AHA.pptx
- 1. Anatomy and HA of Abdomen 2/21/2023 1
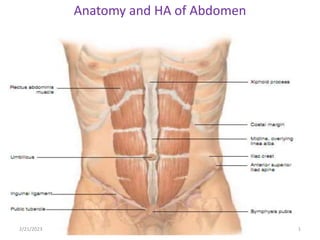
- 3. 2/21/2023 3
- 4. Abdominal examination helps as to identify abnormalities in the abdomen such as:- Organ enlargement, Masses, Peritoneal irritation, Hernias, Fluid accumulation, Abnormal peristaltic movement. 2/21/2023 4
- 5. Abdominal examination…Cont’d Locating abdominal structures • Methods of locating abdominal finding is done by dividing abdomen in to four quadrants by two perpendicular lines. • One vertical pass through the umbilicus and one horizontal line through the umbilicus. 2/21/2023 5
- 6. RUQ which contain:- Rt adrenal gland Liver Gall bladder portion of Rt kidney head of pancreas Duodenum Pylorus loop of small intestine Parts of the colon(hepatic flexure, portion of transverse and ascending colon ). 2/21/2023 6
- 7. RLQ-which contain:- Appendix distended bladder Rt ovary Rt salpnix Portion of ascending colon Lower pole of Rt kidney Cecum Rt spermatic chord Rt ureter Enlarged utreus Loop of small intestine 2/21/2023 7
- 8. LUQ- which contains:- Lt adrenal gland Portion of Lt kidney Body of pancreas Spleen Stomach Loop of small intestine Portion of colon (spleenic flexure, portion of transverse and descending colon). 2/21/2023 8
- 9. LLQ-which contain Distended bladder Left ovary Lt salpnix Lt spermatic chord Lt ureter Enlarged utreus Loop of small intestine Lower pole of Lt kidney Sigmoid and portion of descending colon 2/21/2023 9
- 10. Palpable organs- Often palpable Sigmoid colon Cecum Iliac arteries Distended bladder Pregnant utreus Pulsation of abdominal aorta portion of ascending, transverse and descending colon 2/21/2023 10
- 11. • Rt kidney and liver may palpable only in some pts. • Much of the liver, much of the stomach and all of the usual normal spleen are in the abdominal cavity and extended under the rib cage to the dome of diaphragm, therefore none palpable. • Most of the gall bladder lies deep to the liver, duodenum and pancreas lie deep in the upper abdomen, hence none of them palpable. • Techniques of examination – The usual sequence of inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation is modified in the examination of the abdomen. – Inspection, auscultation , palpation and percussion. 2/21/2023 11
- 13. Inspection • Observe the size and shape of the abdomen: • it is described as flat, round, or scaphoid. • Check for symmetry of the abdomen. • Check for an umbilical hernia. • A slight pulsation may be noted in the mid epigastric area, particularly in very thin clients. This is the pulsation of the abdominal aorta. • In adults, observable veins may reflect major health problems. • Increased peristaltic waves of intestinal obstruction. • Increased pulsation of an aortic aneurysm. 2/21/2023 13
- 14. Auscultation • Auscultation assesses the sounds of peristalsis and vascular abnormalities. • Listen for bowel sounds and note their frequency and character. • Normal sound consists of clicks and gurgles, the frequency which has been estimated from 5 to 34 per minute. • Borborygmus- loud prolonged gurgles of hyper peristalsis. • Bowel sounds may be altered in diarrhea, intestinal obstruction, paralytic ileus, and peritonitis. • Normal blood flow through the abdominal arteries can not be heard. • Blood flow through dilated or constricted blood vessels results in a turbulence that can be detected by auscultation. 2/21/2023 14
- 15. • Recall that the bell detects low-pitched sounds. Place the bell of stethoscope over: – Abdominal aorta in midepigasrium above the umbilicus. – Renal arteries to the right and left slightly above the umbilicus. – Hepatic and splenic arteries in the right and left hypochondrium. • To be considered significant, an abdominal bruit must be heard as the client is moved in to various positions. • Friction rub: rough grating sound, occurs with irritation of the peritoneal surface of an organ, splenic infarction, primary or metastatic tumor of liver, and peritonitis. 2/21/2023 15
- 16. • Percussion Light percussion of the abdomen is performed to determine: – Enlargement of an organ – The presence of masses – The presence of abdominal distension or the amount and distribution of gas in the abdomen. • A dull percussion note will be heard over the area of a dense abdominal organ, such as liver or spleen, and over a solid tumor or fluid. • Dull percussion notes detected in the suprapubic area may be from a distended urinary bladder. 2/21/2023 16
