Endocrine glands and Adrenal (suprarenal) gland
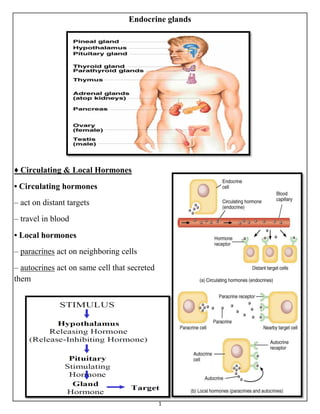
- 1. 1 Endocrine glands ♦ Circulating & Local Hormones • Circulating hormones – act on distant targets – travel in blood • Local hormones – paracrines act on neighboring cells – autocrines act on same cell that secreted them
- 2. 2
- 3. 3
- 5. 5 ◘ Adrenal (suprarenal) gland • Outer layer called the adrenal cortex • Inner layer called the adrenal medulla ♦ Adrenal Cortex: • Adrenal cortex produces Adrenocorticoids ♣ Zona glomerulosa produces mineralocorticoids such as Aldosterone: - Regulation of electrolyte balance ↑ the reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys ↑ the excretion of potassium in the kidneys - Regulation of blood volume and blood pressure ♣ Zona fasciculata produces glucocorticoids such as cortisol and corticosterone: - Regulation of metabolism ↑ gluconeogenesis, ↑ blood glucose ↑ lipolysis, ↑ free fatty acids. - Suppression of the immune system - Help resist long-term stress
- 6. 6 ♣ Zona reticularis produces androgens that are converted in the gonads to the fully functional sex hormones Steroidogenesis
- 7. 7 ◘ The action of ACTH on steroidogenesis • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH, also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. • Its principal effects are increased production and release of cortisol by the cortex of the adrenal gland. • ACTH binds to plasma membrane receptors, which are coupled to adenylyl cyclase (AC) by stimulatory G proteins (Gs). • cAMP rises in the cells and activates protein kinase A (PKA), which then phosphorylates certain proteins (P Proteins). • The P proteins initiate steroidogenesis and stimulate the expression of genes for steroidogenic enzymes.
- 8. 8 ◘ The action of angiotensin II on aldosterone synthesis • Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. • Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II by the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) • Angiotensin II increases aldosterone secretion • Angiotensin II (AII) binds to receptors on the plasma membrane of zona glomerulosa cells, activating phospholipase C (PLC), which is coupled to the angiotensin II receptor by G proteins (Gq). • PLC hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) in the plasma membrane, producing inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). • IP3 mobilizes intracellularly bound Ca. • The rise in Ca and DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC) and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CMK). • These enzymes phosphorylate proteins (P-Proteins) involved in initiating aldosterone synthesis.
- 9. 9 ♦ Adrenal Medulla: • Adrenal Medulla produces catecholamines, which are produced from tyrosine, a non-essential amino acid derived from food or produced from phenylalanine in the liver. • Adrenaline (epinephrine) • noradrenaline (norepinephrine) • They are responsible for the fight or flight (short-term stress) response, characterized by: - Quickening of breathing - Quickening of heart rate - Vasoconstriction, ↑ the blood pressure
- 10. 10 Adrenal gland in stress response Hypofunction of adrenal cortex Hyperfunction of adrenal cortex • A deficiency in steroid hormones production by the adrenal gland. Primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease ) - Due to primary failure of adrenal glands - ACTH is elevated Secondary adrenal insufficiency - Due to a disorder of hypothalamus or pituitary, leading to decreased stimulation of the adrenal cortex - ACTH is decreased Cushing’s disease ACTH-dependent Cushing’s syndrome • It is caused by a pituitary adenoma, which secretes excessive ACTH and stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce large amounts of glucocorticoids. ACTH-independent Cushing’s syndrome • It is a result of an adrenocortical adenoma that secretes large amounts of glucocorticoids. Primary aldosteronism • It is excess production of the hormone aldosterone by the adrenal gland. • It is caused by: - Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia or - Aldosterone-producing adenomas (Conn's syndrome)
- 11. 11 ◘ Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: • Congenital adrenal hyperplasia are a group of several genetic diseases resulting from mutations of genes for enzymes mediating the biochemical steps of production of mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids or sex steroids from cholesterol by the adrenal glands (steroidogenesis). ♦ Hyperfunction of adrenal medulla Pheochromocytoma • A tumor of the adrenal medulla that leads to increased secretion of catecholamines Growth Hormone (somatotropin) ◘ Actions of Growth Hormone: Responsible for the general growth of the body. It increases the size and number of cells by mitotic division. It causes specific differentiation of certain types of cells like bone cells and muscle cells. GH affects: 1. Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats & proteins 2. Bones ◘ Metabolism of Carbohydrates: 1. Decrease in the uptake of glucose by the cell 2. Decrease the peripheral utilization of glucose for the production of energy 3. Increase in the deposition of glycogen in the cells
- 12. 12 ◘ Metabolism of Fats: • GH mobilizes fats from adipose tissue. • Increases the concentration of fatty acids. ◘ Metabolism of Proteins: • GH accelerates the synthesis of proteins by: 1. Increasing amino acid transport through cell membrane 2. Increasing transcription of DNA to RNA 3. Increasing RNA translation 4. Promoting anabolism of proteins 5. Decreasing catabolism of proteins ◘ Effects on Bones: • In embryonic stage, GH is responsible for the differentiation and development of bone cells. • In later stages, GH increases the growth of the skeleton. • It increases both the length as well as the thickness of the bones.
