Defects of Timber - Yusuf Khan
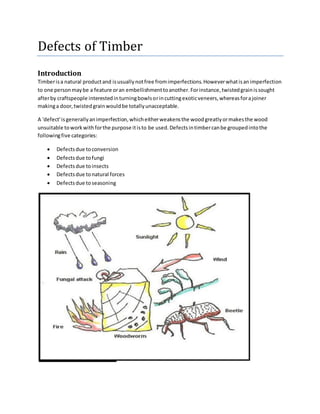
- 1. Defects of Timber Introduction Timberisa natural productand isusuallynotfree fromimperfections.Howeverwhatisanimperfection to one personmaybe a feature oran embellishmenttoanother.Forinstance,twistedgrainissought afterby craftspeople interestedinturningbowlsorincuttingexoticveneers,whereasforajoiner makinga door,twistedgrainwouldbe totallyunacceptable. A 'defect'isgenerallyanimperfection,whicheitherweakensthe woodgreatlyormakesthe wood unsuitable toworkwithforthe purpose itisto be used.Defectsintimbercanbe groupedintothe followingfive categories: Defectsdue toconversion Defectsdue tofungi Defectsdue toinsects Defectsdue tonatural forces Defectsdue toseasoning
- 2. Defects due to conversion Duringthe processof convertingtimbertocommercial form, the followingdefectsmayoccur: Chipmark Diagonal grain Torn grain Wane Chip Mark Thisdefectisindicatedbythe marksor signsplacedbychipson the finishedsurface of timber.Theymay alsobe formedbythe parts of a planingmachine. DiagonalGrain Thisdefectisformeddue toimpropersawingof timber.Itisindicatedbydiagonal markonstraight grainedsurface of timber. TornGrain Thisdefectiscausedwhena small depressionisformedonthe finishedsurface of timberbyfallingof a tool or so. Wane Thisdefectisdenotedbythe presence of original roundedsurface onthe manufacturedpiece of timber.
- 3. Defects due to fungi Fungi are minute microscopicplantorganisms.Theyattacktimberonlywhenthe followingtwo conditionsare satisfiedsimultaneously. i. The moisture contentof timberisabove 12-15%. ii. There ispresence of airand warmthfor the growth of fungi. If any of the above conditionisabsent,decayof wooddue tofungi wouldnotoccur. Hence, drywood havingmoisture contentlessthan12-14 % will remainsoundforcenturies.Similarly,woodsubmerged inwater will notbe attackedbyfungi because of absence of air.Followingdefectsare causedintimber by fungi. Blue stain Brownrot Dry rot Heart rot Sap stain Wet rot Blue Stain Sap of woodis stainedtobluishcolorbythe actionof certaintype of fungi. BrownRot The term rot isusedto indicate decayordisease of timber.Certaintypesof fungi remove cellulose compoundsfromwoodandhence,woodassumesthe browncolor.Thisisknownas brownrot. Dry Rot Certaintypesof fungi feedonwoodandduringfeeding,theyattackonwoodand convertitinto dry powderform.Thisisknownas dry rot. Heart Rot Thisis formedwhenabranch has come out of a tree.In sucha case,heartwoodisexposedtothe attack of atmosphericagents.Ultimately,the tree becomesweakanditgivesouthollow soundwhenstruck witha hammer. Sap Stain Certaintypesof fungi donot bringaboutthe complete decayof timber.Buttheyfeedoncell contentsof sap wood.Indoingso,sap woodlosesitscolor.Thisis knownassap stainand it generallyoccurswhere moisture contentgoesbeyond20%or so. Wet Rot Some varietiesof fungi cause chemicaldecompositionof wood of the timberandindoingsothey converttimberintoa greyishbrownpowder.Thisisknownaswetrot.
