IB Proteins & Enzymes Review (2.4-2.5-7.3)
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
2 likes•3,664 views
Review worksheet covering IB Biology content on Proteins and Enzymes (Topics 2.4, 2.5, and 7.3)
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
IB DNA Structure & Replication Review (2.6-2.7-7.1)

IB DNA Structure & Replication Review (2.6-2.7-7.1)
IB DNA Structure & Replication Review Key (2.6-2.7-7.1)

IB DNA Structure & Replication Review Key (2.6-2.7-7.1)
Protein Synthesis: 7.3 & 7.4 Transcription and Translation AHL (IB)

Protein Synthesis: 7.3 & 7.4 Transcription and Translation AHL (IB)
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (8)
Similar to IB Proteins & Enzymes Review (2.4-2.5-7.3)
Similar to IB Proteins & Enzymes Review (2.4-2.5-7.3) (20)
Protein metabolism and nitrogen fixation and metabolism

Protein metabolism and nitrogen fixation and metabolism
Protein: structure, classification,function and assay methods

Protein: structure, classification,function and assay methods
Chemistry hl human biochemistry option self study guide

Chemistry hl human biochemistry option self study guide
A Novel Statistical Method for Thermostable Proteins Discrimination 

A Novel Statistical Method for Thermostable Proteins Discrimination
IB Proteins & Enzymes Review (2.4-2.5-7.3)
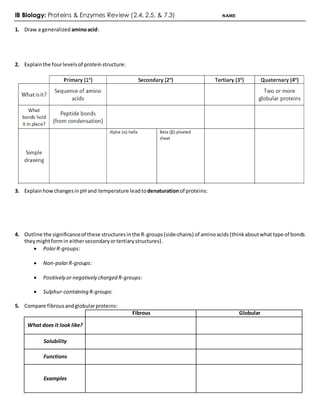
- 1. IB Biology: Proteins & Enzymes Review (2.4, 2.5, & 7.3) NAME: 1. Draw a generalized aminoacid: 2. Explainthe fourlevelsof proteinstructure: 3. ExplainhowchangesinpH and temperature leadtodenaturationof proteins: 4. Outline the significanceof these structuresinthe R-groups(side-chains) of aminoacids (thinkaboutwhattype of bonds theymightformin eithersecondaryortertiarystructures). PolarR-groups: Non-polarR-groups: Positively or negatively charged R-groups: Sulphur-containing R-groups: 5. Compare fibrousandglobularproteins: Fibrous Globular What does it look like? Solubility Functions Examples
- 2. 6. Proteinsare usedonthe plasmamembrane andfor otherdiverse functions.Complete the table below: ProteinFunction Example What doesit do? Gas / Nutrient Transport Catalyst/ Enzyme Immunity/ Defense Hormones Structure / Tensile Strength Movement/ Muscle Contraction DNA Packaging 7. Complete the table describingthe functionsof the six specificproteinexample,below: ProteinExample Function Rubisco Insulin Immunoglobulin (Antibodies) Collagen Rhodopsin Spidersilk 8. Define the following: enzyme “globularprotein which actsas a catalystforbiological reactions” active site denaturation 9. List three examples of enzymes,withtheirfunctions. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 10. Explainenzyme-substratespecificity.Include adiagram: 11. State the functionof polarregions of aminoacidson the active site of the enzyme.
- 3. 12. Explainthe loweringof activation energy byenzymes. 13. Explainthe effectsof temperature,pHandsubstrate concentrationonthe rate of an enzyme-controlledreaction. Draw a sample graphin the space on the leftandthenexplain/describe onthe right: Temperature pH Substrate concentration 14. Explainthe industrial productionof lactose-free milk,including twoadvantagesof lactose-free milk:
