solid waste disposal methods
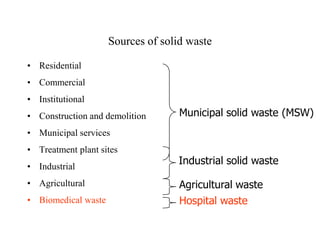
- 1. Sources of solid waste • Residential • Commercial • Institutional • Construction and demolition • Municipal services • Treatment plant sites • Industrial • Agricultural • Biomedical waste Municipal solid waste (MSW) Industrial solid waste Hospital waste Agricultural waste
- 2. Solid waste and disposal methods • Municipal Waste Food waste fruit or vegetable residues (garbage) decompose rapidly Rubbbish Combustible or non combustible solid wastes excluding food wastes or other putrescible materials. Combustible rubbish includes paper, cardboard, plastics,rubber etc. Non combustible rubbish includes glass, crokery, tin cans etc Ashes and residues Materials remaining from the burning of wood, coal and other combustible wastes Demolition and construction wastes Wastes from razed buildings and other structures are classified as demolition waste. Wastes from the construction and repairing of residential, commercial and industrial buildings and similar structures are classified as construction wastes Special wastes Wastes such as street sweepings, roadside litter, dead animals and abandoned vehicles are classified as special wastes Treatment Plant Wastes The solid and semisolid wastes from water, wastewater and industrial treatment facilities
- 3. Nature of Industrial solid waste • Hazardous and Non-hazardous waste • Characteristics - Hazardous – Corrosivity – Flammability – reactivity – Toxicity • Catagories – Chemicals – Biological – Radioactive – Explosives
- 4. • Disposal of refuse • Land filling • Incineration • Disposal into sea • Composting • Disposal by land filling • In this method refuse is carried out and dumped into low lying area
- 5. • Disposal by land filling • In this method refuse is carried out and dumped into low lying area • The refuse is filled up or dumped in layers of 1.5 m or so and each such layer is covered by good earth of atleast 20 cm thickness so that the refuse is not directly exposed. If the thickness of land filling is large filling shall be done in layers and each layer should be compacted by the movement of bull dozers, trucks etc. • Insecticides like D.D.T etc. should be sprayed on the layers to prevent breeding of mosquitoes and flies. A final cover of about 1 m of earth is laid and compacted at the top of the filled up land. • The waste is stabilized by aerobic as well as anaerobic processes • The entire process can be stabilized into five distinct phases • During first phase aerobic bacteria will deplete the available oxygen to effect the oxidation of organic matter. As a result temperature in the fill increases • In the second phase anaerobic and facultative bacteria develop to decompose the organic matter and in third phase methanogenic bacteria develop to cause evolution of methane. • In the fourth phase methanogenic activity get stabilized • In the fifth stage methanogenic activity subsides representing depletion of organic matter and ultimately the system returns to aerobic conditions
- 7. • The refuse get stabilized in a period of 2 to 12 months and settles down by 20-40% of its original height. The filling of land can be utilized for developing some green land, park or recreational spot. • Advantages • This method is simple and economical. No costly equipment is required • Separation of different kinds of refuse as required in incineration method is also not required • There are no residues or byproducts left and hence no further disposal required • Low lying water logged areas and quarry pits can be easily reclaimed and put to better use. • Disadvantages • Unavailability of land in future • The dumped garbage may contain harmful and carcinogenic non biodegradable substances such as plastics, medicines, paints, insecticides etc.During winter season the excess water may seep out through the area as a colored liquid called Leachate. This may contain organic compounds like chlorinated hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene, xylene etc.is likely to seep to contaminate the ground water leading to diseases like cholera, typhoid,etc.
- 8. • Disposal by compositing • Biological method of decomposing solid waste • Under aerobic or anaerobic condition or both • Final end product is manure • In aerobic composting process because it involves piling up of refuse and its regular turning either manually or by mechanically devices so as to ensure sufficient supply of air • The process starts with mesophilic bacteria which oxidize the organic matter to carbon dioxide and liberate heat. The temperature rises to 45oC and at this point thermophillic bacteria take over and continue the decomposition. During this phase the temperature rises to about 60oC. After about 3 weeks the compost is stabilized and this is shown by appreciable fall in temperature. The final compost should have earthy smell and dark brown color. • Moisture content is a critical factor in aerobic composting process. A moisture content of about 55% should be established so that the biological activity may proceed at an optimum rate.