- 4. Defects due to insects Followingare the insectswhichare usuallyresponsible forthe decayof timber: Beetles Marine borers Termites Beetles These are small insectsandtheycause rapiddecay of timber.They formpin-holesof size about2 mm diameterinwood.Theyattackthe sap woodof all speciesof hardwood.Tunnelsare formedinall directionsinsapwoodbythe larvae of these beetles.The timberisconvertedintofine flour-like powder. Theyusuallydonotdisturbthe outershell orcover.Hence,timberpiece attackedbybeetlesmaylook soundtill itcompletelyfails. MarineBorers These are generallyfoundinsaltywater.Mostof the varietiesof marine borersdonotfeedonwood. But theymake holesorbore tunnelsinwoodfortakingshelter.The diameterandlengthof these holes may go as highas25 mmand 60 mm respectively.The woodattackedbymarine borerslosescolorand strength.Itmay be notedthat no timberiscompletelyimmune fromthe attackof marine borers. Termites These are popularlyknownas‘white ants’andtheyare foundinabundance intropical and sub-tropical countries.These insectslive inacolonyandtheyare veryfast ineatingawaythe woodfromcore of the cross section.Theymake tunnelsinsidethe timberindifferentdirectionsandusuallydonotdisturbthe outershell orcover.Hence,timberpiece attackedbytermitesmaylooksoundtill itcompletelyfails. Veryfewgoodtimberssuchas teak,sal,etc.,can resistthe attack of white ants.Such timbershave certainchemicalsintheircompositionandthe smell of these chemicalsisnotfavorable fortermites.
- 5. Defects due to natural forces The main natural forcesresponsible forcausingdefectsintimberare two,namely: Abnormal growth Rupture of tissues Followingdefectsare causedbythese forces: Burls Chemical stain Coarse grain Deadwood Knots Shakes Twistedfibres Upsets Water stain Windcracks Burls These are alsoknownas ‘excrescences’andtheyare particularlyformedwhenatree has receivedshock or injuryinitsyoungage. Due to such injury,the growthof tree iscompletelyupsetandirregular projectionsappearonthe bodyof the timber. ChemicalStain Wood issometimesdiscoloredbythe chemical actioncausedtoitby some external agency.Thisis knownas chemical stain. CoarseGrain If a tree growsrapidly,annual ringsare widened.Itisknownascoarse grainedtimberandsuchtimber possesseslessstrength. Dead Wood Timberwhichisobtainedfromdeadstandingtreescontainsdeadwood.Itisindicatedbylightweight and reddishcolor. Knots These are basesof branchesor limbswhichare brokenorcut off from the tree.The portionfromwhich the branch isremovedreceivesnourishmentfromthe stemfora prettylongtime and itultimately resultsinthe formationof dark,hard ringswhichare knownasknots.As continuityof woodfibersis brokenbyknots,theyforma source of weakness.
- 6. Knotsare classifiedonthe basisof theirsize. Sl. No Type of Knot Size 1 Pinknot Diameterupto6.5 mm 2 Small knot Diameterbetween6.5mm and 20 mm 3 Mediumknot Diameterbetween20mm and 40 mm 4 Large knot Diametergreaterthan40 mm Knotscan alsobe classifiedonbasisof theirformand quality. Sl. No Type of Knot Description 1 Deadknot The fibersof knotare not properlyinterconnectedwiththose of surroundingwood.Hence,itcanbe easilyseparatedoutfrom the bodyof wood.It isnot safe touse woodwithsucha knot for constructionpurposes. 2 Decayedknot It isalso knownasan unsoundknotand itis formedbythe actionof fungi onwood. 3 Live knot It isalso knownasa soundknot.It isfree fromdecayand cracks. It isthoroughlyfixedinwoodandhence,itcannotbe separatedoutfromthe body of wood.Presence of suchknots makeswooddifficulttoplane.However,woodcontainingsuch knotscan be usedforconstructionpurposes. 4 Loose knot It indicatespreliminarystage of deadknot.The fibersof this knotare not firmlyheldinthe surroundingwood. 5 Roundknot Cross-sectionof thistype of knotiseitherroundoroval .It is obtainedbycuttingthe knotat right anglestoitslongaxis. 6 Tightknot It indicatespreliminarystage of live knot.The fibersof knotsare firmlyheldinthe surroundingwood Rind Galls Rindmeansbark andgall indicatesabnormal growth.Hence,peculiarcurvedswellingsfoundonthe bodyof a tree are known asRind Galls.Theydevelopatpointsfromwhere branchesare improperlycut off or removed.
