , we can use concrete objects around us to represent these ideas. Thus, these undefined terms can only be described. 2.Presenting examples/instances of the new lesson Present activity 1 on page 188 Present activity 3 on page 193 Look at the hands of the clock. Do you see the representation of an angle? The bent arm of the man also represents an angle. The legs of the chair represent an angle; so do the edged of the table. Look around you and describe objects in the classroom which represent angles. Present exercises page 8 3.Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 (Explore) Discuss questions to ponder on page 188 and Definition of terms. Refer to page 187, Teacher’s Guide Discuss activity 4 on page 194, Teacher’s Guide Define angle based on previous activity. Discuss angle, sides and vertex. Refer to page 200. Teacher’s Guide Present something more page 9 4.Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 Present exercises #1 and 2 page 189, Teacher’s Guide Discuss activity 5 on pages 195 -196, Teacher’s Guide Discuss and answer activity 8 page 201. Discuss the different types of angles. Refer to page 202. Teacher’s Guide Present sharpen your skill on page 9
- 3. 5.Developing mastery (Explain) Present exercise # 3 pages 189- 190, Teacher’s Guide Worksheet that define segments and rays And present activity 6 pages 197-198, Teacher’s Guide Without using protractor let the students state if the measures are correct and which are wrong in exercise 9. Refer to pages 201- 202, Teacher’s Guide Present challenge on page 10 6.Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living (Elaborate) Let some students name practical application Let some students name practical application Best angle the television set be installed on the wall. Name parts of a house that used angle 7.Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson Let some students generalize of what they learned about the lesson Or Make a summary what the students should learned Let some students generalize of what they learned about the lesson. Or You may say, in this two days you learned about the basic terms in geometry which are point, line, segment and ray. Also you learned how to perform set operations on segments and rays. Let some students generalize of what they learned about the lesson Or Make a summary what the students should learned Essay writing of what they learned about parts of an angle ,its measure and classifications 8.Evaluating learning (Evaluate) Call some students to give examples of objects that maybe used to represent the point, line and plane Call some students to define segments and ray Call some students to 1. define angle and its parts classify angles according to their measures Call some students to share their write-ups 9.Additional activities for application or remediation (Extend) Name objects at home that represent: 1. Point 2. Line 3. Plane Name objects at home that represent: 1. Segment 2. ray Measure the angle you usually seat and the television set you have at home if any or a portrait on the wall and your eyes when standing. Research other application of the angle aside from what already mentioned V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson
- 4. D.No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these works? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I used/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: Checked by: Noted: EDELMAR G. BENOSA VIRGINIA G. ORTIZ CARLOS G. CORPUZ, Ph.D. Teacher II Head Teacher III School Principal I