- 17. • Tympany is the normal percussion note present through out the abdomen except for areas over the liver, spleen and pubic symphysis. • With gaseous distension tympany will be elicited throughout the abdominal area. • The vertical span of liver dullness represents the size of the liver in the adult; this is normally about 6-12cm in the mid clavicular line& 4-8cm in mid sternal line. • Vertical span is greater in men than women, tall person than short. • Percuss down the right anterior chest in the mid clavicular line (MCL). 2/21/2023 17
- 18. • Resonance over the lung will be detected until about the 5th to 7th intercostal space, where liver dullness begins. • Continue percussion down ward until the lower edge of liver dullness is heard. The normal lower level is at the costal margin. • Ask the client to inhale, and percuss down ward again on inspiration, there should be an increase of about 2 to 4cm from the previous lower edge of liver dullness, because the liver moves down ward on inspiration. 2/21/2023 18
- 19. • The spleen lies slightly posterior to the left mid axillaries line, b/n the 8th and 11th ICS. • Below the 12th find dullness is called positive spleenic percussion sign. 2/21/2023 19
- 20. Palpation • The client should be as comfortable and relaxed as possible. • Light palpation-feeling the abdomen gently is especially helpful in identifying abdominal tenderness, muscular resistance, some superficial organs & masses. – If resistance is present, try to distinguish voluntary guarding from involuntary muscular spasm. – Feel for the relaxation of abdominal muscles that normally accompanies exhalation. – Ask the pt to mouth- breath with jaw dropped open, voluntary guarding usually decreases with this maneuvers. – Involuntary rigidity (muscular spasm) typically persists despite these maneuvers. 2/21/2023 20
- 21. • Visceral pain generally is a poorly localized, dull pain, where as peritoneal pain usually is easily localized and is described as sharp, stabbing pain. • Abdominal pain on coughing or with light palpation suggests peritoneal inflammation. • Test for rebound tenderness by gently and slowly pressing the examining hand deep in to the abdomen away from the site of the pain, quickly release your hand. • the client with rebound tenderness will experience induced pain or increased pain, immediately inquire where the pain is felt. 2/21/2023 21
- 22. • Deep palpation is usually required to delineate abdominal masses. • Again using the palmar surfaces of your fingers, feel in all four quadrants. Identify any masses and note their location, size, shape, consistency, tenderness, pulsations and mobility. –Note-palpation may not be justified in some abdominal problems such as appendicitis when diagnosis is clear and there is risk of rapture with manipulation. 2/21/2023 22
- 23. Liver Place your right hand just below the lower right costal margin with your fingers pointing toward the client's right shoulder and parallel with the abdominal rectus muscle. • Push the fingers deeply in to the abdomen with a constant pressure and simultaneously push up under the rib cage. • Ask the client to take a deep breath: this will cause the liver to descend. • On inspiration, the liver below is palpable about 4cm below the right costal margin in the mid clavicular line. 2/21/2023 23
- 24. • An obstructed, distended gall-bladder may form an oval mass below the edge of the liver and merging with it. It is dull to percussion. • Tenderness over the liver suggests inflammation, as in hepatitis, or congestion, as in heart failure. •Spleen • The spleen may be palpable in the normal infant and young child; however, with the older child and adult, the spleen must be considerably enlarged before it can be palpated. • Place your left hand under the client's left flank at the level of the 11th and 12th ribs. 2/21/2023 24