- 7. Shakes These are cracks whichpartlyor completelyseparate the fibersof wood.Followingare the different varietiesof shakes: Cup Shakes:These are causedby the rupture of tissue ina circulardirection.Itisa curvedcrack and itseparatespartlyone annual ringfromthe other.Itdevelopsdue tonon-uniformgrowth. It may notprove to be harmful,if itcoversonlya portionof ring. Heart Shakes:These cracks occur in the centre of cross-sectionof tree andtheyextendfrom pithto sap woodinthe directionof medullaryrays.These cracksoccur due to shrinkage of interiorpartof tree whichisapproachingmaturity.Heartshakesdividethe tree cross-section intotwo tofour parts. Ring Shakes: Whencup shakescoverthe entire ring,theyare knownasring shakes. Star Shakes:These are cracks whichextendfrombarktowardsthe sap wood.Theyare usually confineduptothe plane of sapwood.Theyare wideronthe outside endsandnarroweronthe inside ends.Theyare usuallyformeddue toextremeheatorfrost. Radial Shakes: These are similartostar shakes.Buttheyare fine,irregularandnumerous.They usuallyoccurwhenthe tree isexposedtosunfor seasoningafterbeingfelleddown.Theyrun for a short distance frombarktowardsthe centre,thenfollow directionof annual ring,and ultimatelyruntowardspith. Twisted Fibers These are alsoknownas wanderingheartsandtheyare causedby twisting of youngtreesbyfast blowingwind.The fibersof woodare twistedinone direction.Timberwithtwistedfibersisunsuitable for sawing.Itcan however,be usedforpostsandpolesinan unsawncondition.
- 8. Upsets These are alsoknownas rupturesand they indicate woodfiberswhichare injuredbycrushingor compression.Upsetsare mainlydue toimproperfellingof tree andexposure of tree initsyoungage to fastblowingwind. Water Stain Wood issometimesdiscoloredwhenitcomesintocontactwithwater. Thisisknownaswater stainand thisdefectisusuallyfoundinconvertedtimber. Wind Cracks If woodis exposedtoatmosphericagencies,itsexteriorsurface shrinks.Suchashrinkage resultsin cracks .These are knownas windcracks.
- 9. Defects Due to Seasoning Followingdefectsoccurinseasoningprocessof wood. Bow Case-hardening Check Collapse Cup Honey-combing Split Twist Wrap Bow The defectisindicatedbythe curvature formedinthe directionof lengthof timber. Case-hardening The exposed surface of timberdriesveryrapidly.It,therefore,shrinksandisundercompression.The interiorsurface whichhasnotcompletelydriedisundertension.Thisdefectisknownascase-hardening and itusuallyoccursin timberswhichare placedatthe bottomduringseasoning. Check A checkis a crack whichseparatesfibersof wood.Itdoesnotextendfromone endtothe other. Collapse Due to unevenshrinkage,woodsometimesflattensduringdrying.Thisisknownascollapse. Cup Thisdefectisindicatedby the curvature formedinthe transverse directionof timber. Honey-combing Due to stressdevelopedduringdrying,variousradial andcircularcracks developinthe interiorportion of timber.Timberthusassumeshoney-combtextureandthe defectsodevelopedisknownashoney- combing. Split Whena crack extendsfromone endtothe other,itis knownas a split. Twist Whena piece of timberhasspirallydistortedalongitslength,itisknownastwist. Warp Whena piece of timberhastwistedoutof shape,itis saidto have warped.