- 10. Composting has 3 phases: Mesophilic (pseudomonads) Thermophilic (Bacillus, then Thermus) Cooling/maturation (Bacillus, pseudomonads, others)
- 11. What chemical and physical factors are important in a compost pile? • temperature • C/N ratio: the ratio of carbon to nitrogen • nutrients: usually plenty in the organic residues • oxygen • pH • moisture: optimal is 50-60% • particle size
- 12. Temperature • A result of microbial action – energy is produced • Too cool – decomposition will be too slow • Too hot – beneficial microbes will die • Do need temperature to be at or above 55oC for part of the time to destroy human and plant pathogens
- 13. C/N ratio (carbon/nitrogen) – why is it important? •Carbon acts both as an energy source and the basic chemical building block. •Nitrogen is needed to make both amino acids and nucleic acids. •If nitrogen is limiting , microbial population will be small and long time for decomposition •Ideal ratio for composting = 30:1
- 14. C/N ratio (carbon/nitrogen) • High C/N items: – Dead leaves – Straw – Wood chips or sawdust – Bark – mixed paper – Newspaper – Corrugated cardboard • Low C/N items: – Vegetable scraps – Coffee grounds – Grass clippings – Manure
- 15. Most microbes can tolerate a pH range of 5.5 - 8.5 • Initially, a lowered pH favors the growth of fungi – More breakdown of lignin and cellulose • If pH drops too low, even fungi are affected – Decomposition slows or stops! • Aeration – providing oxygen – returns the pH to an acceptable range
- 16. Moisture • Most rapid decomposition takes place in thin film of water on surfaces of organic particles. • Too little – poor bacterial activity • Too much – anaerobic pockets and odor, nutrient leaching, slower decomposition • Ideal: 50-60%;
- 17. Particle size Small – more surface area for more microbes = faster decomposition. Can compact. Large – prevents compaction; allows oxygen flow and aeration. Less surface area
- 18. • Disposal by incineration • Burning of refuse at high temperature in furnaces called incinerators • Separation of combustible matter from incombustible will reduce the load on incinerators • The left out ashes and clinkers (fused masses of incombustible materials) have to be disposed by land filing or for other use. Clinker can be used as aggregate for making low grade concrete and ashes can be used for bricks • The heat prodced can be used in the form of steam power for running turbines to generate electricity • The maximum temperature in the combustion chamber should be sufficient (> 670oC). If steam is to be generated then a temperature of 10000C is required in the combustion chamber. • Merits • Ensures complete destruction of pathogenic bacteria • No odor trouble • Requires less space for refuse disposal • Some cost can be recovered by selling power • Demerits • Costly method and require a technical know how • Solid waste to be burnt should have high calorific value
- 19. SW Management elements • Incineration.. – Heat recovery through boilers - efficiency – 70% – Amount of steam produced varies from 1.0 to 3.5 kg/kg of MSW – Four basic unit operations • Preparation (auxillary fuel) and transportation of waste to incinerator • Combustion of organic waste into flue gases • Heat transfer from flue gases • Exhaust of cooled flue gases with pollutants through for APCDs for removal of pollutants
- 20. SW Management elements Heat recovery efficiency – 70% Amount of steam produced varies from 1.0 to 3.5 kg/kg of MSW • Incineration..
- 21. Properties of solid waste • Physical – Density – Weight per unit volume (kg/m3) – Varies with • Waste constituents • Degree of compaction • State of decomposition • Depth of waste • Season • Length of storage time – Examples (mass/density)– food wastes (19.6/288); paper (19.6/81.7); Glass (3.4/194) – Uncompacted waste
- 22. Properties of solid waste • Physical – Moisture content – Percentage of wet weight of material – Important role in • Compaction • Decomposition • Leaching of inorganic components • And use in incineration – Examples – food waste (50-80%); plastics (1-4%); construction combustibles (4-15%) – .
- 23. Properties of solid waste • Physical – Particle size and distribution – Important for • recovery • & compaction of wastes – Field Capacity – Moisture retained in a waste after gravitational pull – Excess – forms leachate – Leachate – transport of contaminants to ground water table – Varies with compaction pressure and state of decomposition – Typical uncompacted waste – 50-60%
- 24. Properties of solid waste • Chemical – Proximate analysis – Includes four tests – • loss of moisture at 105 deg.C for 1 hour; • Volatile combustion matter • Fixed carbon • Ash Type Moisture Volatiles Carbon Ash Mixed food 70 21 4 5 Mixed paper 10 75 9 6 Residential MSW 21 52 7 20
- 25. Properties of solid waste – Elemental Analysis (also called ultimate analysis) – Determination of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur and ash – Used to characterize waste in terms of organic matter Type C H O N S Ash Mixed food 73 11 15 .4 .1 rest Mixed paper 43 `5.8 44 .3 .2 rest Refuse driven fuel 44 7 38 .7 <.1 rest