- 25. • kidneys – They may be felt in children and in adults with scaphoid abdomens. – Palpation of the right kidney: • Although kidneys are not usually palpable, you should learn and practice the techniques. • Place your left hand behind the pt just below and parallel to the 12th rib, with your fingertips just reaching the costovertebral angle. • Lift, trying to displace the kidney anteriorly. • Place your right hand gently in the right upper quadrant, lateral and parallel to the rectus muscle. 2/21/2023 25
- 26. • Ask the pt to take a deep breath. • At the peak of inspiration, press your right hand firmly and deeply in to the right upper quadrant, just below the costal margin, and try to capture the kidney between your two hands. • Causes of kidney enlargement include hydronephrosis, cysts, and tumors. • Bilateral enlargement suggests poly cystic disease. 2/21/2023 26
- 27. Palpation of the left kidney • To capture the left kidney, move to the pt’s left side. • Use your right hand to lift from in back, and your left hand to feel deep in the left upper quadrant. • Instruct the client to take a deep breath while you apply pressure with the examining hand. 2/21/2023 27
- 28. • Assessing kidney tenderness • Use fist percussion- place the ball of your hand in the costovrtebral angle and strike it with the ulnar surface of your fist. • Pain with pressure or with fist percussion in the costovertebral angle suggests kidney infection, but it may also have a musculoskeletal cause. • Urinary bladder –The bladder is non palpable unless it is distended well above the pubic symphysis. 2/21/2023 28
- 29. • ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION: SPECIAL TECHNIQUES 1. To Assess Possible Ascites • A protuberant abdomen with bulging flanks suggests the possibility of ascitic fluid • The presence and extent of ascites are assessed by perccusing the abdomen for shifting dullness or by detecting a fluid wave. A. Test for shifting dullness. • After mapping the borders of tympany and dullness, ask the pt to turn on to one side percuss and mark the borders again. • In ascites, dullness shifts to the dependent side, while tympany shifts to the top. 2/21/2023 29
- 30. B. Test for a fluid wave • An assistant’s hand is placed along the pt’s midline of the abdomen. • This pressure helps to prevent the fluid wave from being transmitted through the tissues of the abdominal wall. The examiner places the hands along the side of the pt’s flank, then strikes or tap one flank sharply, feel on the opposite flank for an impulse transmitted through the fluid. • A fluid wave is likely to be found only when there is a large amount of fluid present. 2/21/2023 30
- 31. 2. To identify an organ or amass in an ascetic abdomen. • Try to ballotte the organ or mass, exemplified here by an enlarged liver. • Straighten and stiffen the fingers of one hand together, place them on the abdominal surface, and make a brief jabbing movement directly toward the anticipated structure. • This quick movement often displaces the fluid so that your finger tips can briefly touch the surface of the structure through the abdominal wall. 2/21/2023 31
- 32. 3. To assess possible appendicitis • Ask the patient to point to where the pain began and where it is now. • Ask the patient to cough. • Determine whether and where pain results. • The pain of appendicitis classically begins near the umbilicus and then shifts to the right lower quadrant, where coughing increases it. 2/21/2023 32
- 33. –Search for an area of local tenderness • Localized tenderness anywhere in the right lower quadrant may in dictate appendicitis. • Feel for muscular rigidity • Early voluntary guarding may be replaced by involuntary muscular rigidity • Check the tender area for rebound tenderness • Rebound tenderness suggests peritoneal inflammation, as from appendicitis. 2/21/2023 33
- 34. • Check for Rovising’s sign and for referred rebound tenderness. • Press deeply and evenly in the LLQ and quickly withdraw your finger. Pain in the right lower guardant during left- sided pressure suggests appendicitis (a positive Rovising’s sign). Rt quadrant pain quickly withdrawal termed as rebound tenderness. • Look for a psoas sign. Place your hand just above the pt’s right knee and ask the pt to raise that thigh against your hand. • Increased abdominal pain on this maneuver constitutes a positive psoas sign, suggesting irritation of the psoas muscle by an inflamed appendix. 2/21/2023 34
- 35. Images