- 13. 13 ◘ Regulation of GH secretion • GH secretion is under negative feedback control Hypothalamus releases GHRH, which in turn promote the release of GH from anterior pituitary. GH activates the liver cells to secrete somatomedin C (Insulin-like growth factor 1, IGF-1), which increases the release of GHIH from hypothalamus. GHIH, in turn inhibits the release of GH from anterior pituitary. IGF-1 also inhibits release of GHRH from hypothalamus. It acts on pituitary directly and inhibits the secretion of GH. - Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) - growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
- 14. 14 GH secretion is stimulated by: GH secretion is inhibited by: 1. Hypoglycemia 2. Fasting 3. Starvation 4. Exercise 5. Stress and trauma 6. Initial stages of sleep 1. Hyperglycemia 2. Increase in free fatty acids in blood 3. Later stages of sleep ◘ Pituitary dysfunctions Gigantism: hyper-secretion of growth hormone in children. Dwarfism: hypo-secretion of growth hormone in children. Acromegaly: hyper-secretion of growth hormone in adult, especially in hands and feet. Sex Hormones (gonadocorticoids) Cause different sexual characteristics in males and females Control fertility or the ability to have offspring. Categories of sex hormones Androgens Estrogens Progestogens Androstenediol Androstenedione Dehydroepiandrosterone Dihydrotestosterone Testosterone (the most potent androgen) Estetrol Estriol Estrone 17 Β-Estradiol (the most potent estrogen) Progesterone
- 16. 16 ◘ Regulation of reproduction in females: The hypothalamus processes information obtained from the external and internal environment using neurotransmitters that regulate the secretion of GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone). FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles. LH induces ovulation and regulates the secretion of progesterone from the corpus luteum. Both LH and FSH regulate follicular steroidogenesis and androgen & estradiol secretion. ♣ The ovary produces 3 hormones: - Inhibin: suppresses the secretion of FSH. - Activin (an inhibin-binding protein): increases the secretion of FSH. - Follistatin (an activin-binding protein): reduces the secretion of FSH.
- 17. 17 ♦ What is Estrogen? Estrogens are hormones found in females and in low levels in males. These hormones control different stages of the reproductive cycle in females. In females, estrogens control the development of secondary sex characteristics. In males and females, estrogen promotes normal bone development. Progesterone Estrogen It maintains the uterus function during gestation period. It promotes the development of female secondary sexual characteristics. It induces the release of LH, which then stimulates ovulation by releasing the egg from the ovary. It promotes and maintains the uterus lining in preparation for implantation of fertilized egg.
- 18. 18 ◘ Regulation of reproduction in males: The hypothalamus processes information obtained from the external and internal environment using neurotransmitters that regulate the secretion of GnRH LH binds to receptors on the Leydig cells FSH binds to receptors on the Sertoli cells ♣ Sertoli cells produces 3 hormones: - Inhibin: suppresses the secretion of FSH. - Activin (an inhibin-binding protein): increases the secretion of FSH. - Follistatin (an activin-binding protein): reduces the secretion of FSH.
- 19. 19 ♦ What is Testosterone? Testosterone is found in males and in smaller amounts in females. In males, testosterone controls the development of secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair and increased muscle mass. Testosterone initiates spermatogenesis.
- 20. 20 Thymus gland The thymus gland is located in the upper thorax region. It produces the thymosin hormone. It is the site of T lymphocytes maturation. Pineal gland The pineal gland is located in the middle of the brain. It secretes melatonin, a hormone that regulates when you sleep at night and wake up in the morning. Melatonin production is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light ◘ Measurement of Hormone Concentrations • The concentration of hormone present in a biological fluid is measured to: Study basic endocrine physiology. Make a clinical diagnosis of a suspected endocrine disease. Bioassay Radioimmunoassay (RIA) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