- 38. 4. To assess possible acute cholecystitis • Cholecystitis may be detected by pressing the fingers gently in to the right hypochondrium as the patient takes a deep breath in, a sudden catch of breath when the gallbladder touches your fingers indicates inflammation (a positive Murphy’s sing). 5. To assess ventral hernias – If you suspect this type of hernia but do not see an umbilical or incisional hernia, ask the patient to raise both head and shoulders off the examination coach. – The bulge of a hernia which usually appear with this action. 2/21/2023 38
- 39. 6. To distinguish an abdominal mass from a mass in the abdominal wall. – Ask the patient either to raise the head and shoulders or to strain down, thus tightening the abdominal muscles. Feel for the mass again. – A mass in the abdominal wall remains palpable an intra abdominal mass is obscured by muscular contraction. 2/21/2023 39
- 40. 7. Localized bulges in the abdominal wall • Include ventral hernias and subcutaneous tumors such as lipomas. – The more common ventral hernias are umbilical, incisional, and epigastric. – Hernias usually become more evident when the patient raises head and shoulders from a supine position. • Lipomas, small or large, they are usually soft and often lobulated. When your finger presses down the edge of lipoma the tumor usually slips out from under it. 2/21/2023 40
- 41. 8. Sounds in the abdomen a. Bowel sounds • May be increased in clients with diarrhea or early intestinal obstruction. • Decreased, in paralytic ileus and peritonitis. • High-pitched tinkling sounds suggest intestinal fluid and air under tension in a dilated bowel. b. Bruits • A hepatic bruit suggests carcinoma of the liver or alcoholic hepatitis. • Arterial bruits with both systolic and diastolic components suggest partial occlusion of the aorta or large arteries. 2/21/2023 41
- 42. 9. Tender abdomens • Abdominal wall Tenderness • Tenderness may originate in the abdominal wall. • When the patient raises head and shoulders, this tenderness persists; whereas tenderness from a deeper lesion decreases. a. Visceral tenderness: Example – Enlarged liver may be tender to deep palpation. b. Tenderness from disease in the chest and pelvis 2/21/2023 42
- 43. • Acute pleurisy – Abdominal pain and tenderness may be due to acute pleural inflammation. • Acute salphingitis • Frequently bilateral, the tenderness of acute salphingitis is usually maximal just above the inguinal ligaments. 2/21/2023 43
- 44. • Tenderness of peritoneal inflammation • Severe than visceral tenderness. • Muscular rigidity and rebound tenderness are frequently present. 10. Liver enlargement • A palpable liver does not necessarily indicate hepatomegaly. • Clinical estimates of liver size should be based on both percussion and palpation. 2/21/2023 44
- 45. A. Down wards displacement of the liver by a low diaphragm. • Common finding in emphysema. • The liver edge may be readily palpable well below the costal margins. B. Normal variations in liver shape • In some persons, especially those with a lanky build, the liver tends to be somewhat elongated so that its right lobe is easily palpable as it projects downward toward the iliac crest. • Riedel’s lobe – represents a variation in shape, not an increase in liver volume or size 2/21/2023 45
- 46. C. Smooth large non tender liver • Cirrhosis may produce an enlarged liver with a firm non tender edge. • Many other diseases may produce similar finings. D. Smooth large tender liver • An enlarged liver with a smooth tender edge suggests inflammation, as in hepatitis, venous congestion, as in right sided heart failure. 2/21/2023 46
- 47. E. Large irregular liver • An enlarged liver that is firm or hard and has an irregular edge or surface suggests malignancy. • There may be one or more nodules. • The liver may or may not be tender. 2/21/2023 47
- 48. Reference • Health assessment lecture notes for nursing students by kemal ahmed 2010. • Nitisbin medicine 1st edition-(revised).pdf
- 49. Acknowledgment • For Wollo university college of medicine and health sciences, department of adult health nursing. • For Dr. Kumar • For my audience
Notes de l'éditeur
- scaph·oid ab·do·men. a condition in which the anterior abdominal wall is sunken and presents a concave rather than a convex contour. Synonym(s): navicular abdomen